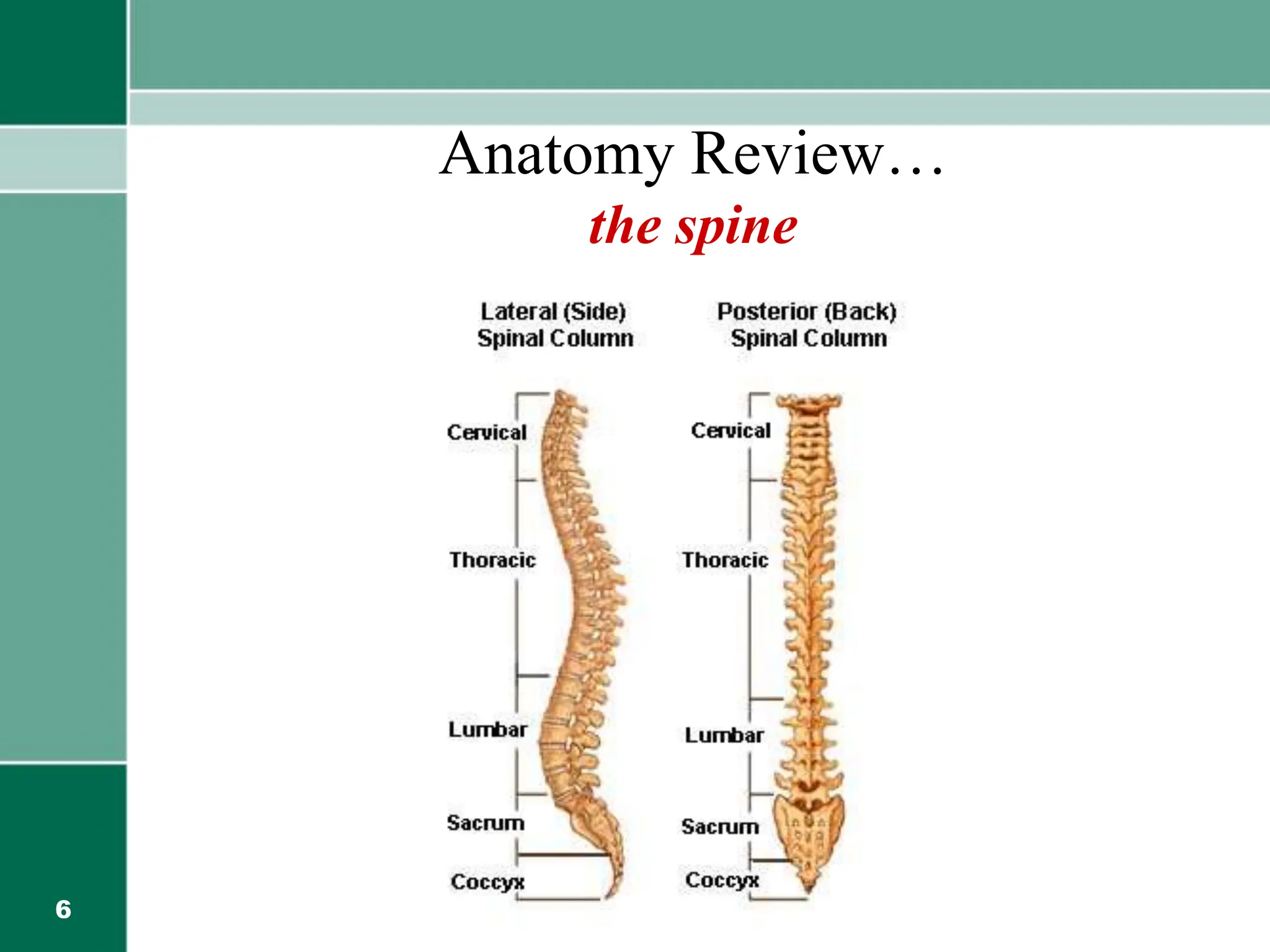
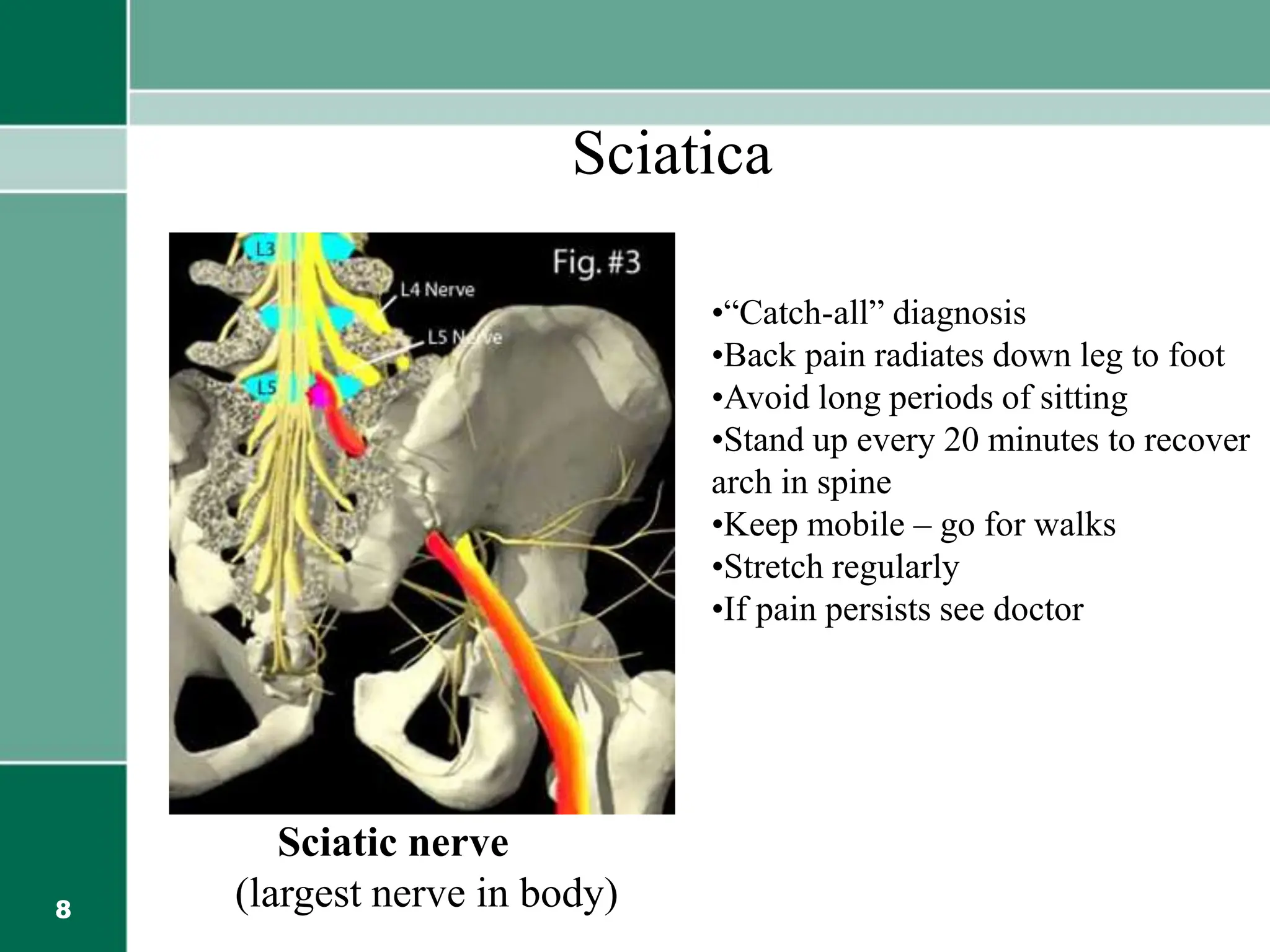
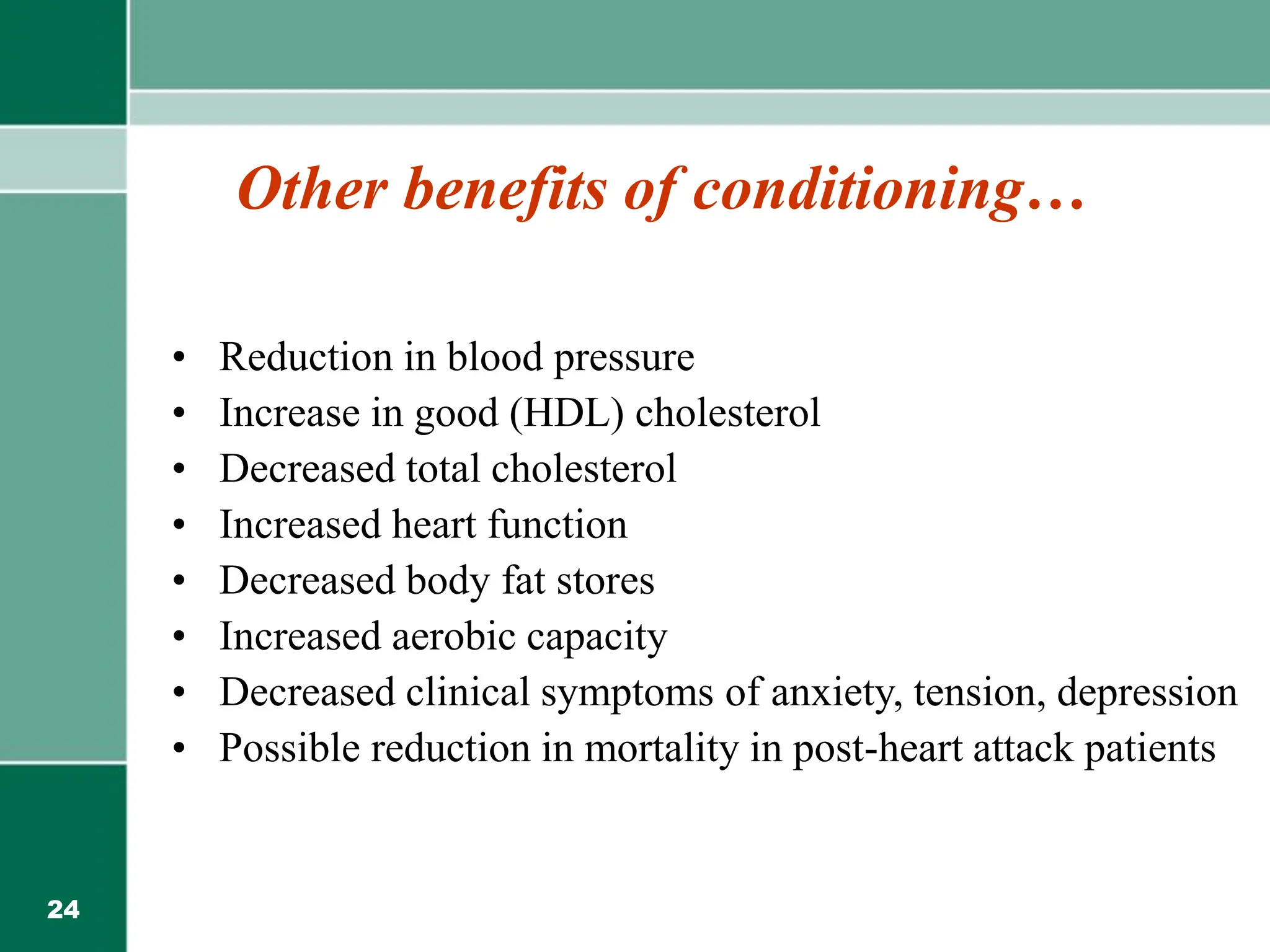
This document provides information on back safety and prevention of back problems. It discusses that low back pain is very common, affecting 87.5 million people in India. While treatments like surgery and chiropractic care offer no long-term benefits over no treatment, prevention is key. Personal factors like age, gender, and physical fitness can impact back pain. Maintaining good posture, lifting properly, and regular exercise can help prevent back problems and injuries from everyday activities at home, work, and in the car. Strength training and flexibility are important for back health.