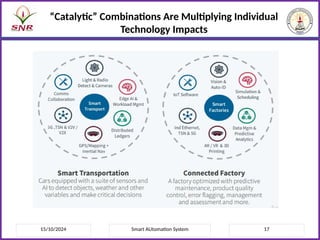
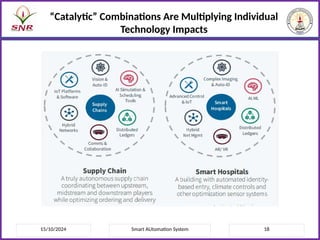
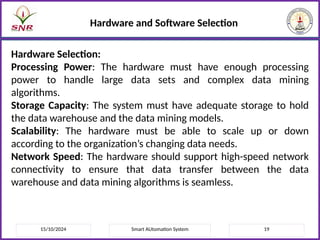
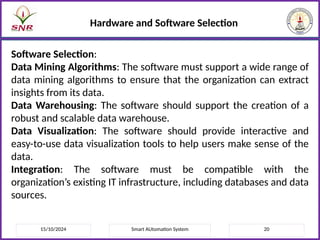
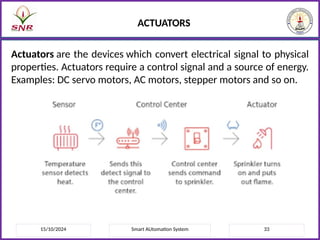
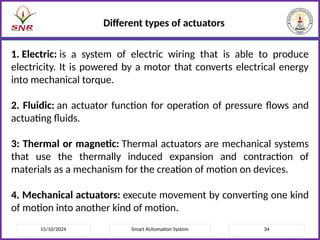
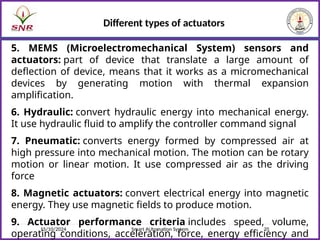
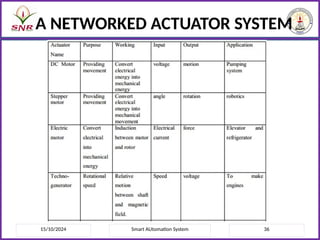
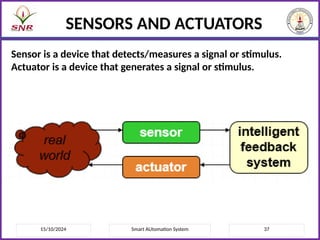
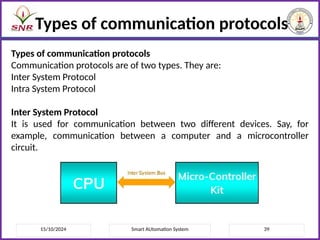
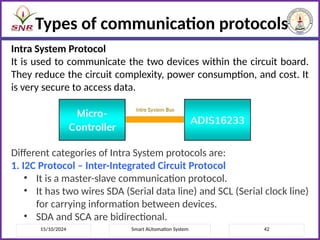
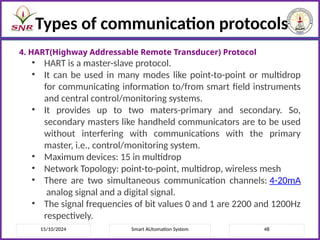
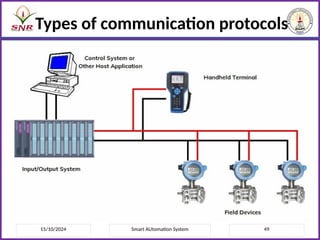
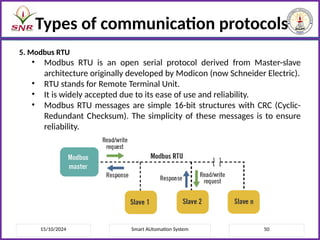
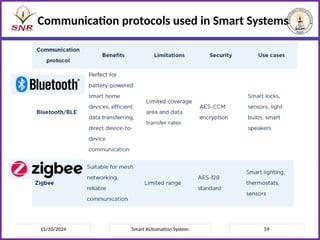
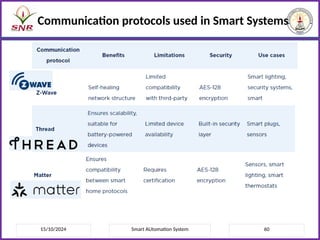
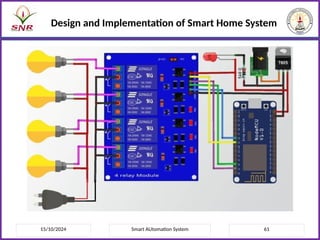
The document outlines a course on Smart Automation Systems at Sri Ramakrishna Engineering College, focusing on concepts, design, and applications of smart systems in areas like home automation, energy management, and robotics. It includes course outcomes, modules covering topics such as smart sensors and actuators, communication protocols, and various types of actuators, along with relevant textbooks and references. The course aims to enhance students' knowledge in embedded systems and improve their employability and entrepreneurial capabilities.
![15/10/2024 1
Smart AUtomation System
SRI RAMAKRISHNA ENGINEERING COLLEGE
[Educational Service: SNR Sons Charitable Trust]
[Autonomous Institution, Reaccredited by NAAC with ‘A+’ Grade]
[Approved by AICTE and Permanently Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai]
[ISO 9001:2015 Certified and all eligible programmes Accredited by NBA]
Vattamalaipalayam, N.G.G.O. Colony Post, Coimbatore – 641 022.
Course Instructors:
Dr.K.Balamurugan, Asso. Prof/EEE
No. of Credits: 3
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
20EE2E24 – SMART AUTOMATION SYSTEM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sasmodule-1-241015033228-1514a906/75/Smart-Automation-System-Module-1-pptx-1-2048.jpg)