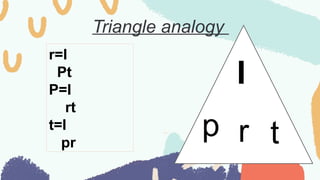
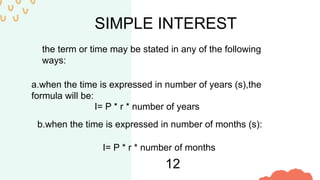
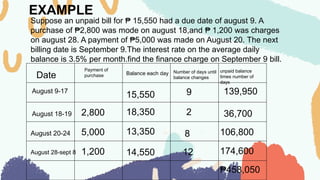
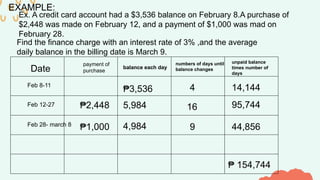
The document explains the concepts of simple and compound interest, including their definitions, calculations, and formulas. It covers credit cards, consumer loans, types of loans, and investments in stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. Key examples illustrate how these financial concepts apply in real-life scenarios.