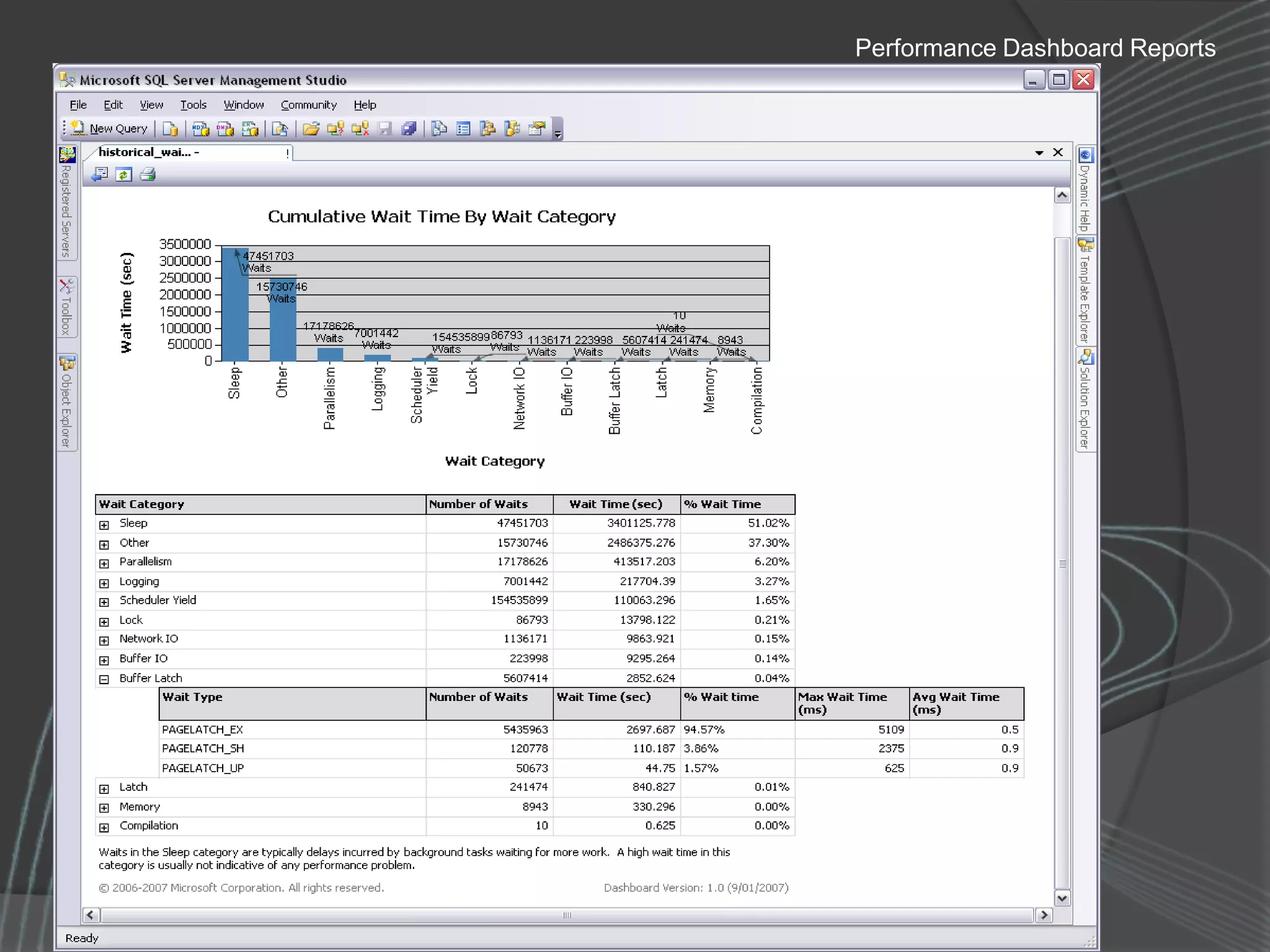
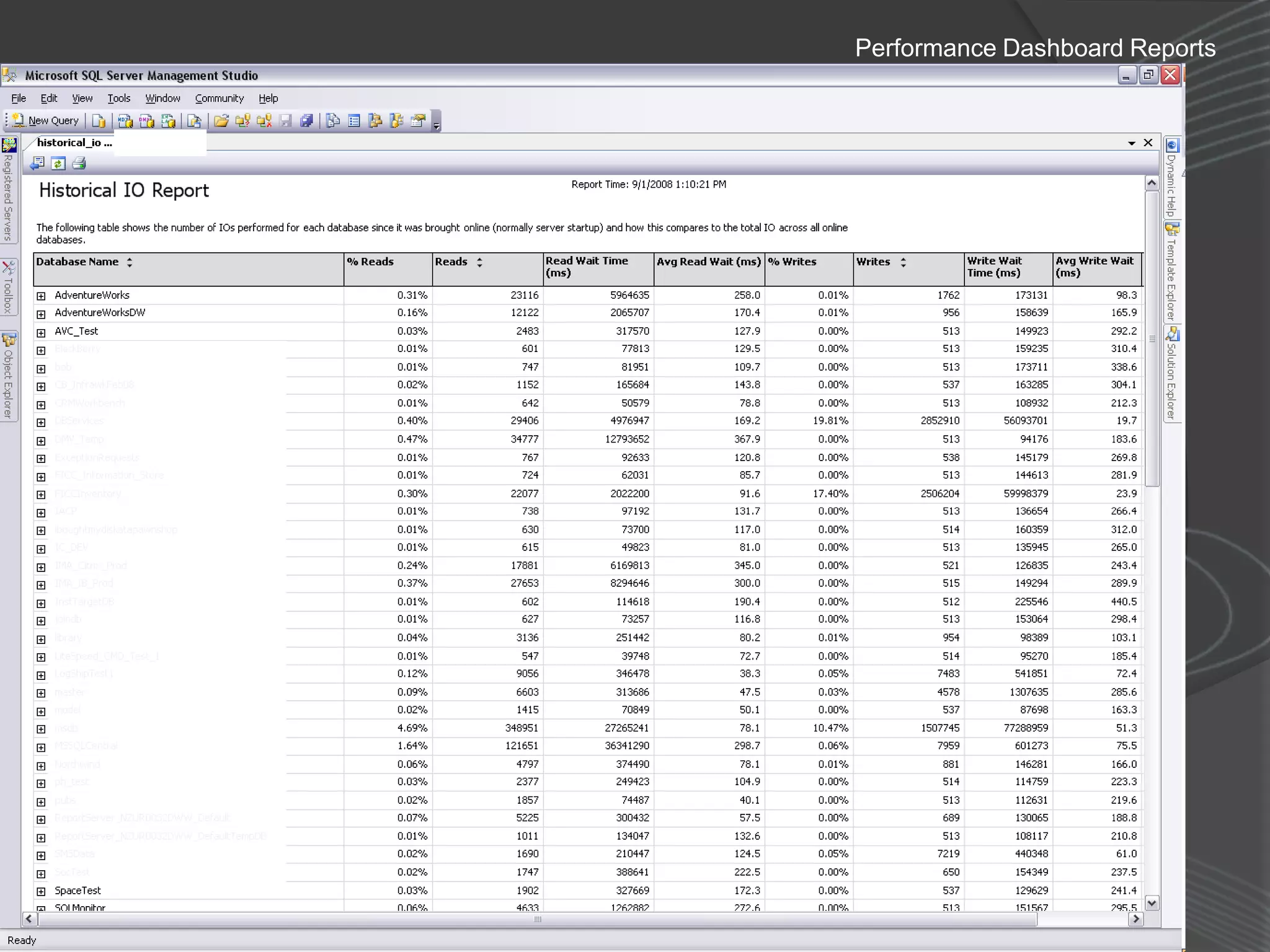
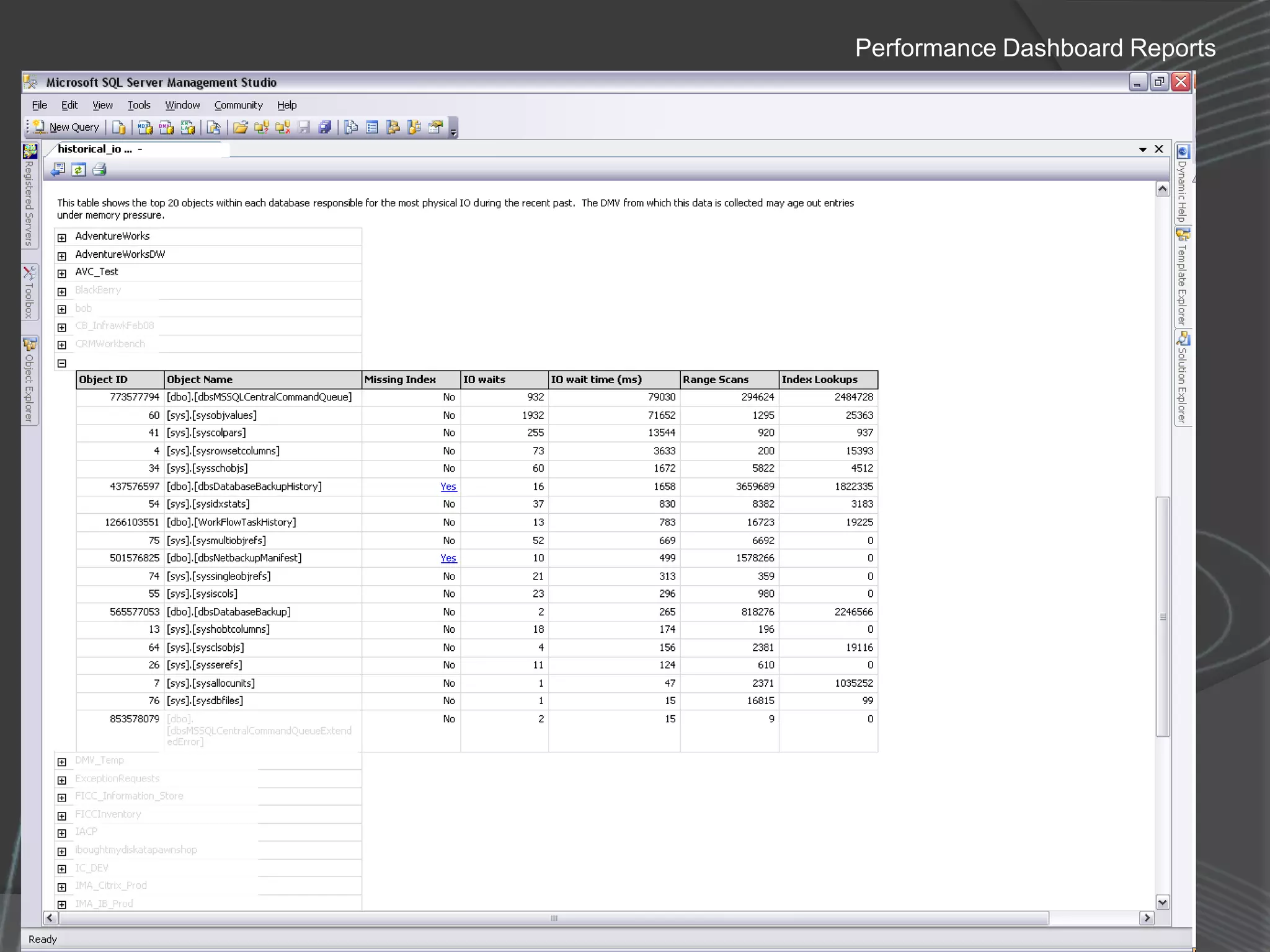
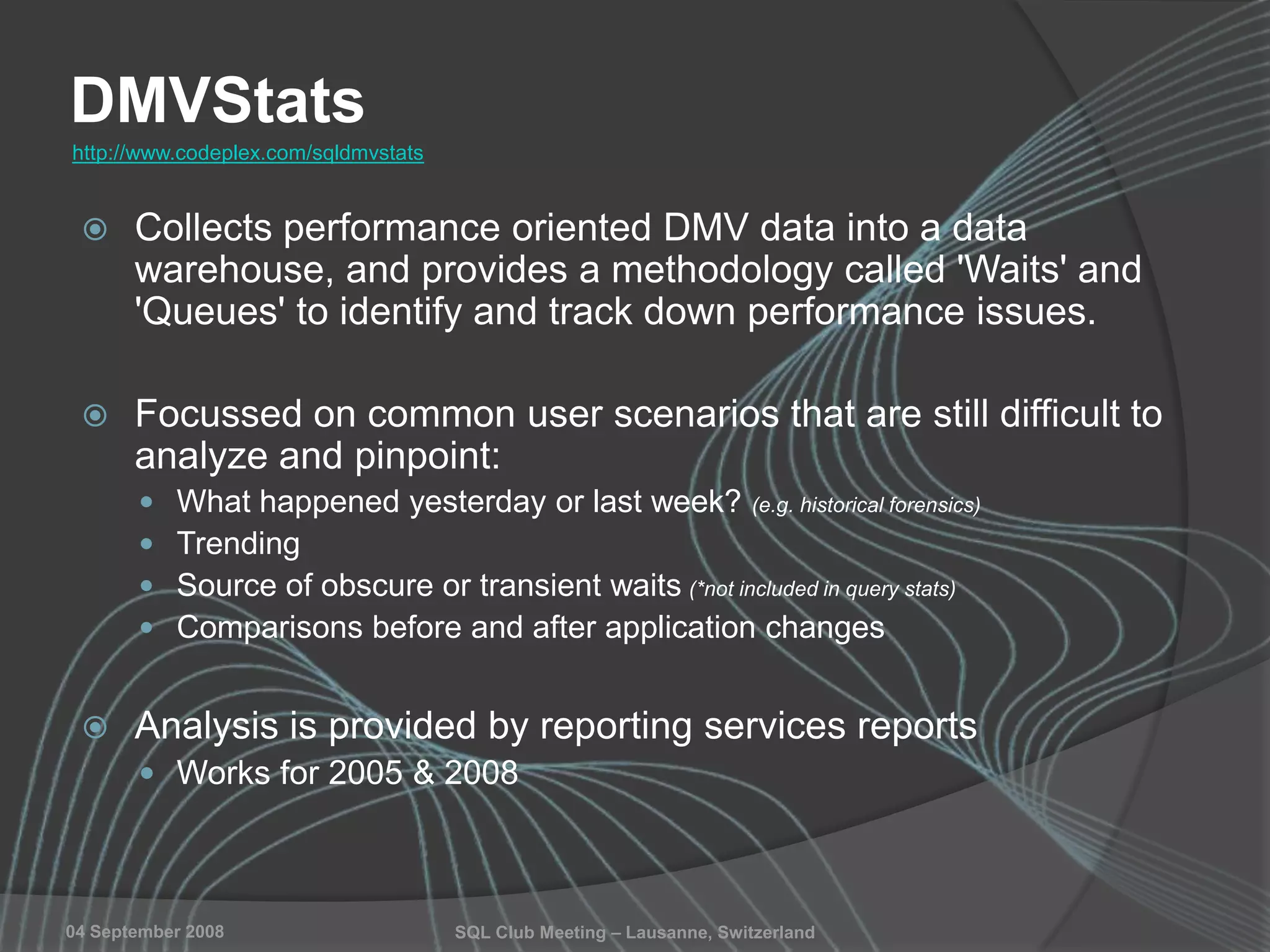
