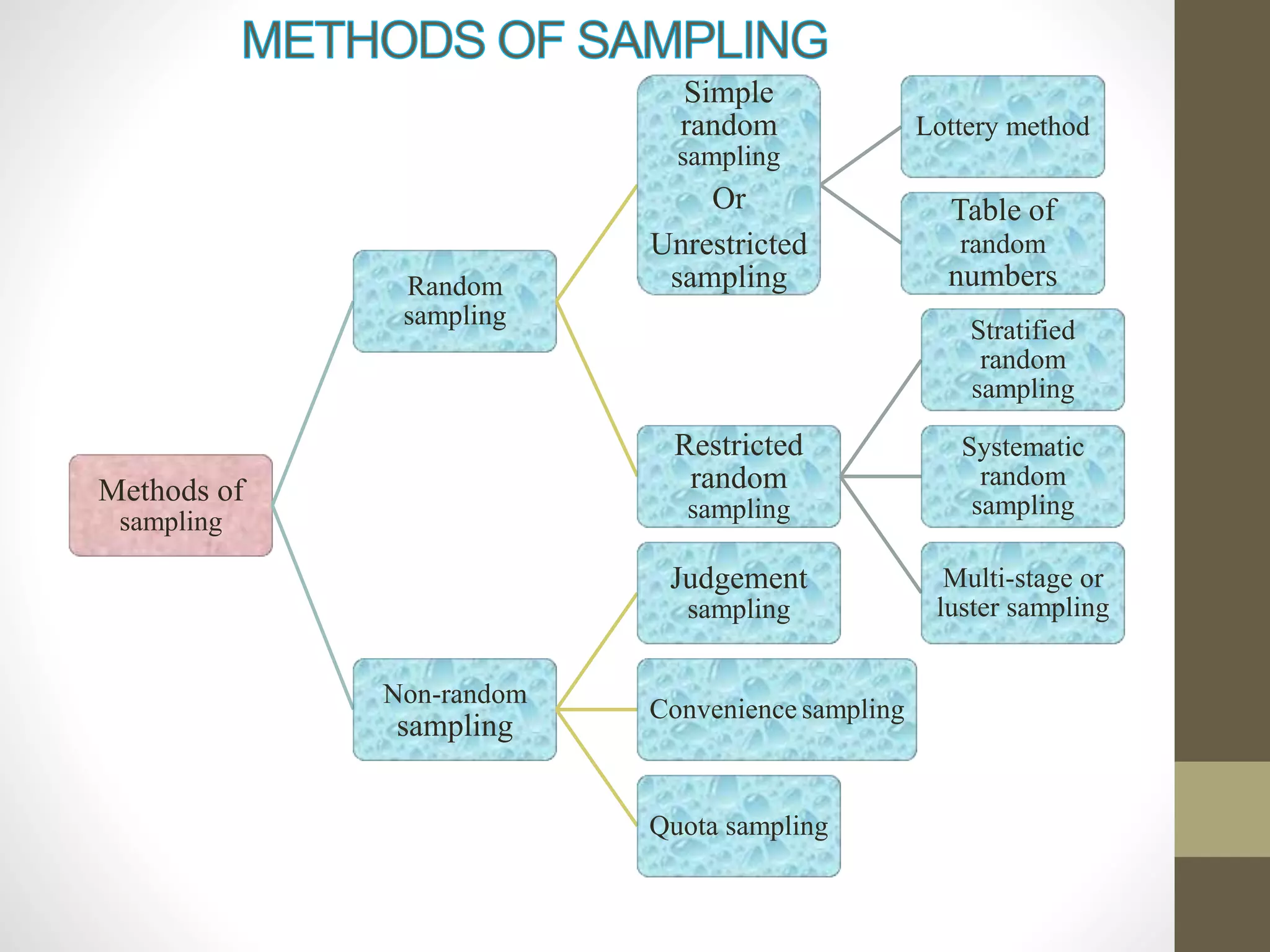
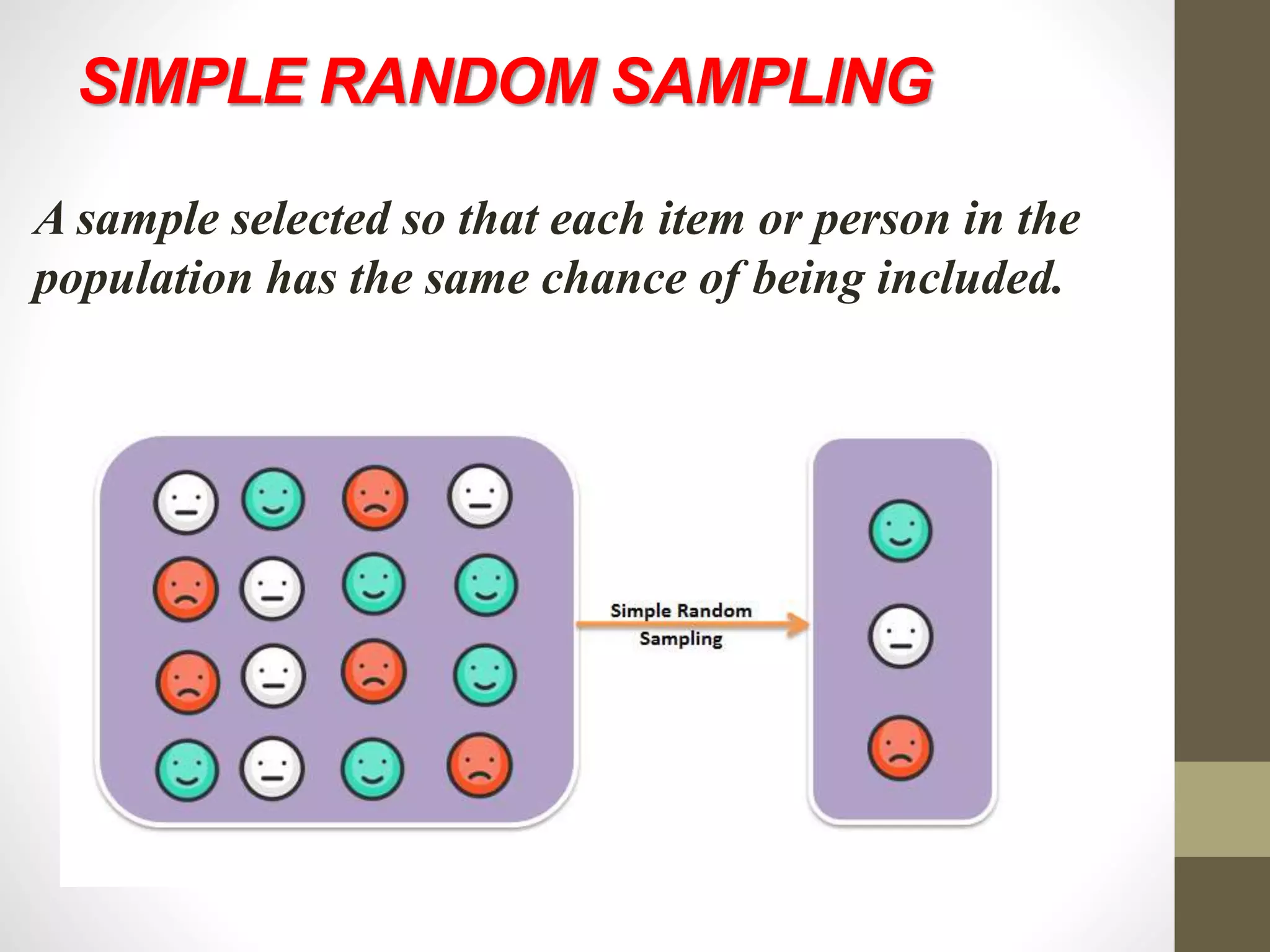
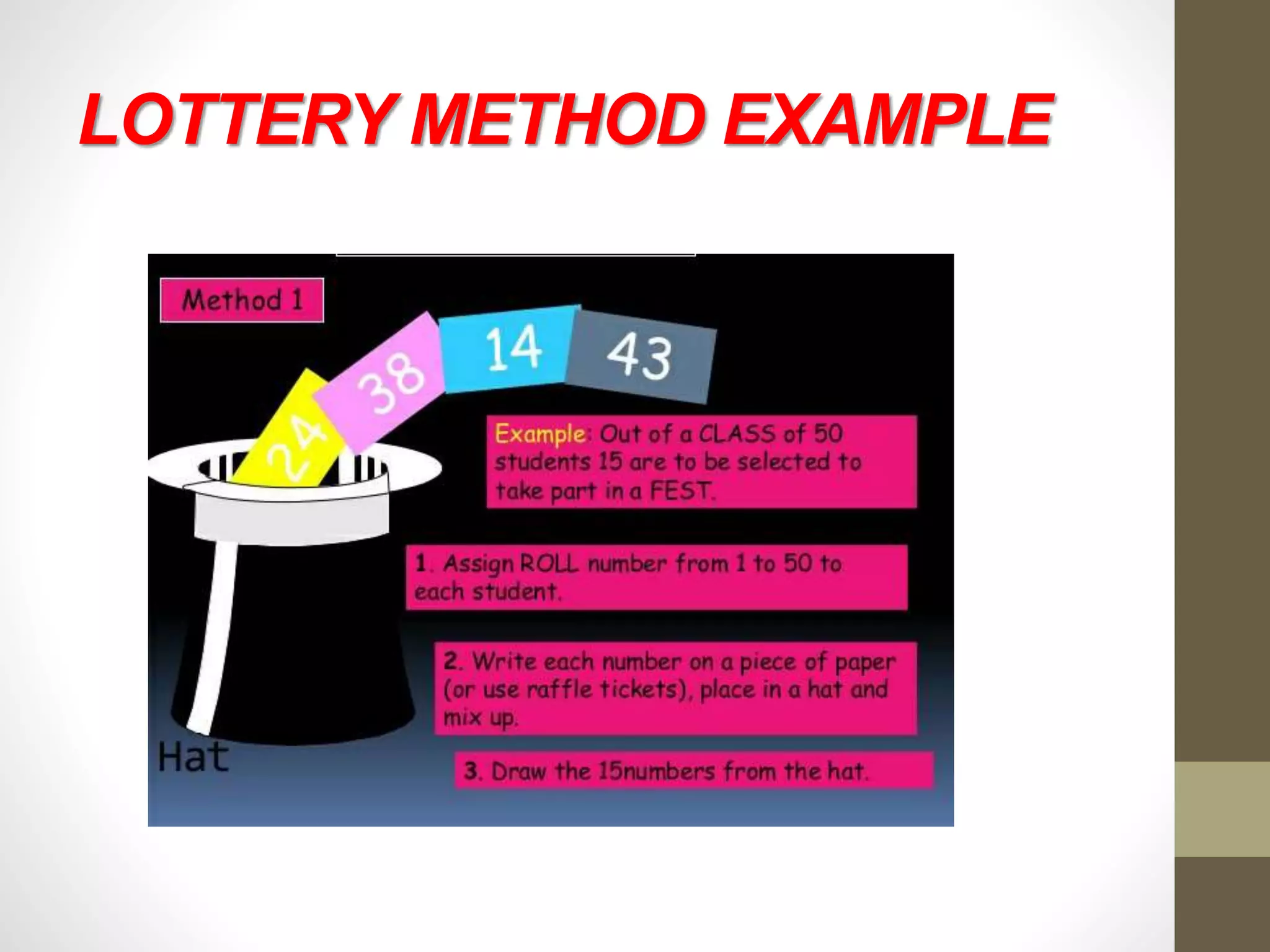
