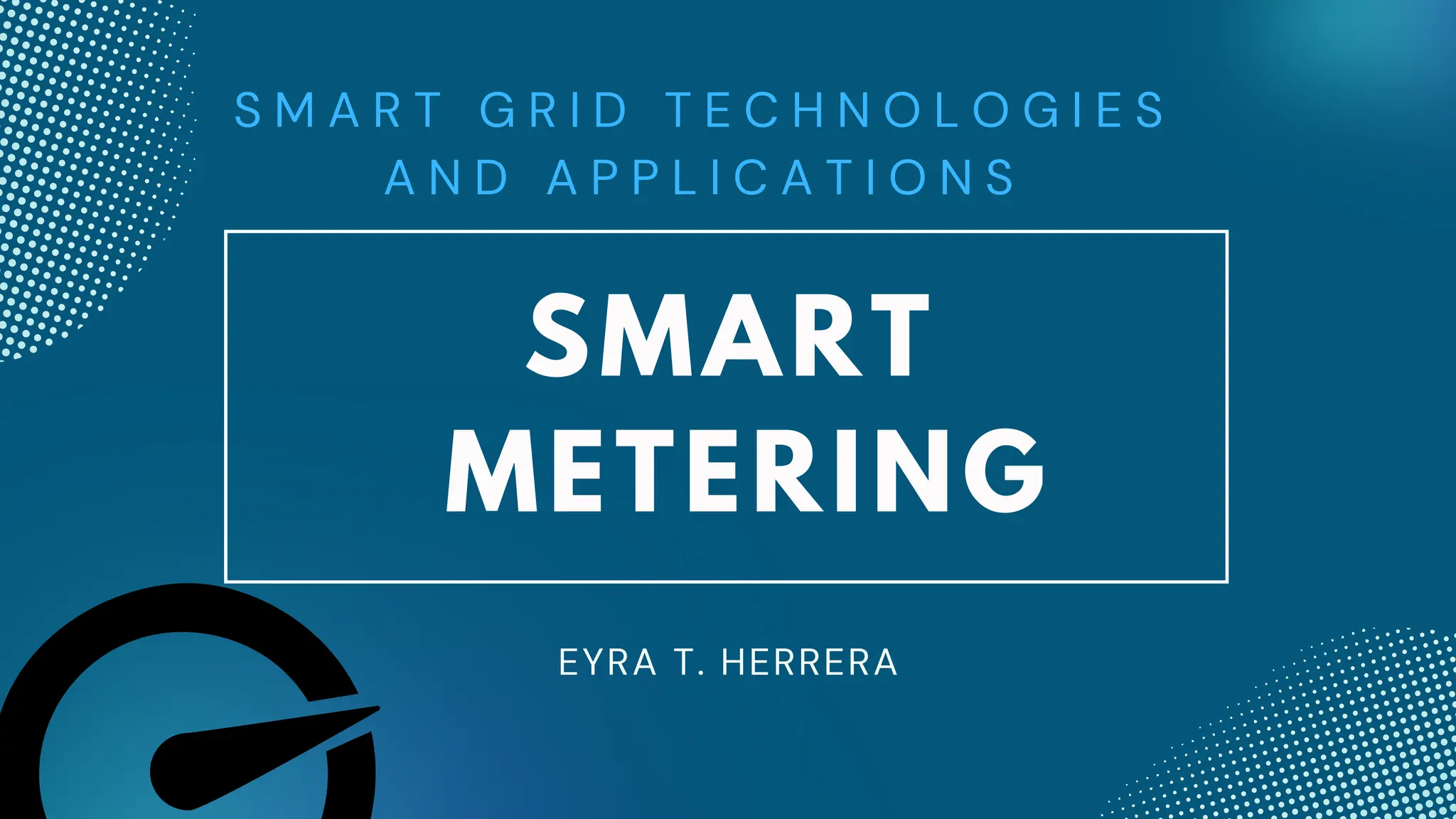
Smart metering involves installing digital electricity meters that can measure consumption remotely in real-time and enable two-way communication between the utility and customer. This allows utilities to remotely read usage, detect outages, reduce billing errors and fraud. It provides customers with more timely usage data to help manage consumption. Smart metering is a key enabling technology for modernizing the electric grid and integrating renewable energy through demand response and time-varying pricing schemes. A large-scale rollout in Italy saved utilities 500 million euros annually through reduced operating costs while lowering overall power consumption 5%.