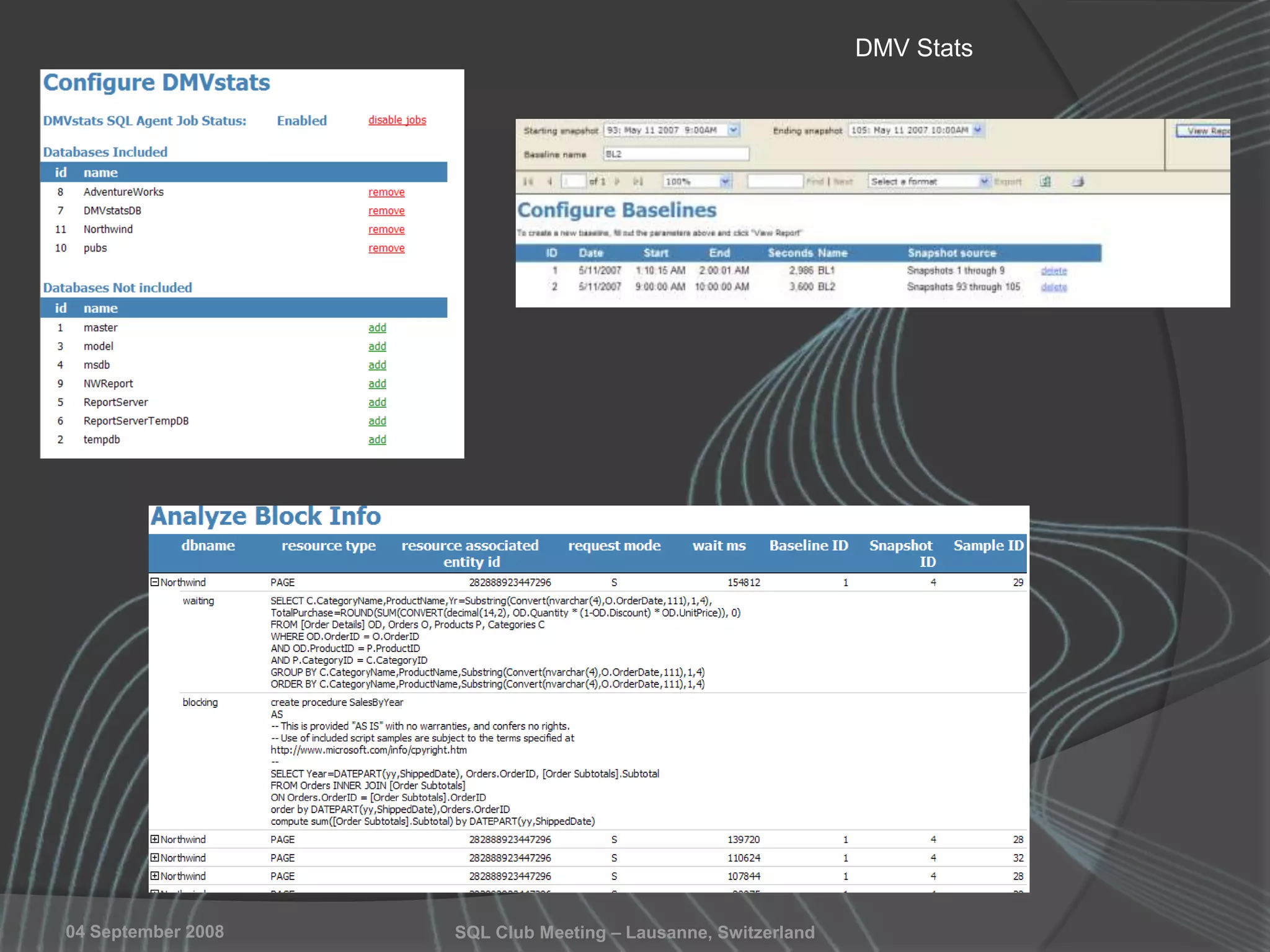
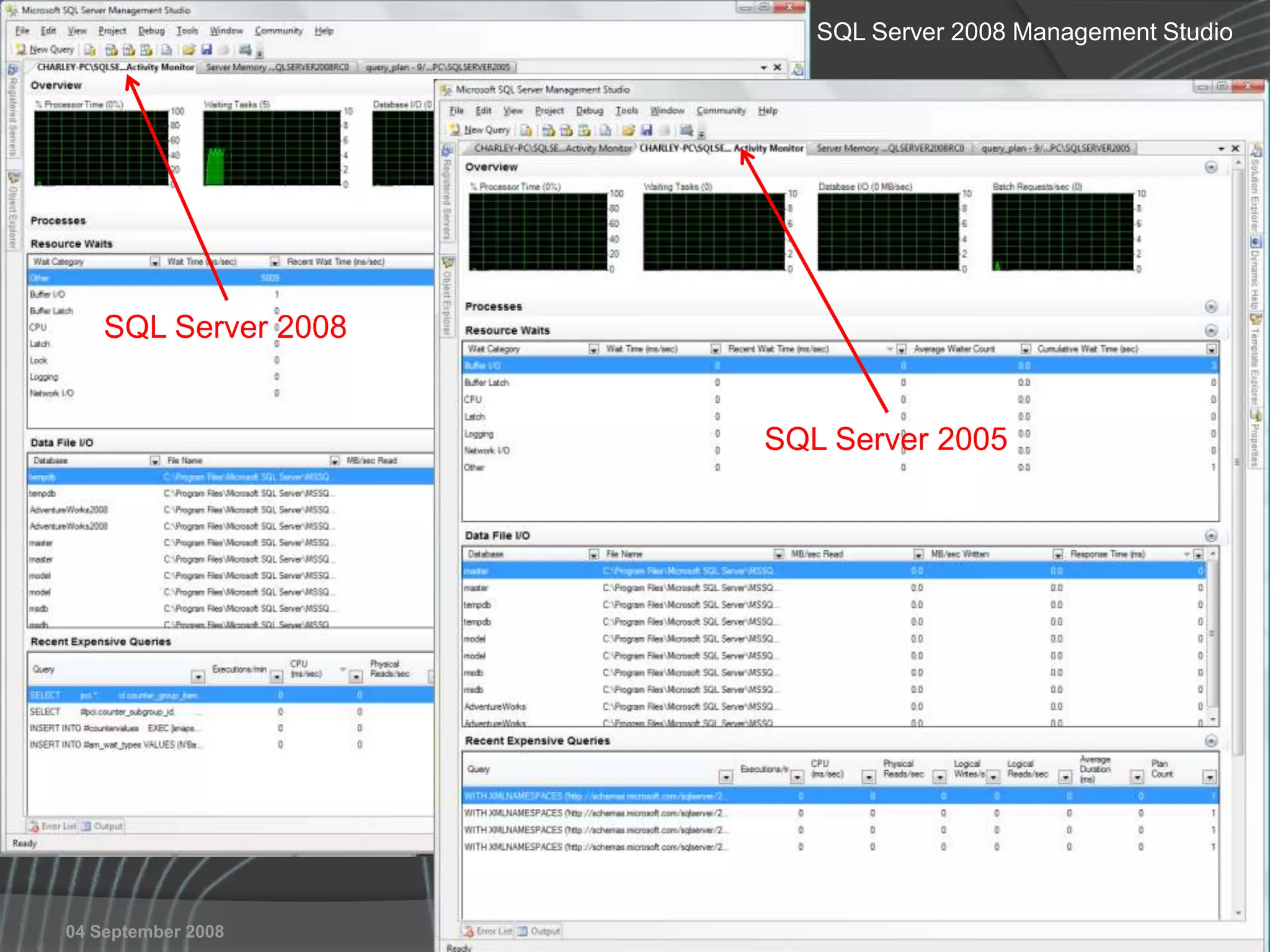
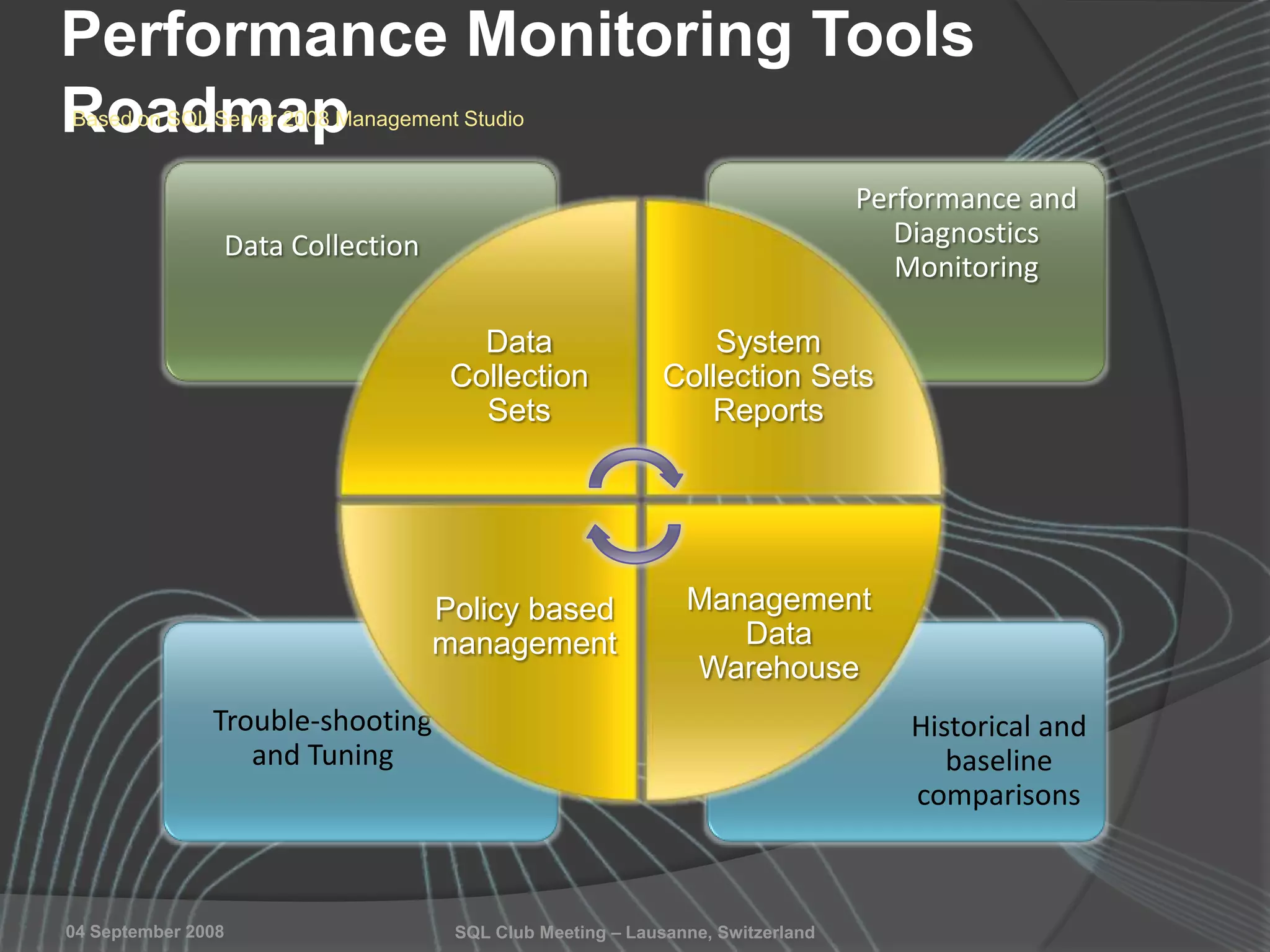
