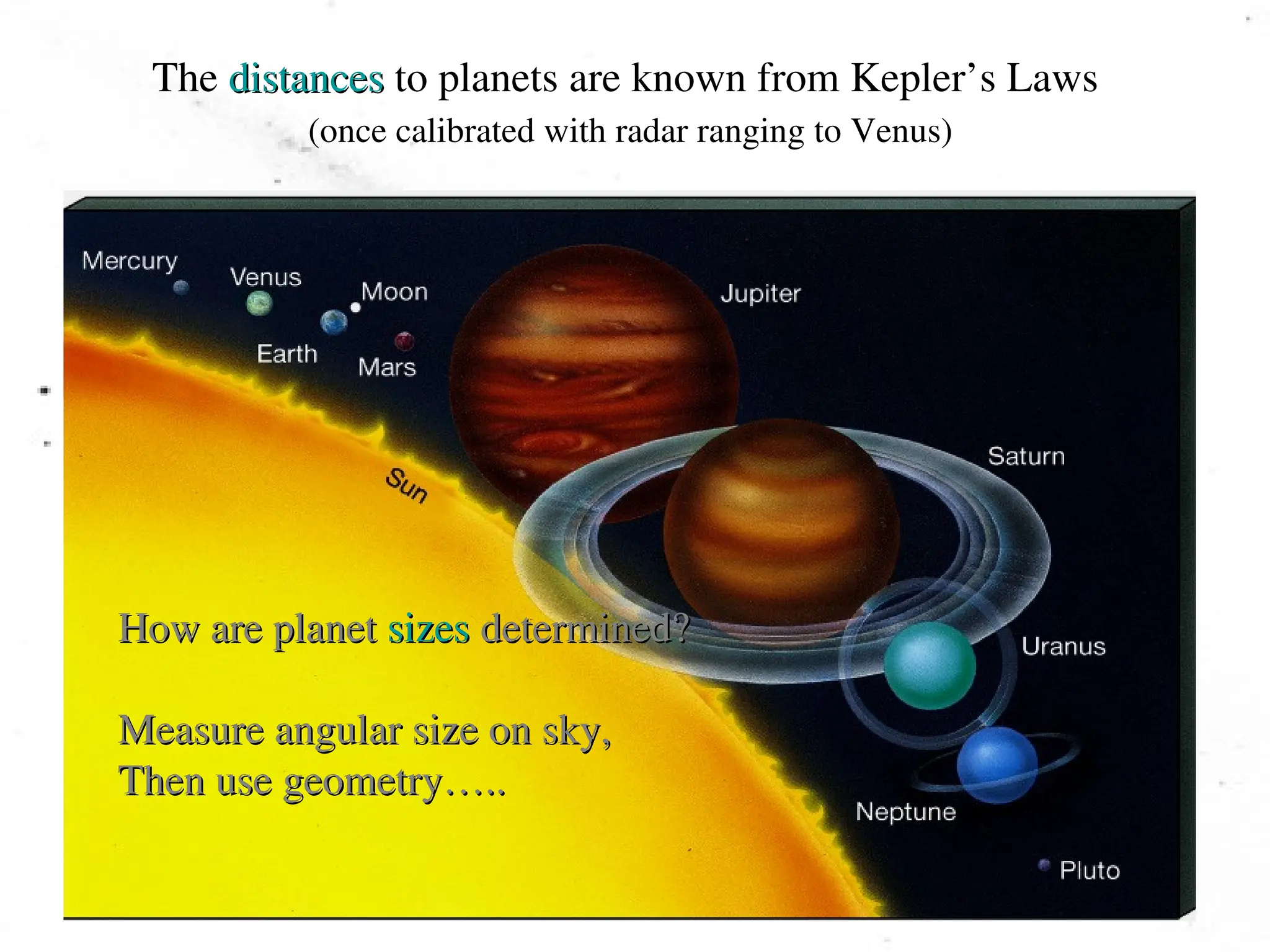
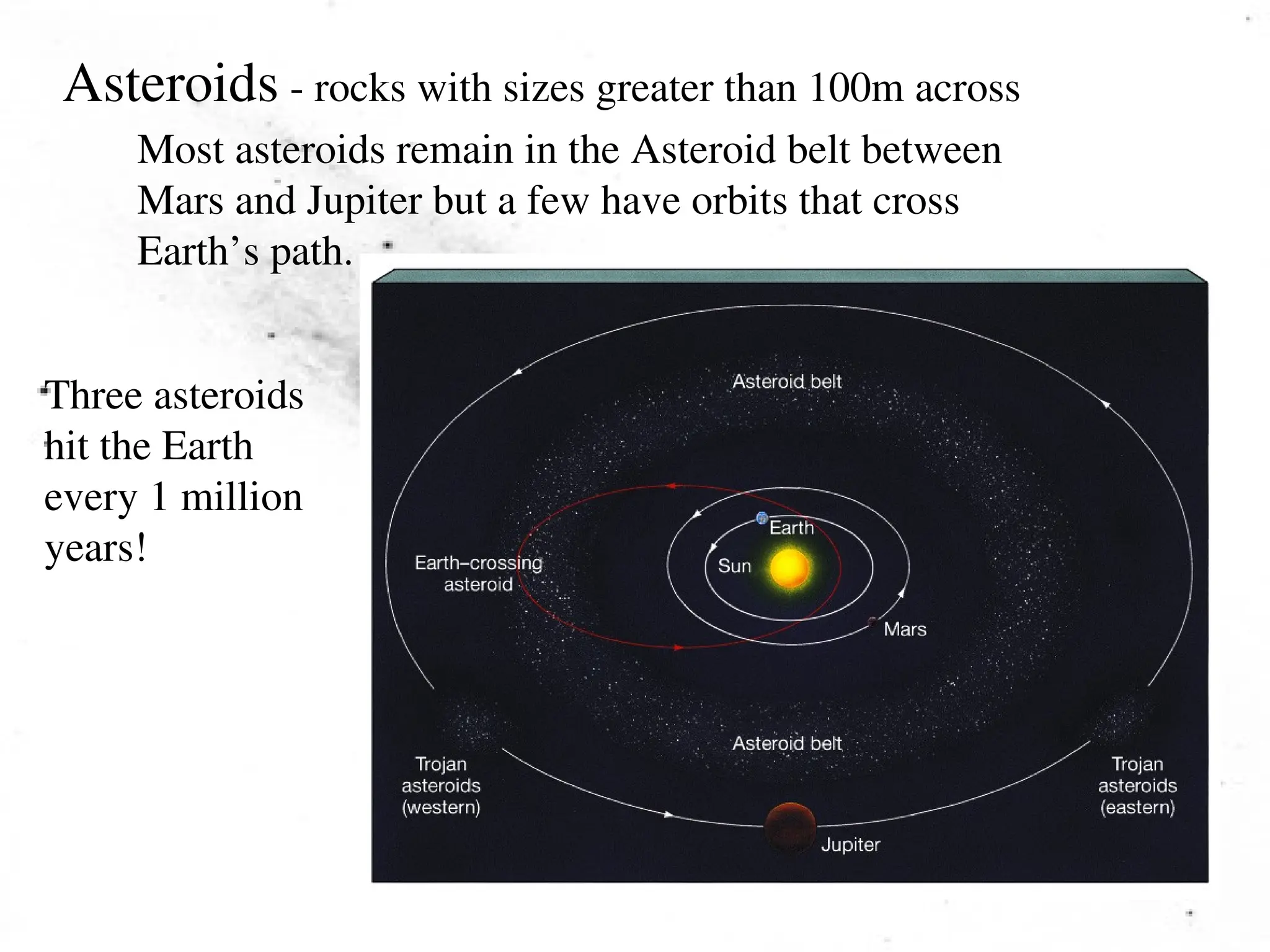
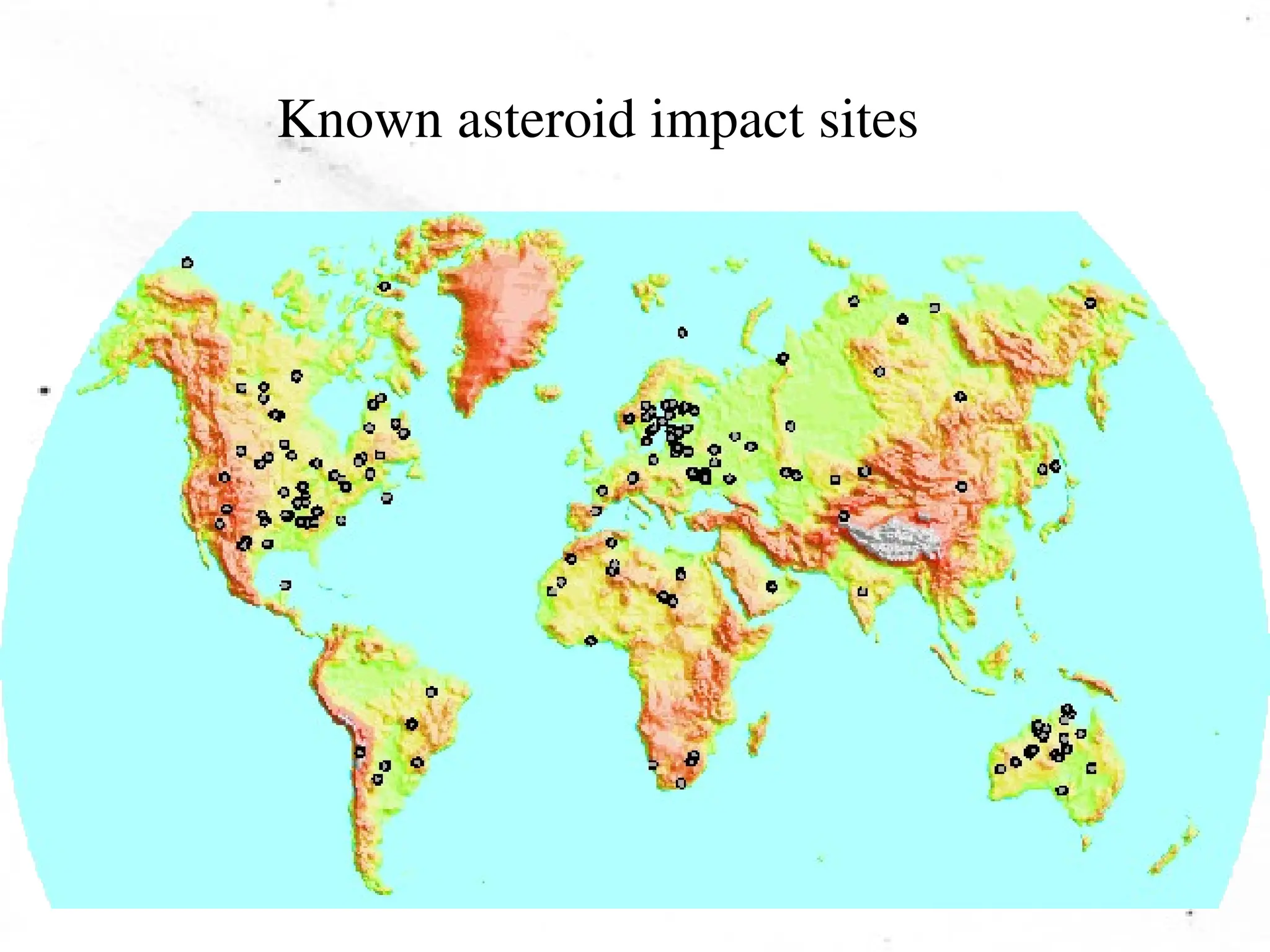
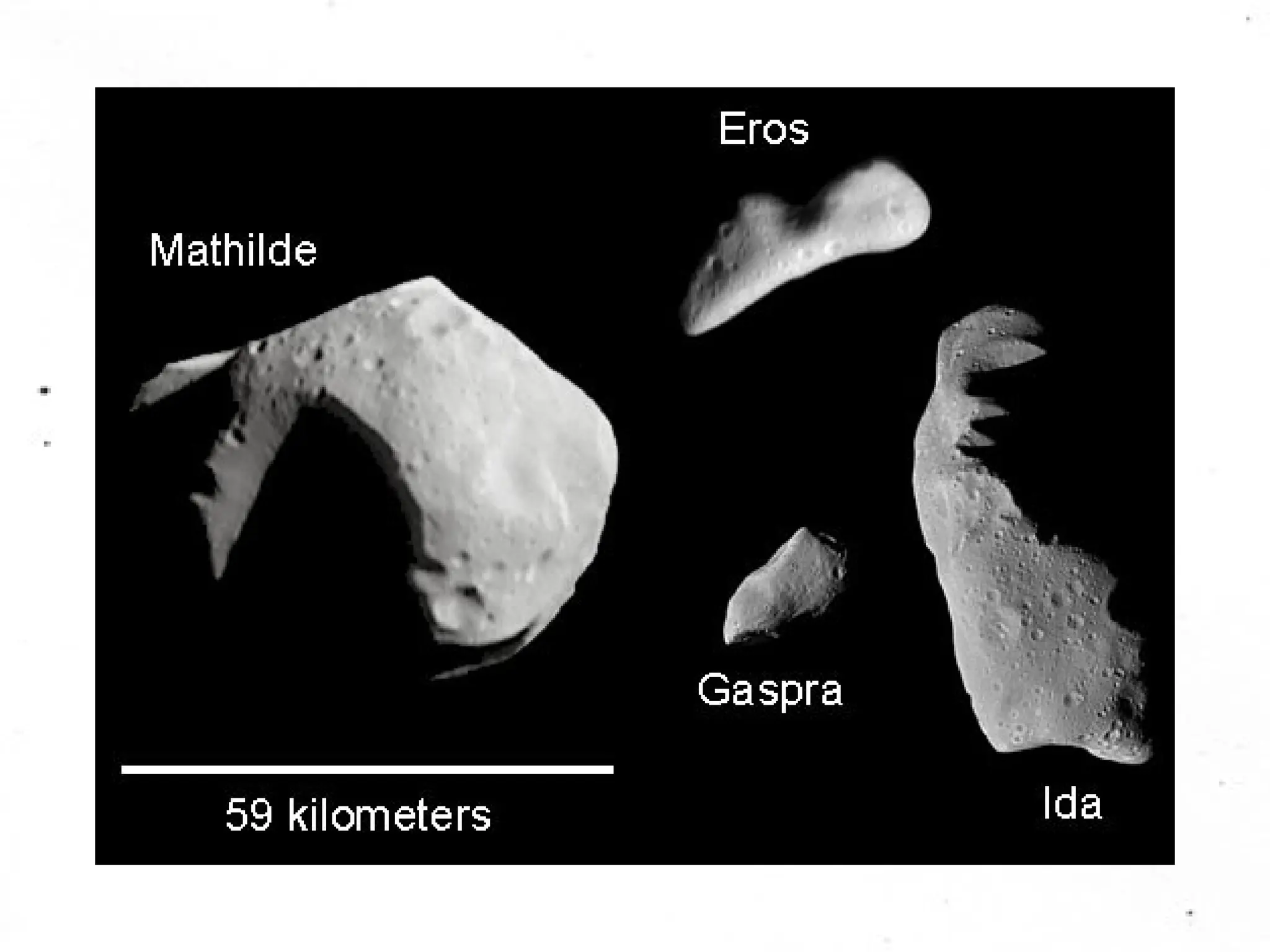
The document provides an overview of the solar system, detailing its structure, including the sun, planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. It explains the characteristics of terrestrial and jovian planets, the formation of the solar system through nebular and condensation theories, and the role of temperature in the formation of different types of planets. Additionally, it touches on meteoroids and meteor showers while outlining the properties and behaviors of asteroids and comets.