Embed presentation
Download to read offline
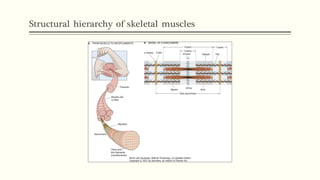
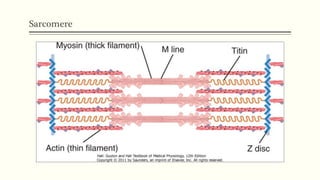
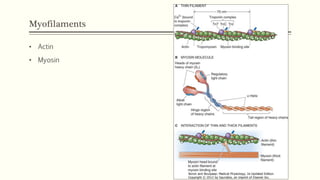
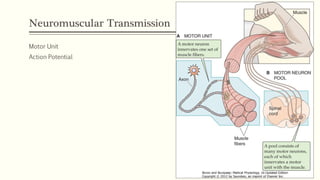

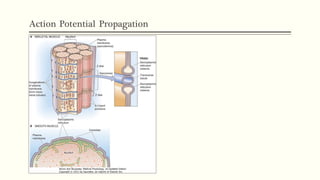
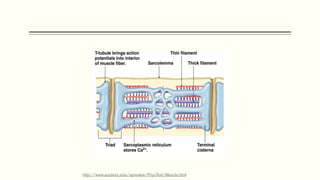
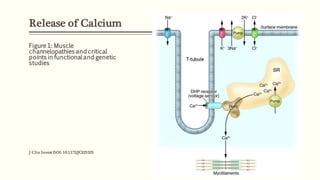
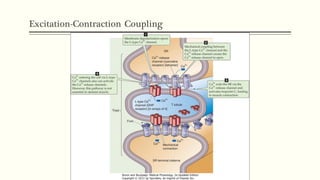
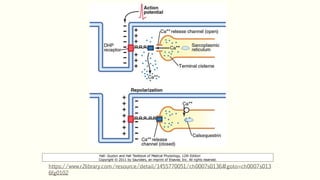
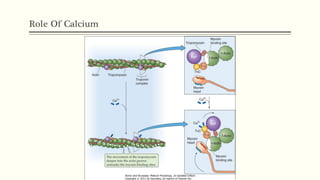
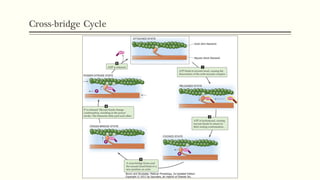
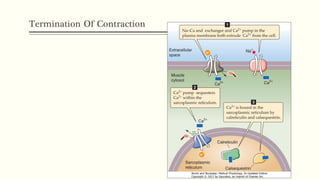
This document outlines the structural hierarchy and function of skeletal muscles. It begins with the smallest functional unit, the sarcomere, and describes the organization of actin and myosin myofilaments. It then explains the process of neuromuscular transmission where a motor unit receives an action potential from the central nervous system via the end plate. This causes excitation-contraction coupling and the release of calcium ions which trigger the cross-bridge cycling of actin and myosin to generate muscle contraction.