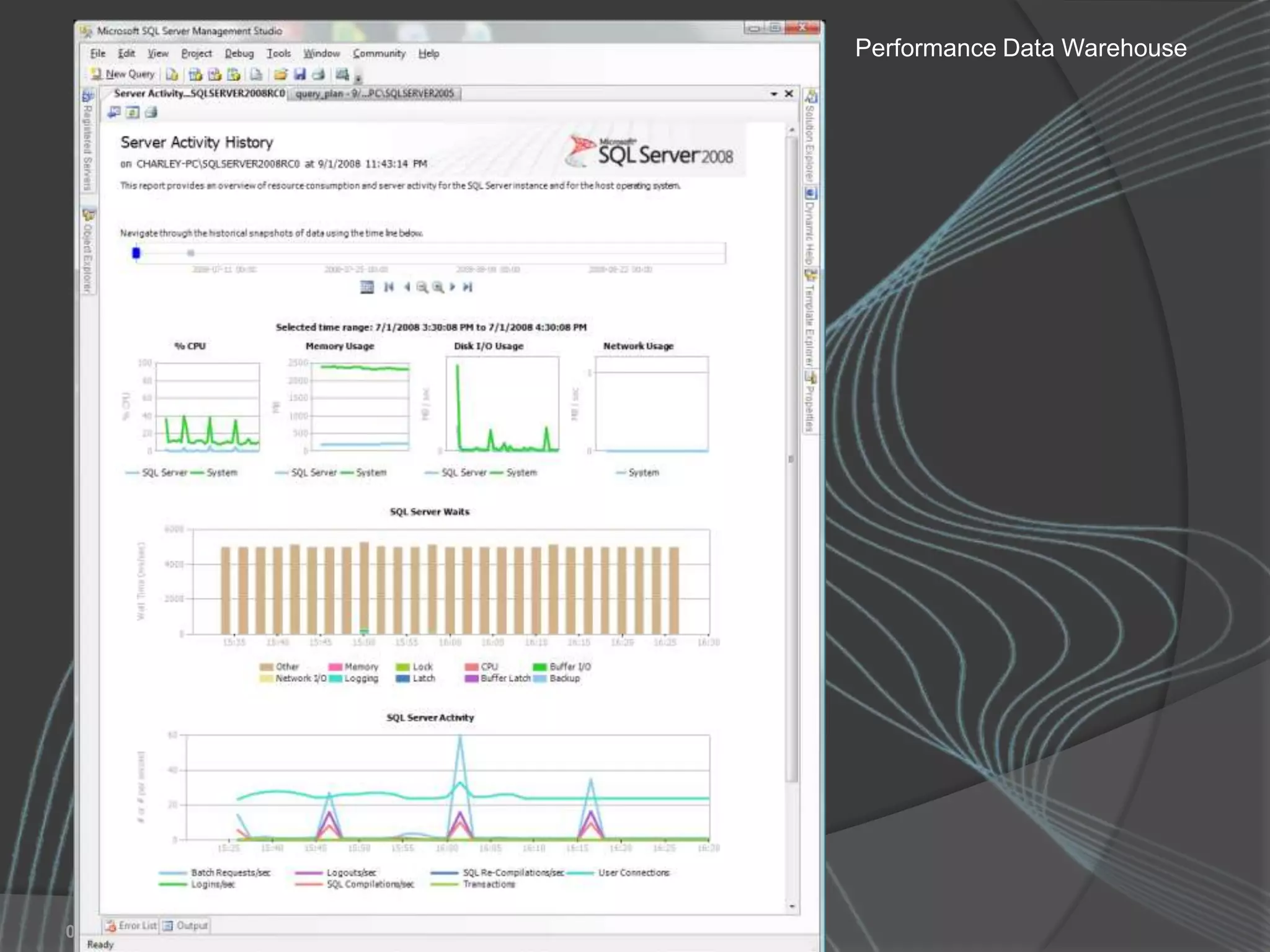
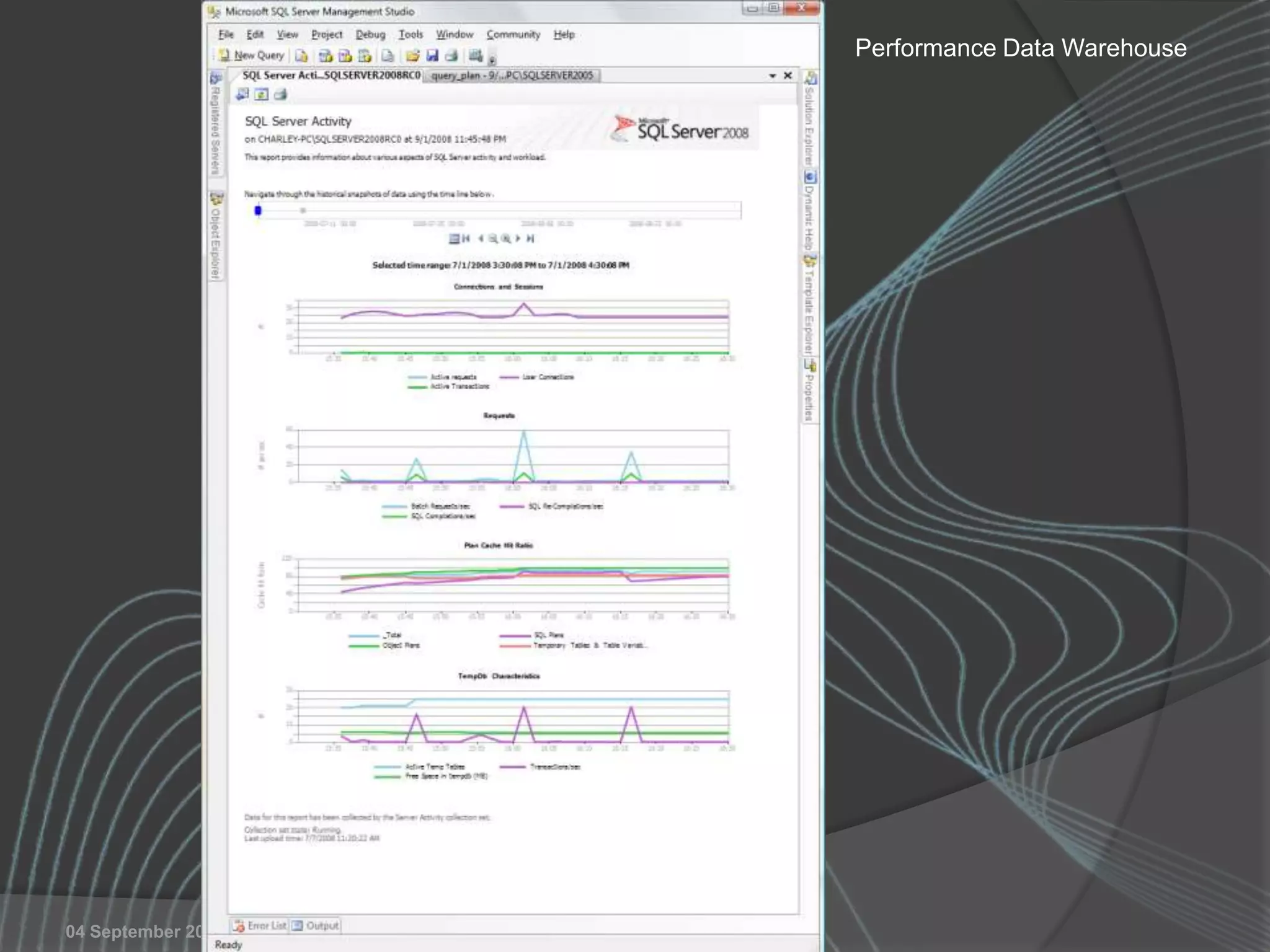
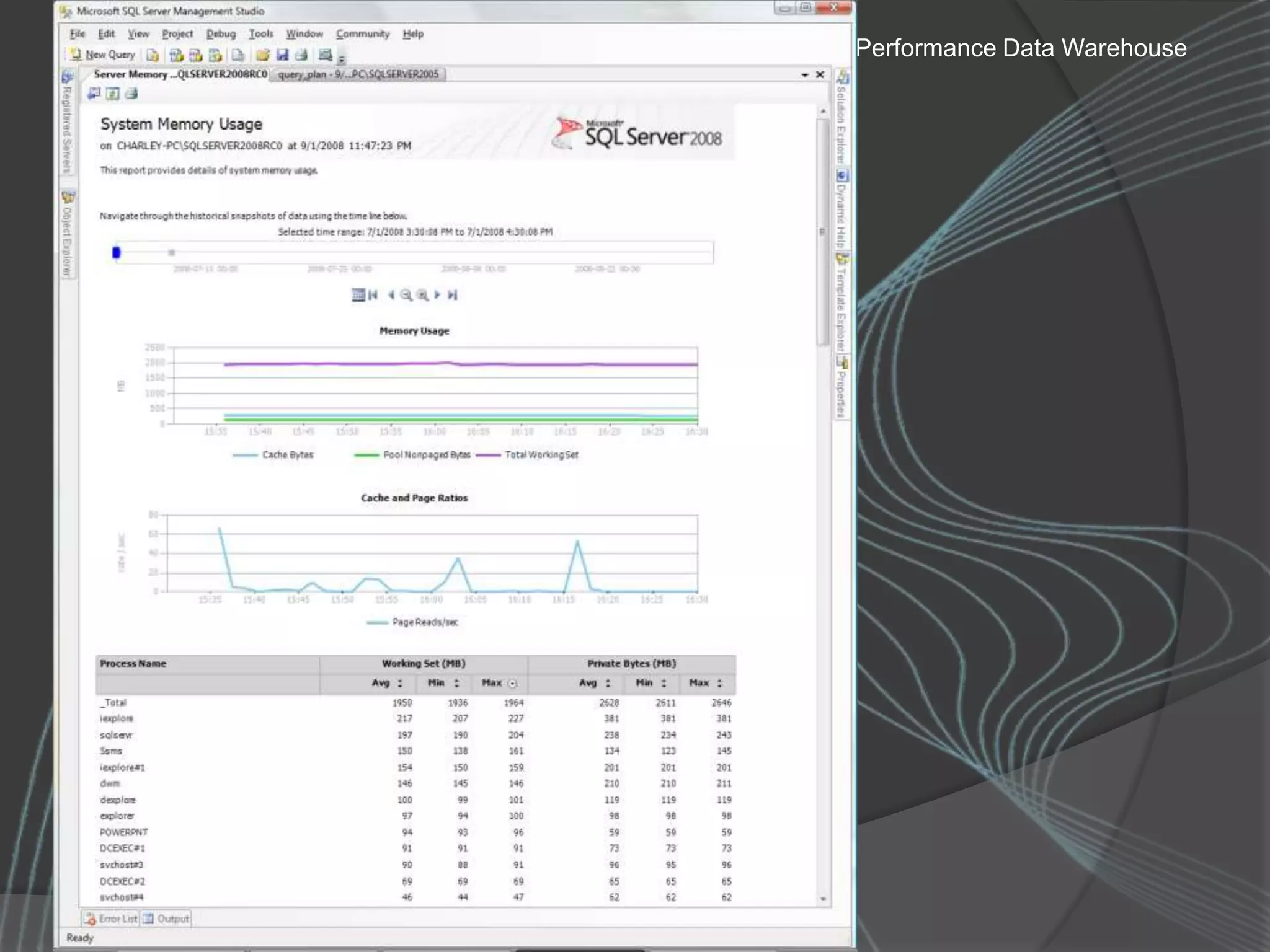
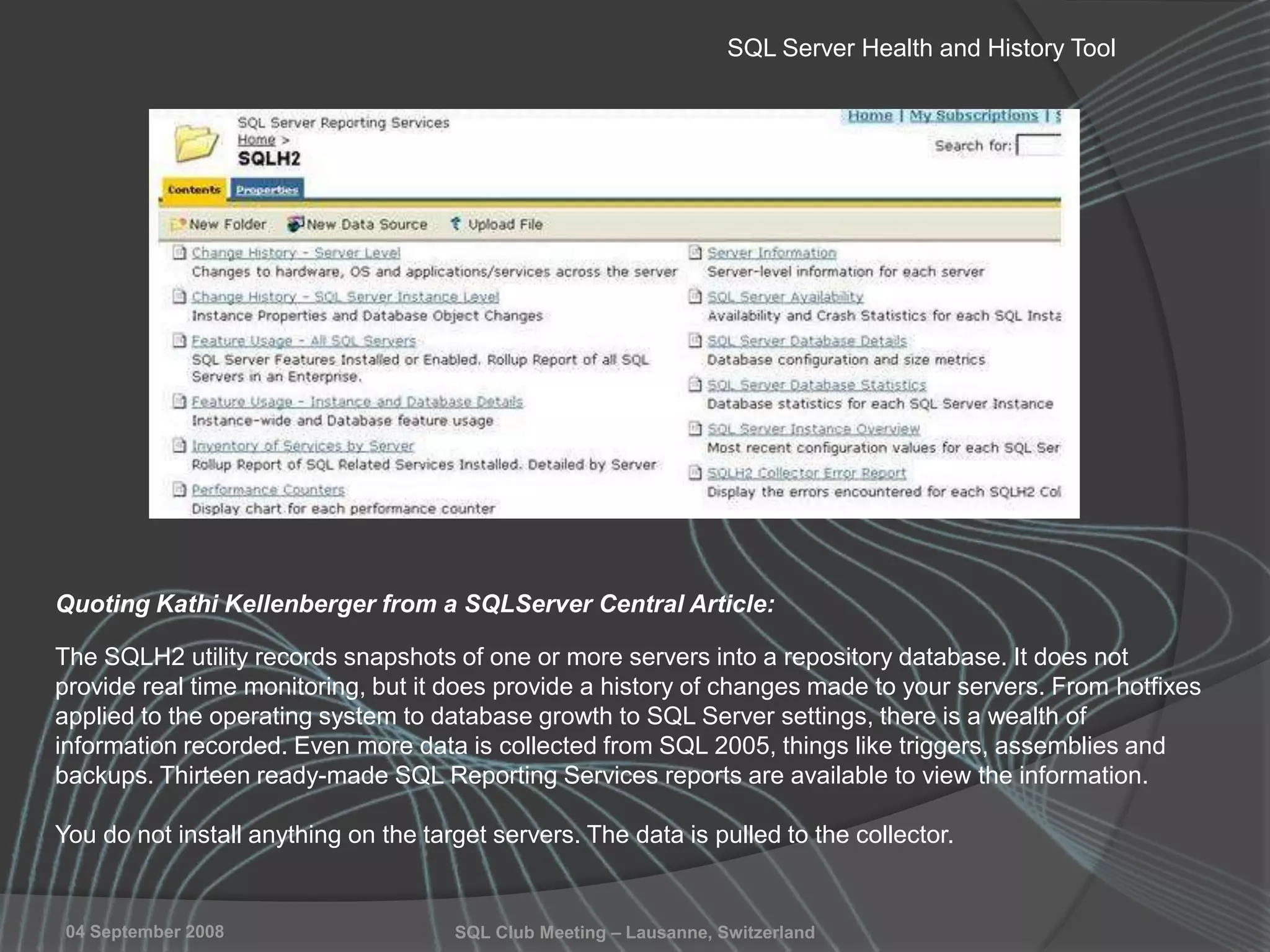
