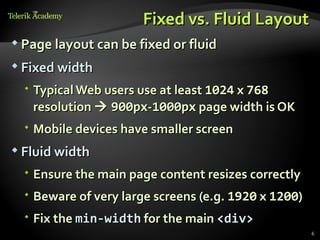
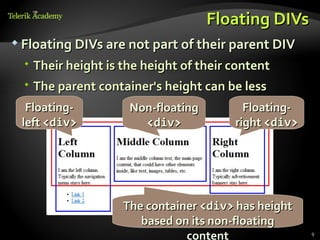
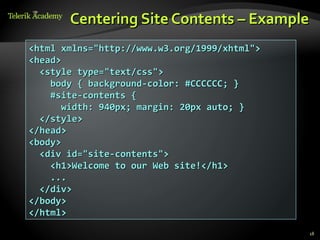
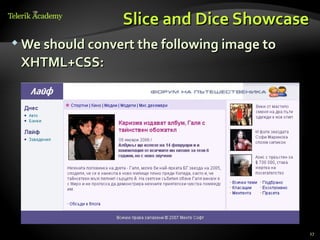
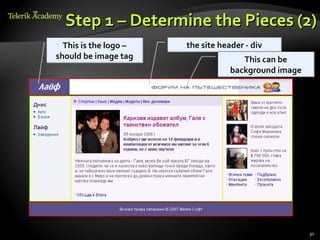
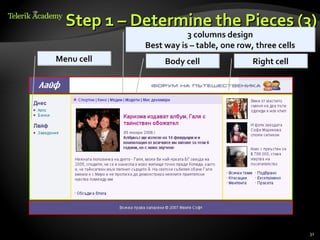
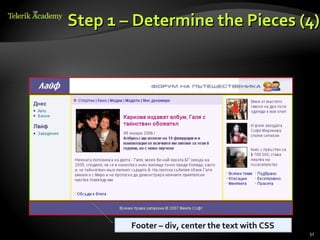
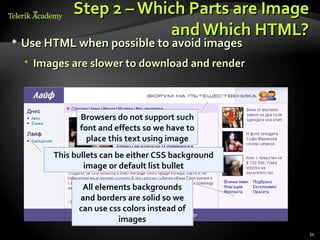
This document provides steps for converting a web site design from a PSD image to XHTML and CSS. It discusses identifying sections, choosing a layout type, distinguishing content from style, and testing across browsers. Floating DIVs and tables are recommended over frames. Details like images types, centering content, and vertical alignment are covered. Case studies demonstrate analyzing images to extract text vs images and small design details. Homework assigns recreating sample web page designs using semantic HTML and CSS only.