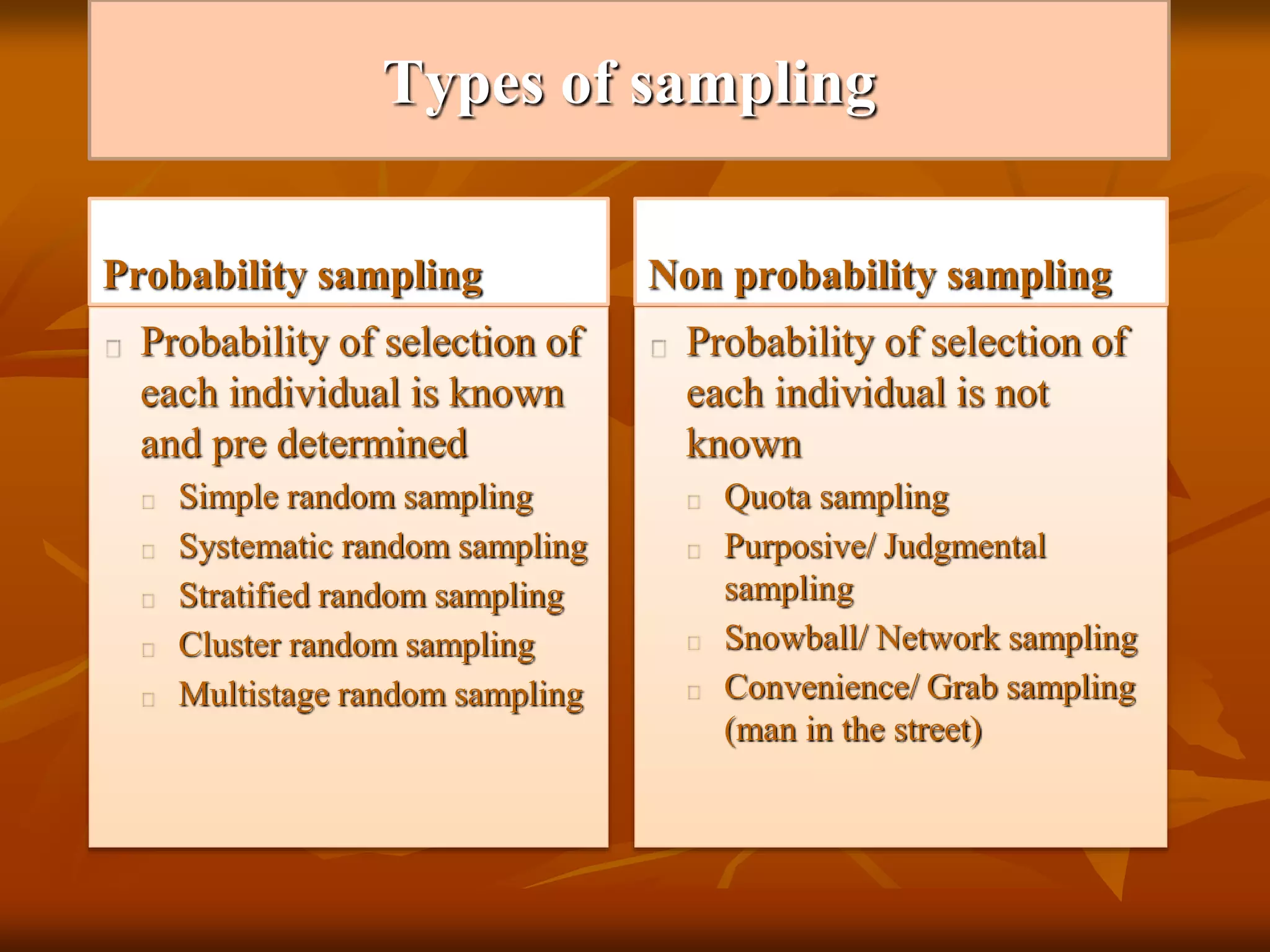
There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. Probability sampling involves methods where the probability of selection of each individual is known, such as simple random sampling, systematic random sampling, stratified random sampling, and cluster random sampling. Simple random sampling involves selecting a sample that gives each individual an equal chance of being selected by identifying the population, determining sample size, listing all population members, assigning them numbers, selecting numbers at random from a table, and including individuals in the sample if their number is selected. The advantages are it is easy to conduct and requires minimum population knowledge, while disadvantages include needing all population member names and potential over or under representation.