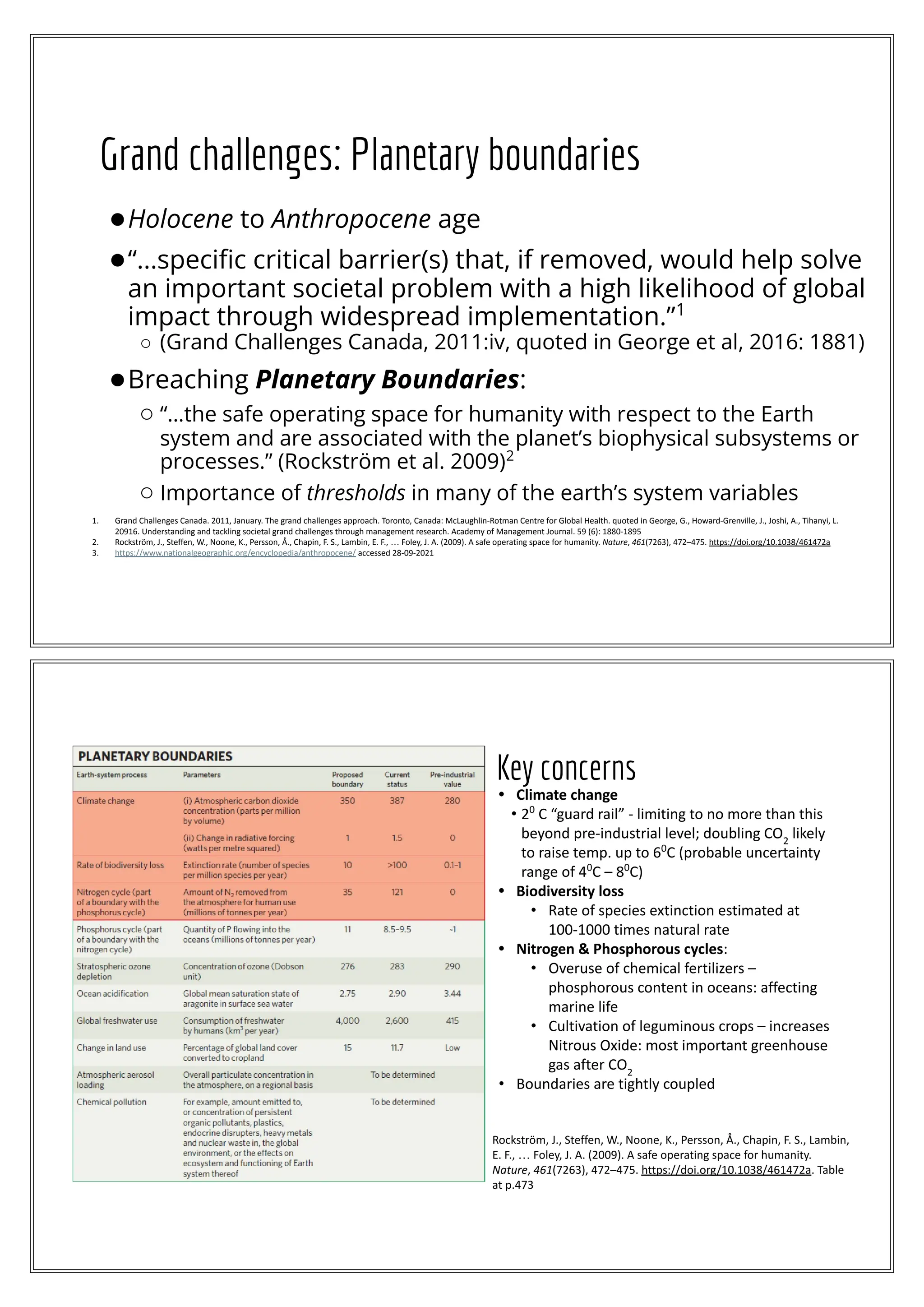
The document discusses the concept of 'grand challenges,' which are critical societal issues that, if addressed, could lead to significant global benefits. It highlights various environmental and social challenges, including climate change and resource management, and emphasizes the importance of sustainability in development efforts. Additionally, it outlines international policy initiatives and the role of the UN's Sustainable Development Goals in addressing these challenges.