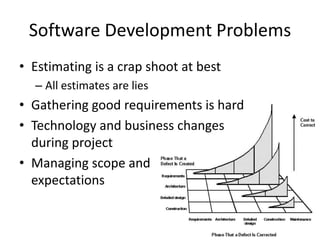
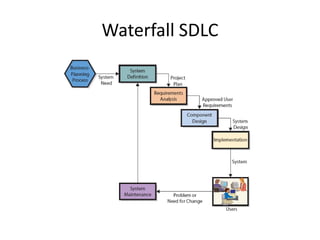
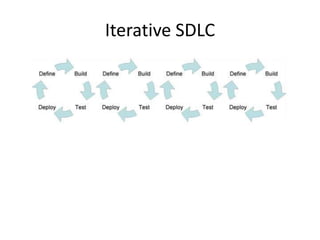
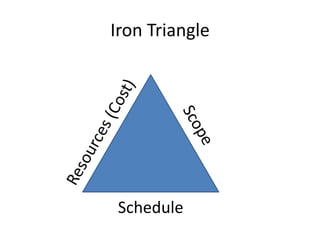
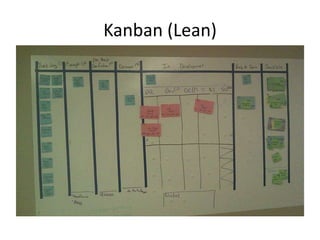
The document discusses systems development and the software development lifecycle. It describes common steps in the lifecycle including definition, analysis, design, implementation, and support. Key points include gathering requirements is important but difficult, estimating timelines is imprecise, and newer agile methodologies help address issues like scope changes. The document provides an overview of different approaches like waterfall and iterative development and tools like the iron triangle and mythical man month concept.