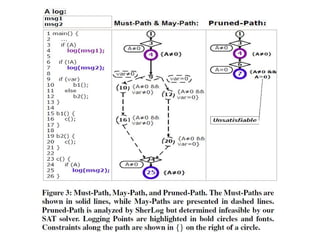
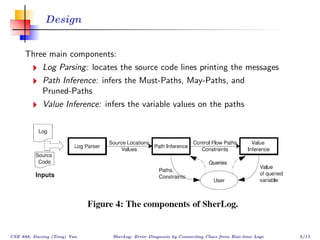
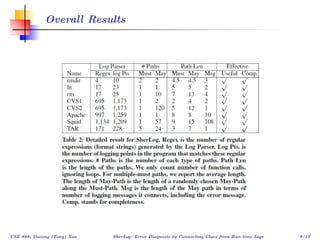
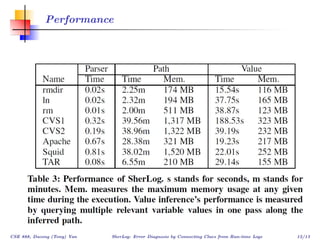
The document describes SherLog, a tool for error diagnosis in software by analyzing runtime logs. It infers possible execution paths, variables, and their values to identify root causes of failures without reproducing the exact failure environment. The tool works by parsing logs, inferring paths and variable values, and was evaluated on several cases where it successfully identified useful information for debugging. The discussion considers how results from the tool could be used to automate further debugging steps.