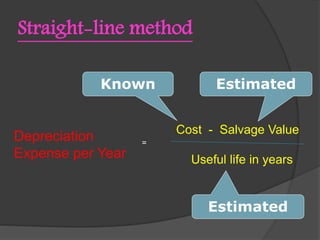
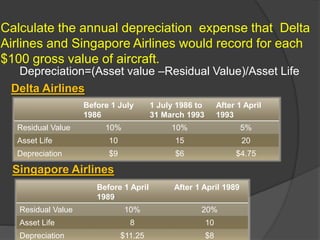
This document compares the depreciation methods used by Delta Airlines and Singapore Airlines. Both airlines use the straight-line depreciation method, but use different salvage values and estimated useful lives for their aircraft. Singapore Airlines assumes a higher salvage value and shorter useful life, resulting in higher annual depreciation expenses compared to Delta Airlines. The differences relate to the companies' overall strategies, with Singapore focusing on newer aircraft to provide a better customer experience.