This document describes using SQL stored procedures to automate performance checks across multiple SQL Server instances. It provides a code sample to collect wait statistics from linked servers and databases. The summary explains how to set up the necessary permissions and infrastructure to execute the stored procedure across multiple servers from a central location on a scheduled basis.
![Contact: EliasBlake
prosperdatasystems@gmail.com
www.prosperidata.com
Using SQL Stored Procedures to automate performance checks
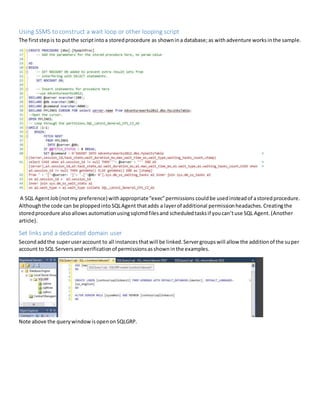
Code Sample from SQL Server Management Studio to demonstrate collecting wait statistics.
use YourDatabaseHere;
DECLARE @server nvarchar(100);
DECLARE @db nvarchar(100);
DECLARE @command nvarchar(4000);
DECLARE DBLINKS CURSOR FOR select SERVER,db from YourDatabaseHere.dbo.TableofLinkedServers
--Open the cursor.
OPEN DBLINKS;
-- Loop through the partitions.SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS
WHILE (1=1)
BEGIN;
FETCH NEXT
FROM DBLINKS
INTO @server,@db;
IF @@FETCH_STATUS < 0 BREAK;
SET @command = N'INSERT INTO YourDatabaseHere.dbo.waits
(Server,session_id,task_state,wait_duration_ms,max_wait_time_ms,wait_type,waiting_tasks_count,stamp
)
select CASE when a3.session_id != null THEN'''+ @server + ''' END
server,a3.session_id,a3.task_state,a2.wait_duration_ms,a1.max_wait_time_ms,a1.wait_type,a1.waiting_
tasks_count,CASE when a3.session_id != null THEN getdate() ELSE getdate() END as [stamp]
from ' + '['+@server+ ']'+ '.['+@db+ N'].sys.dm_os_waiting_tasks a2 inner join sys.dm_os_tasks a3
on a2.session_id = a3.session_id
inner join sys.dm_os_wait_stats a1
on a2.wait_type = a1.wait_type collate SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS
where a2.wait_type in (''CXPACKET'',''ASYNC_IO_COMPLETION'',''ASYNC_NETWORK_IO'')
OR a2.wait_type LIKE ''LCK%'' OR a2.wait_type like ''%LATCH%''
order by a2.wait_duration_ms desc,a2.session_id desc';
EXEC sp_executesql @command;
PRINT N'Executed: ' + @command;
END
CLOSE DBLINKS;
DEALLOCATE DBLINKS;
Thiscode sample assumesanenvironmentwithmultipleSQLServerInstancesbeyondthe 30 that can be monitored
usingthe UCP service (UtilityControl Point) introduced inSQLServer2008 R2 enterprise.Alsohave abackgroundin
Oracle thisis somewhatequivalenttotakingsnapshotsinAWR. AswithUCP there isa requirementfora“super”service
account withsysadmaccesson monitoredinstances butalsolinkedservers andservergroupsregisteredin management
studio. Thiswill notworkinenvironmentswherethe rpcand rpcoutare restricted. Itispossible to install otherinstances
to run UCP on a single serverbut UCPonlyprovidesawindow intothe hardware bydisplayinggrowthof datafiles, CPU
and memory.If more detail isneededforrootcause analysis inside the database andsp_whodoesn’tshedlight, the
waitstats fromthe example canprovide awindow into the processesand sessionID/usersthatcreate unsavory wait
types. Althoughthe SQLServerextendedeventsandProfilerService cancreate histories thisscriptcanbe a goodway to
target whatserversneed attention inacentral way withoutrandomlyrunningtracesandextendedsessionevents. Then
hopefullythe DBA can avoidthe performance impacts of collectingperformance metricswhere it’snotneeded. If using
SQL Server](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/be5e2dd6-d084-419b-980b-30eb44833656-160128152847/75/SSMS-waitstats-1-2048.jpg)