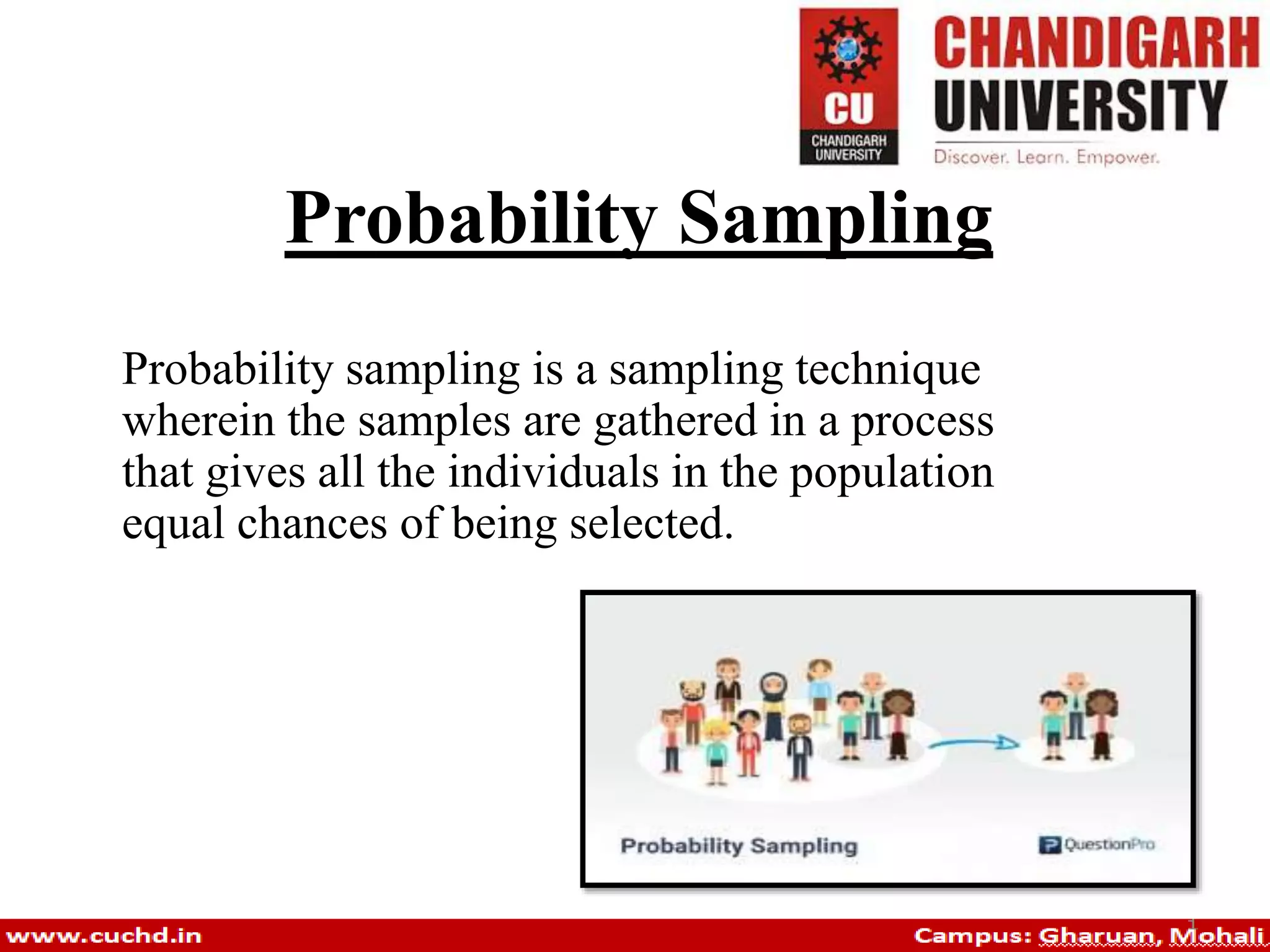
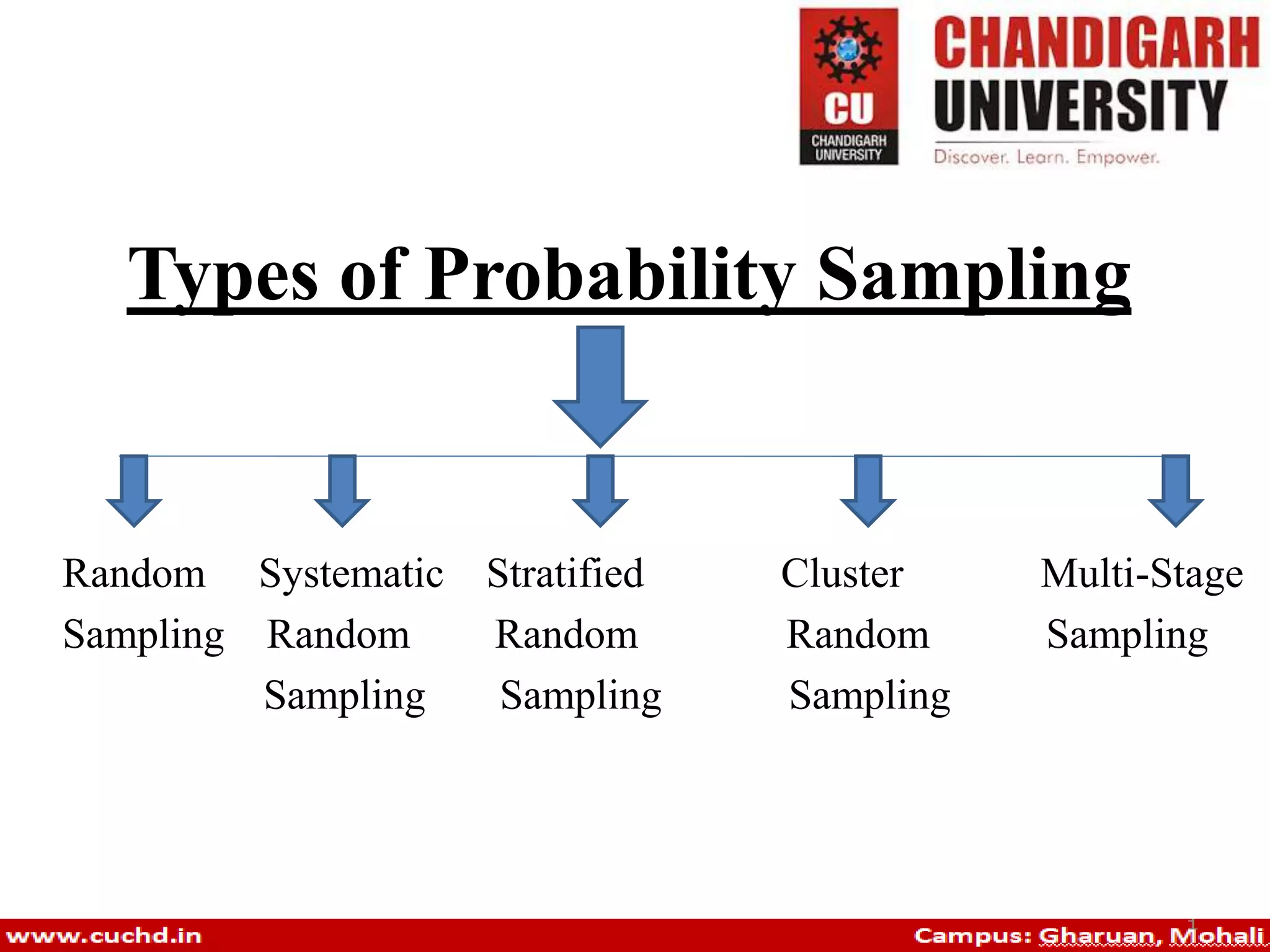
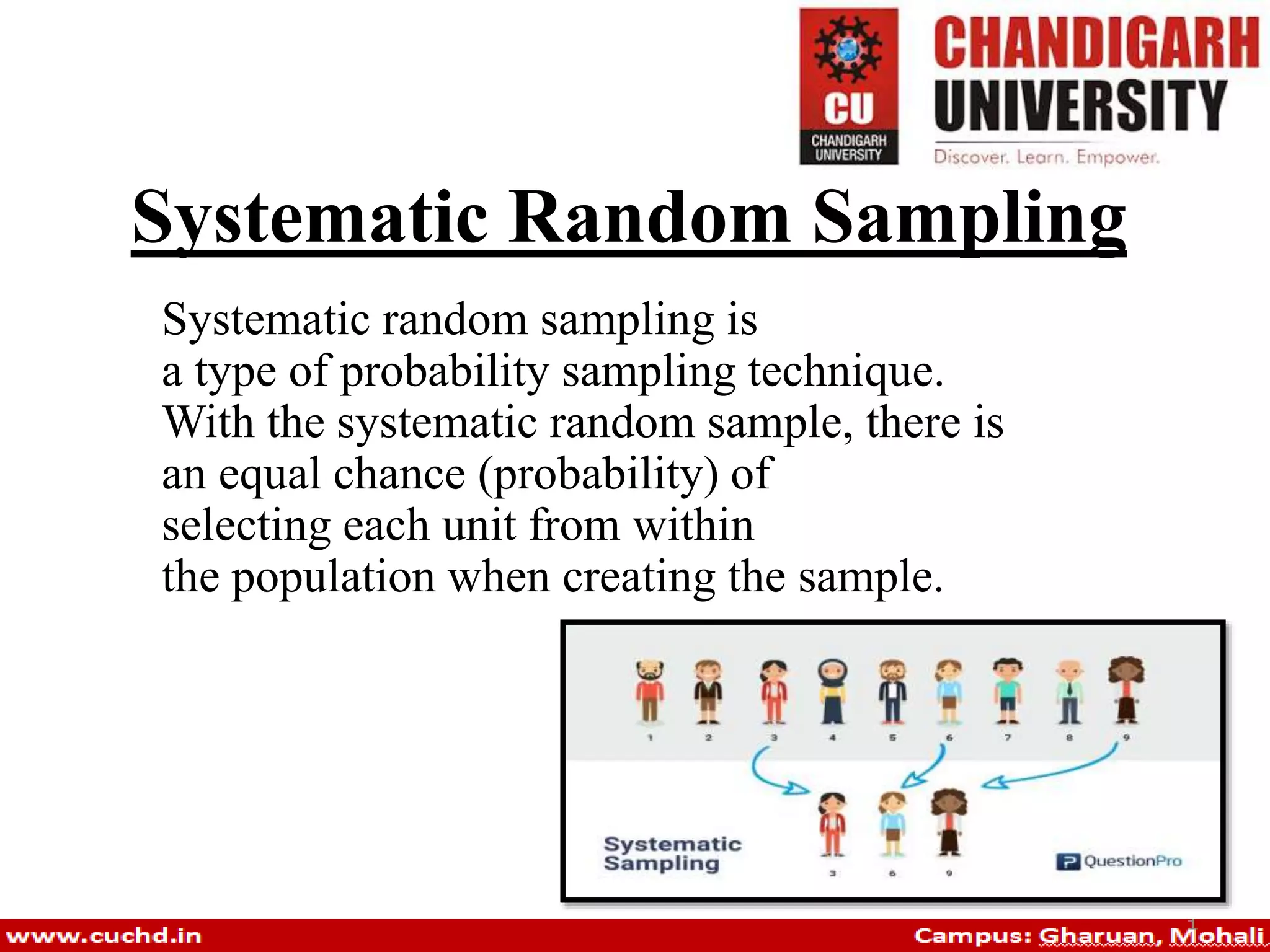
Probability sampling is a technique that ensures all individuals in a population have equal chances of being selected. Various types include random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and multi-stage sampling, each with specific methods and examples for implementation. These techniques are essential for accurately representing populations in surveys and studies.