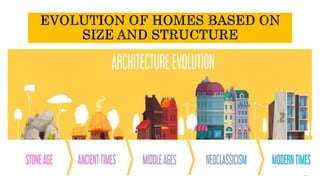
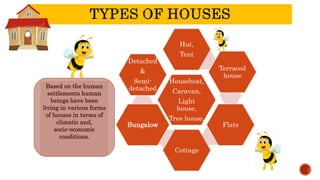
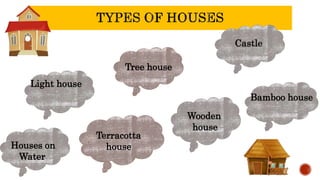
Homes have changed significantly over time based on societal and technological developments. Early humans lived nomadically and built temporary shelters from available natural materials like animal skins, leaves, and branches. As humans began farming and settling into communities, more permanent structures emerged like huts made of mud, wood, and thatch. Housing continued evolving with advances in building materials, from stone and timber to bricks, concrete, and metals. Today's homes range from traditional structures still used by some tribes to modern apartments, houses, and other building types that reflect changes in lifestyles and construction capabilities. Housing plays an important role in protecting humans from the environment and is shaped by factors like climate, resources, and societal needs over history.