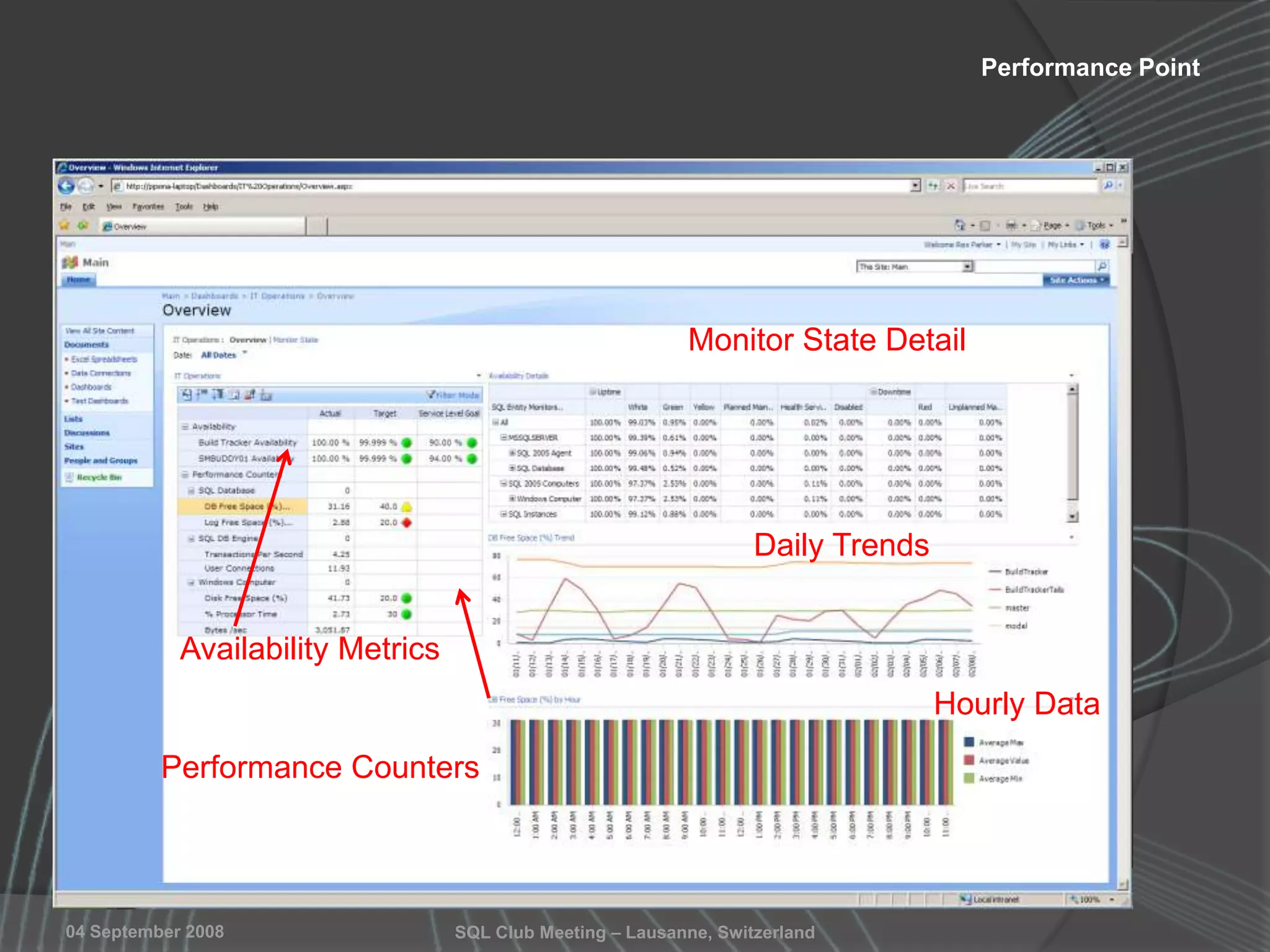
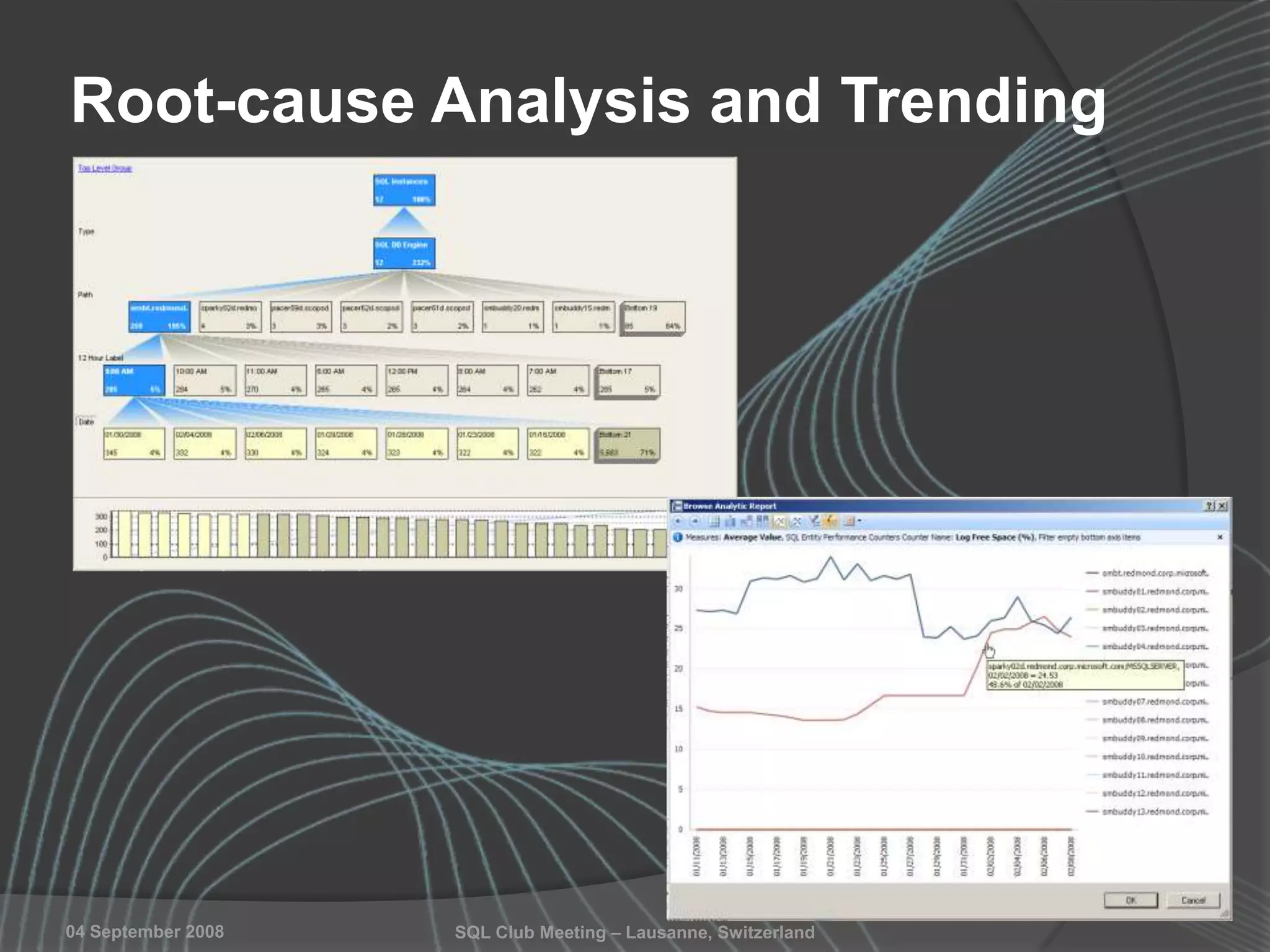
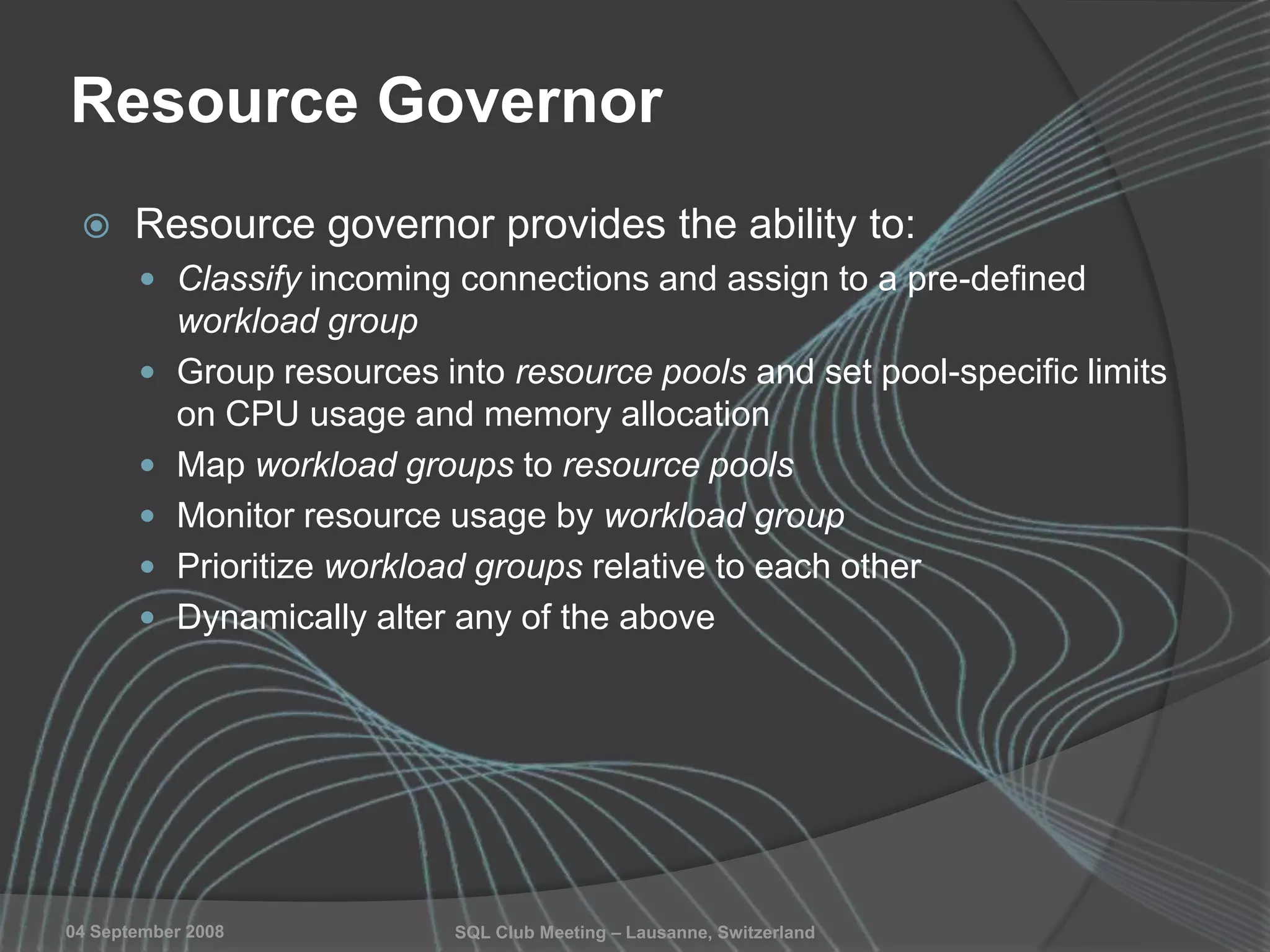
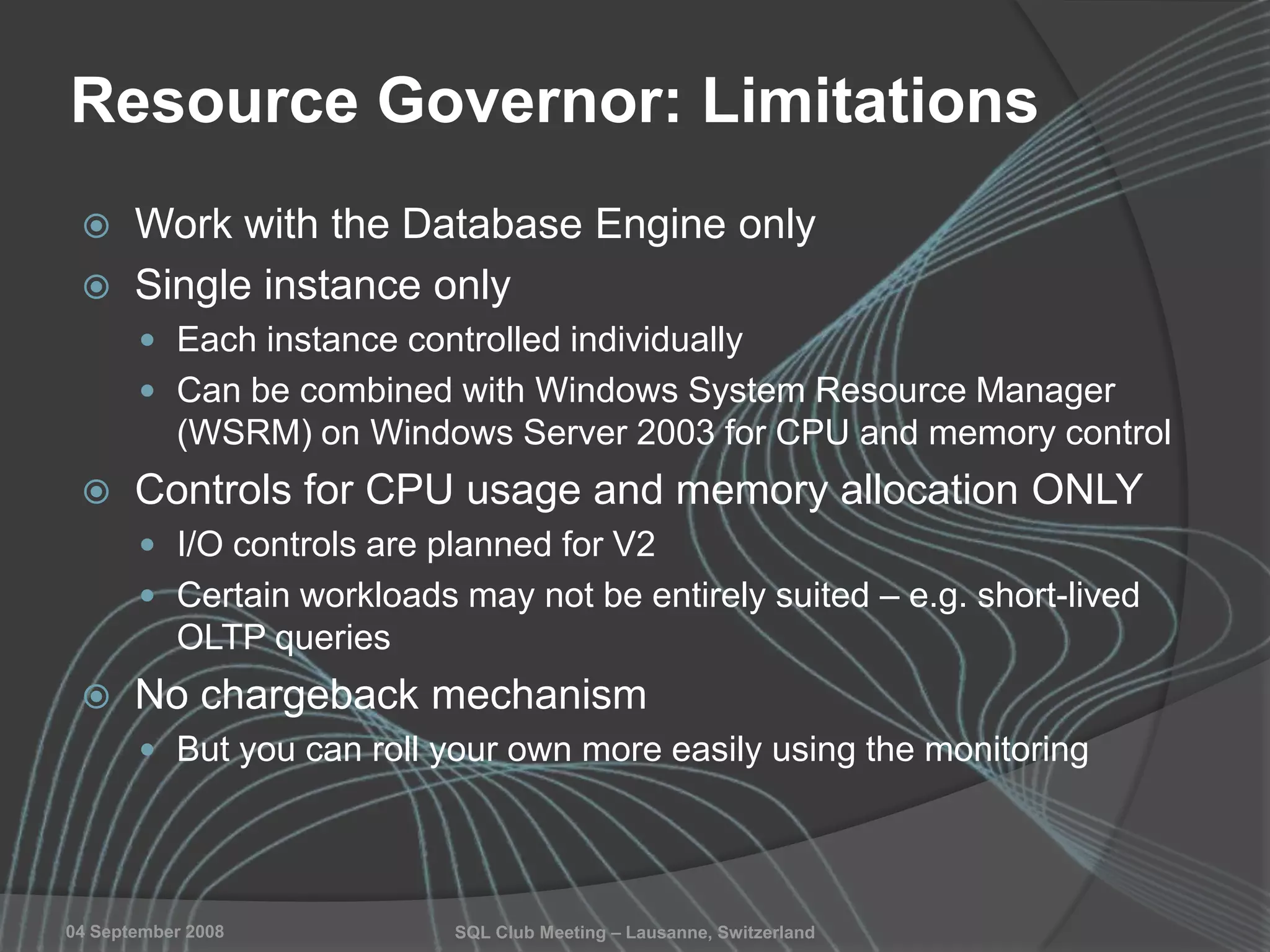
