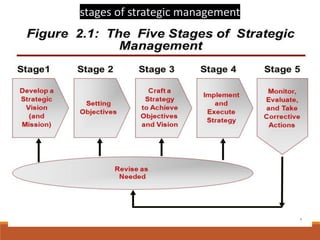
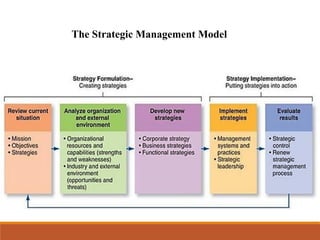
1) Strategic management involves analyzing an organization's internal/external environment, formulating strategies to achieve long-term goals, implementing plans, and evaluating performance.
2) It integrates strategic analysis, planning, implementation across functions like marketing, finance, production to match the organization to its environment.
3) Strategic management provides direction, competitive advantage, and performance improvement through effective resource allocation, adaptation to changes, and alignment of organizational activities.