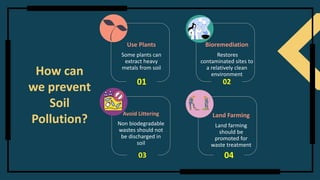
This document summarizes a presentation on soil pollution. It begins by defining soil and its composition. Soil pollution is then defined as the buildup of toxic compounds, radioactive materials, or disease-causing agents in soil that harm plant growth and animal health. The causes of soil pollution are identified as deforestation, overuse of pesticides, landfill waste, and discharge of industrial waste. The effects are reduced soil fertility, increased erosion, loss of nutrients, increased salinity, release of pollutants, and reduced vegetation. Methods to control soil pollution discussed are reducing chemical fertilizer and pesticide use, reusing minerals, recycling, reforestation, using plants to extract heavy metals, bioremediation to