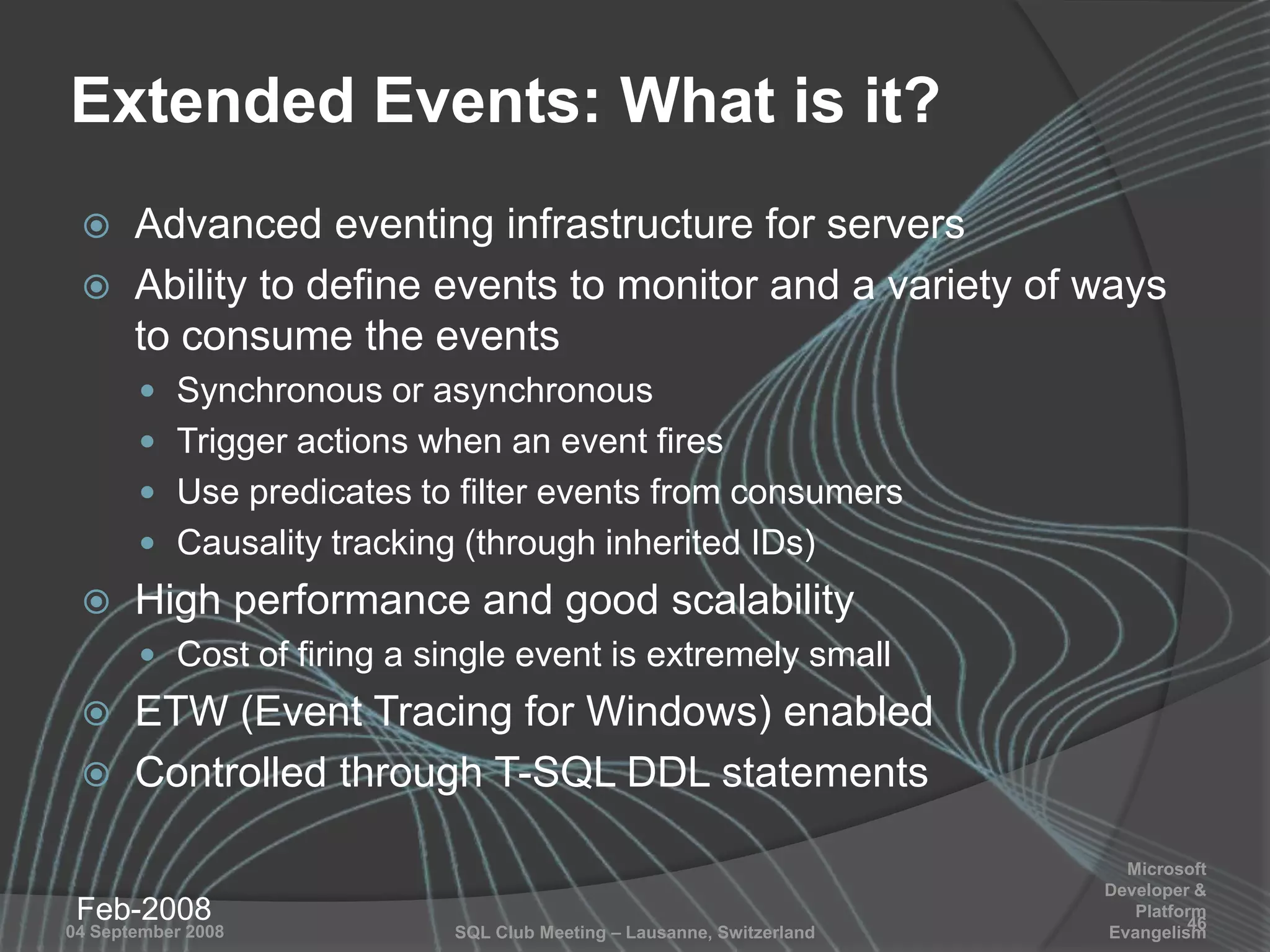
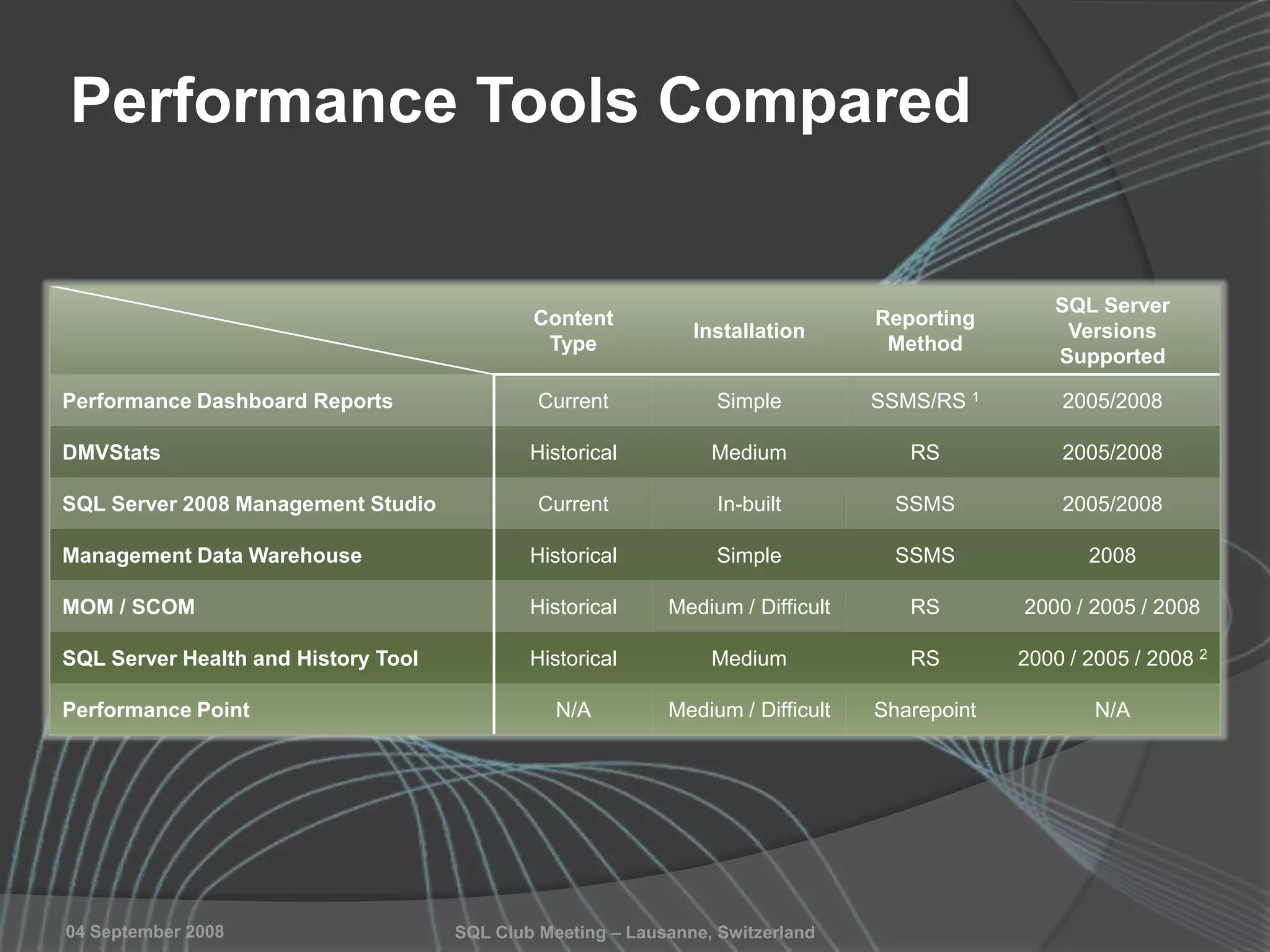
The document summarizes a SQL Club meeting about enterprise performance management. It discusses tools like Performance Dashboard Reports, DMVStats, SQL Server Management Studio, the Management Data Warehouse, Operations Manager, the SQL Server Health and History Tool, and Performance Point. It covers how these tools can be used to measure performance, identify issues, perform historical analysis, and present metrics and KPIs. It also discusses new capabilities in SQL Server 2008 like Resource Governor and Extended Events.