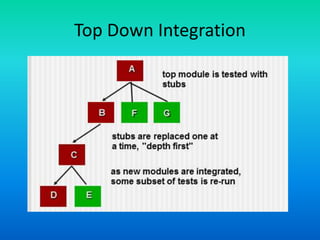
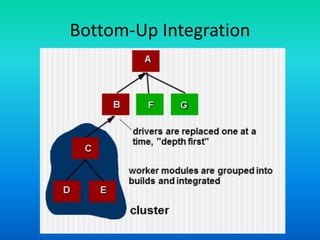
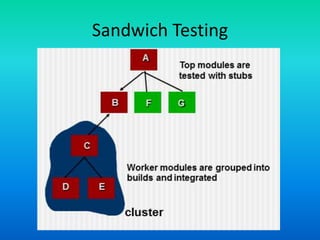
The document outlines various integration testing strategies, including big bang, incremental construction, and regression testing, highlighting the importance of verifying that changes do not introduce errors. It also details the process of smoke testing and object-oriented testing, emphasizing the need for correct analysis and design models in testing software applications. Furthermore, it discusses comprehensive testing approaches for web applications, complete systems, and includes assignments related to these concepts.