Dokumen ini adalah ringkasan sesi pelatihan tentang concurrency di Java, berfokus pada proses, thread, dan mekanisme seperti sleep, interrupt, dan join. Dijelaskan cara membuat dan mengelola thread serta pentingnya sinkronisasi untuk mencegah kesalahan saat menggunakan resource bersama. Selain itu, dibahas penggunaan timer untuk penjadwalan tugas secara periodik.





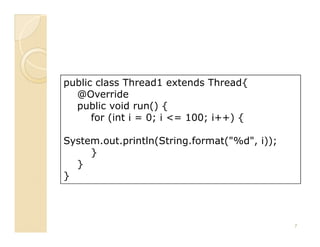
![public class Main {
public static void main(String argv[]) {
Thread1 thread1 = new Thread1();
thread1.start();
}
}
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slide-sesi6-javaconcurrency-100418052719-phpapp01/85/Slide-sesi-6-java-concurrency-8-320.jpg)
![public static void main(String argv[]) {
Thread1 thread1 = new Thread1();
Thread1 thread2 = new Thread1();
Thread1 thread3 = new Thread1();
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slide-sesi6-javaconcurrency-100418052719-phpapp01/85/Slide-sesi-6-java-concurrency-9-320.jpg)





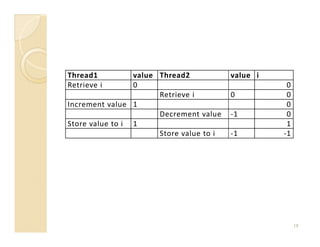
![public static void main(String argv[]) {
Thread2 thread2 = new Thread2();
thread2.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
thread2.interrupt();
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
}
}
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slide-sesi6-javaconcurrency-100418052719-phpapp01/85/Slide-sesi-6-java-concurrency-15-320.jpg)

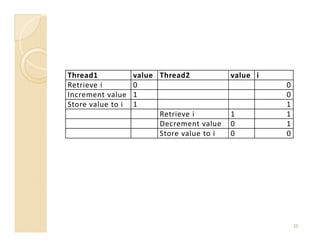
![public static void main(String argv[]) {
Thread1 thread1 = new Thread1();
thread1.start();
for (int i = 0; i <= 1000; i++) {
System.out.println(String.format("%d", i));
if (i == 30){
try {
System.out.println("Joining");
thread1.join();
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
}
}
}
}
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slide-sesi6-javaconcurrency-100418052719-phpapp01/85/Slide-sesi-6-java-concurrency-17-320.jpg)




![public class ContohTask extends TimerTask {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
System.out.println(String.format("%d", i));
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String argv[]) {
Timer t = new Timer();
t.schedule(new ContohTask(), 1000);
}
}
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slide-sesi6-javaconcurrency-100418052719-phpapp01/85/Slide-sesi-6-java-concurrency-25-320.jpg)


