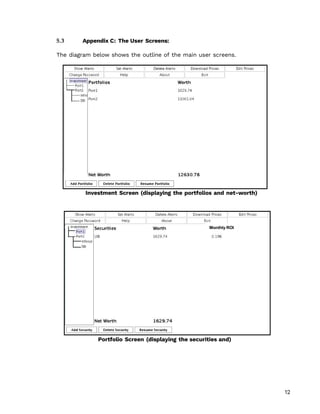
This document provides a software requirements specification (SRS) for the Goya Investment System (GIS). The SRS outlines the purpose, scope, definitions, and overall description of the GIS. It describes functional requirements through use cases for features such as portfolio management, security management, transaction management, computations, alerts, and downloading share prices. The document is intended to guide developers and serve as a validation document for clients.