This presentation summarizes key concepts about sets, including:
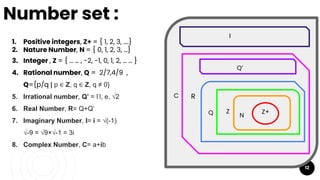
- Definitions of sets, order n-tuples, and the differences between them
- The four types of set elements and how to represent sets
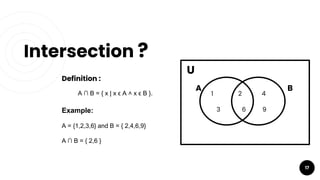
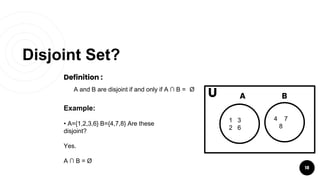
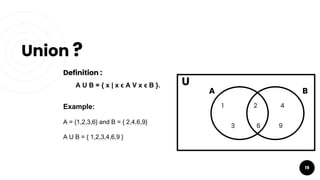
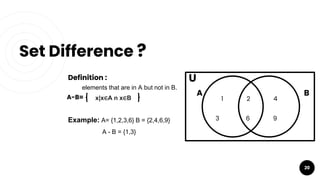
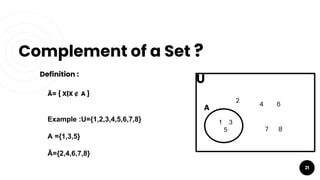
- Operations on sets such as union, intersection, difference, and complement
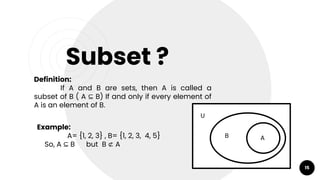
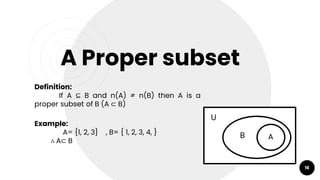
- Concepts like subsets, cardinality, and Venn diagrams
- Advanced topics like power sets and Cartesian products
It concludes with an example problem applying set operations and complement.