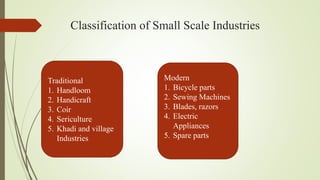
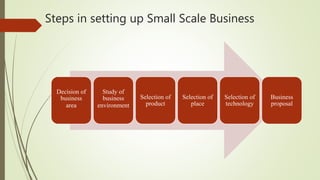
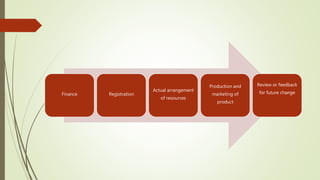
Small scale industries and businesses are defined as those that require less capital, labor, and machines to operate. According to the MSMED Act of 2006, a small business in India is classified as such if its capital investment is less than 1 crore rupees. Examples of small scale industries include businesses that produce napkins, tissues, chocolates, toothpicks, water bottles, small toys, paper products, and pens. These industries typically require only a one-time investment in machinery, plants, and other capital assets. Small businesses face challenges such as poor capacity utilization, inadequate management and financing, shortages of raw materials, and lack of marketing support. Steps to starting a small business include deciding on an industry,