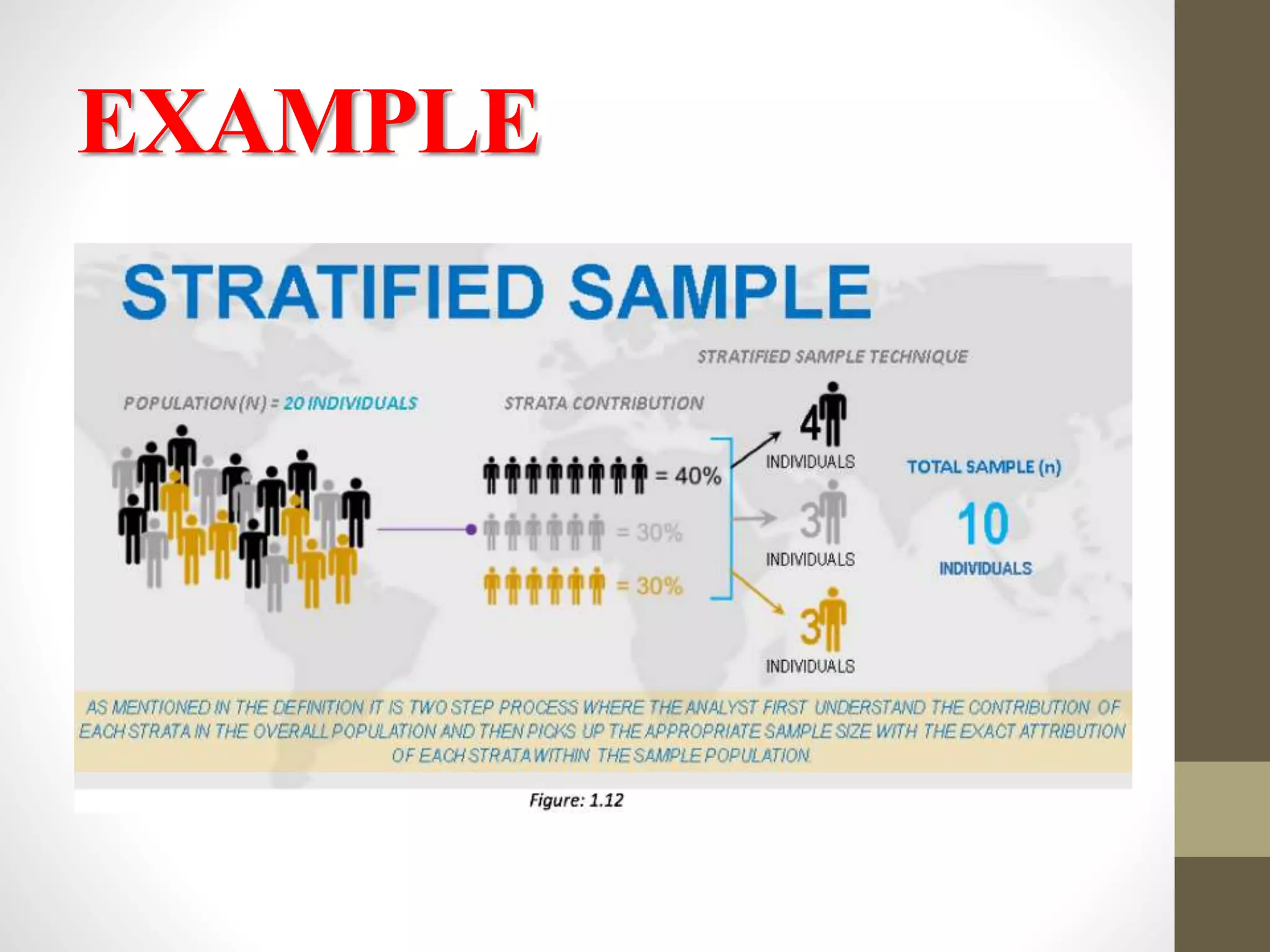
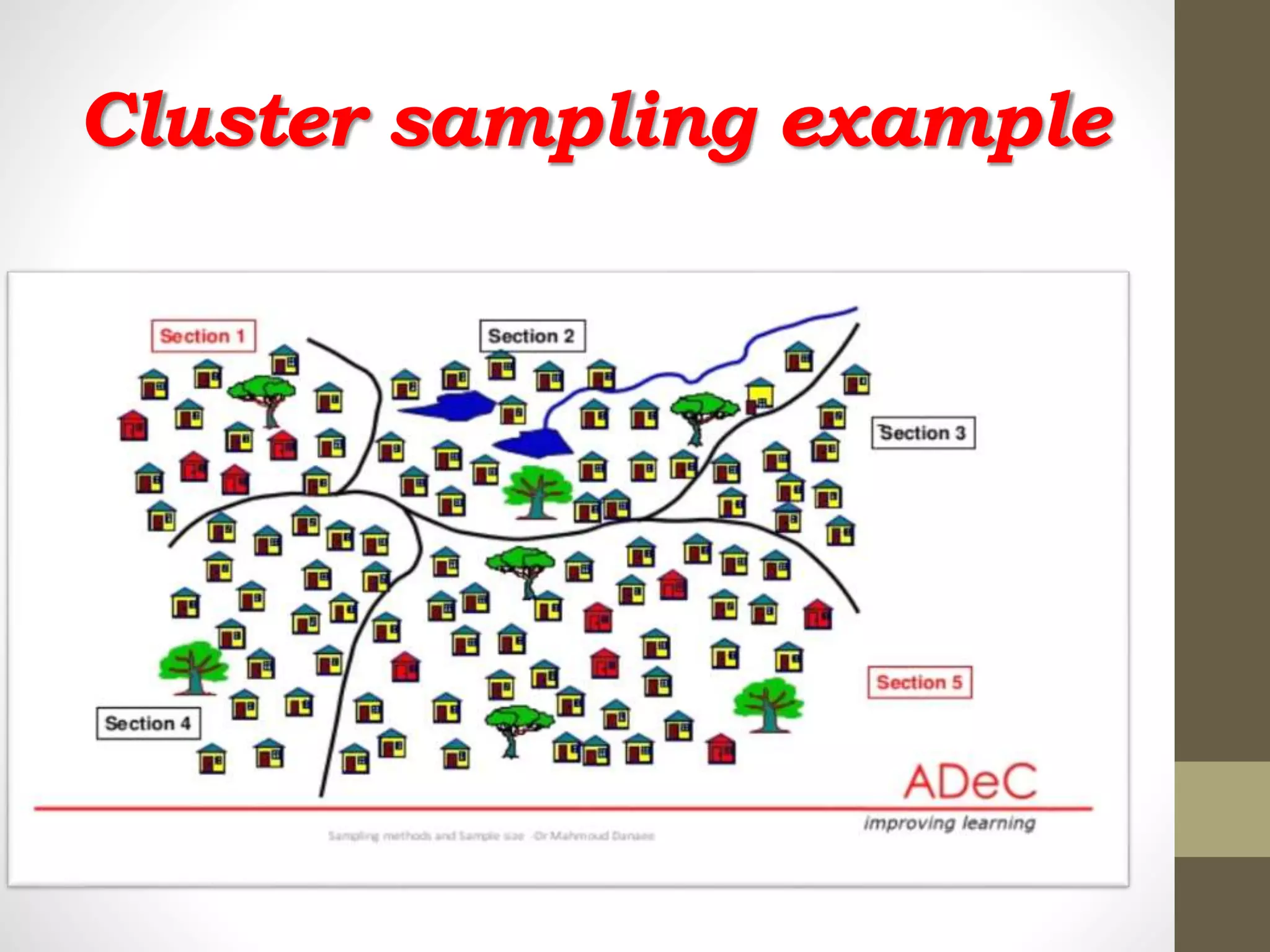
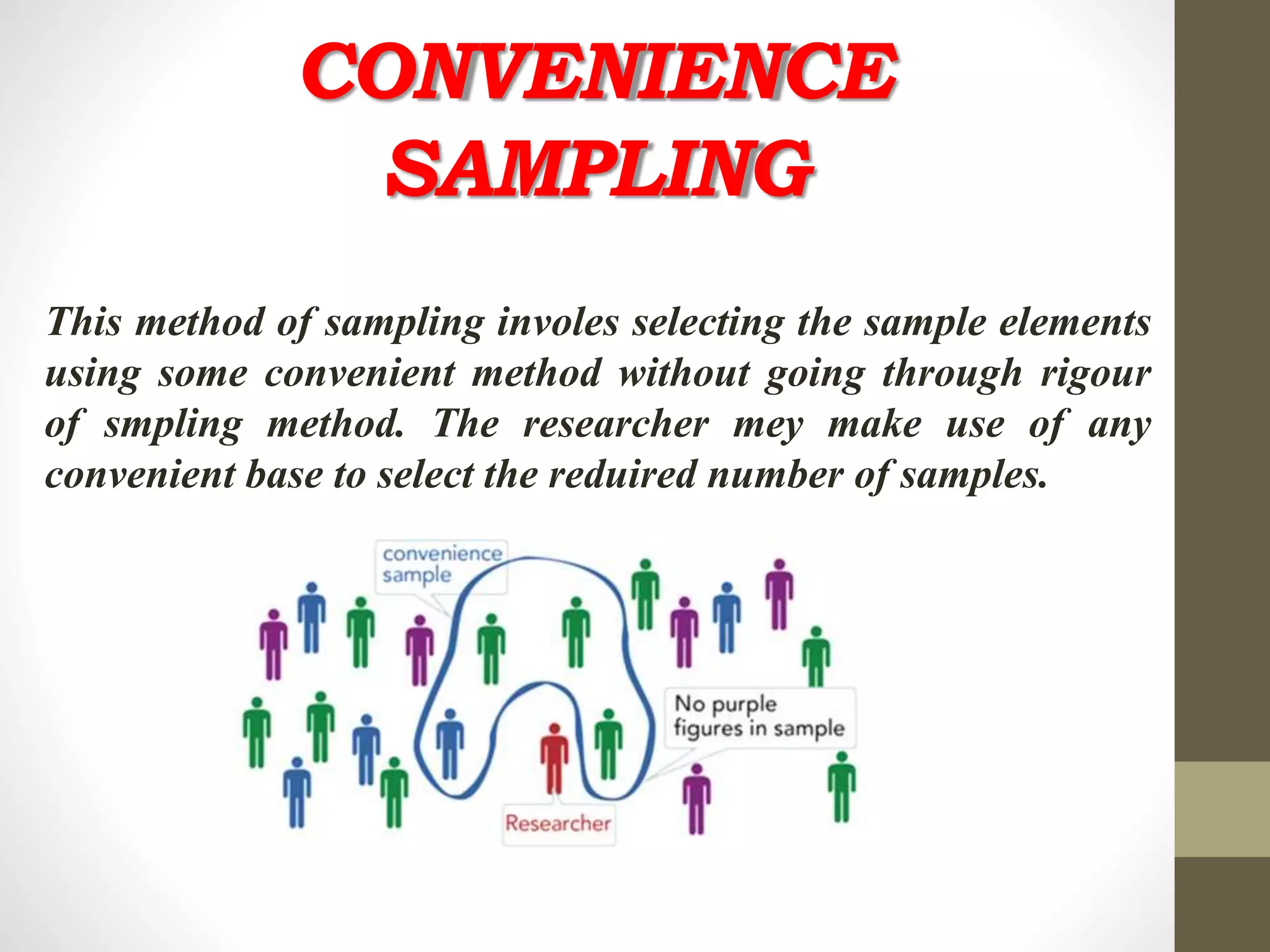
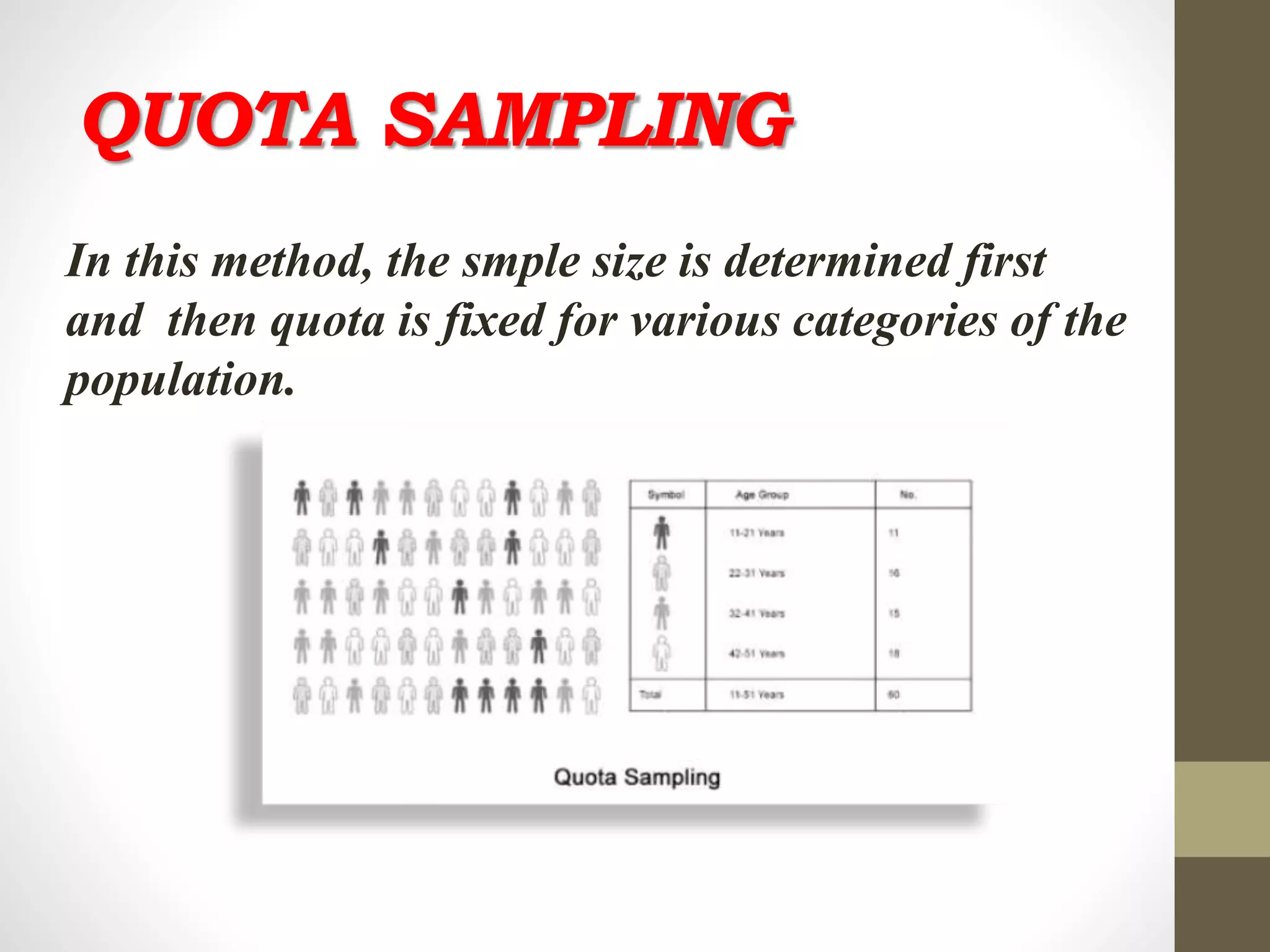
This document discusses different methods of sampling used in research. It describes random sampling methods like simple random sampling using lottery or random number tables, stratified random sampling which divides the population into layers and samples from each, and systematic random sampling which selects items at regular intervals. Non-random sampling methods include judgement, convenience, and quota sampling which select items non-randomly based on researcher judgement or quotas. The key points are that random sampling gives each item an equal chance while non-random sampling does not, and random sampling can be simple, restricted to subgroups, or multi-stage.