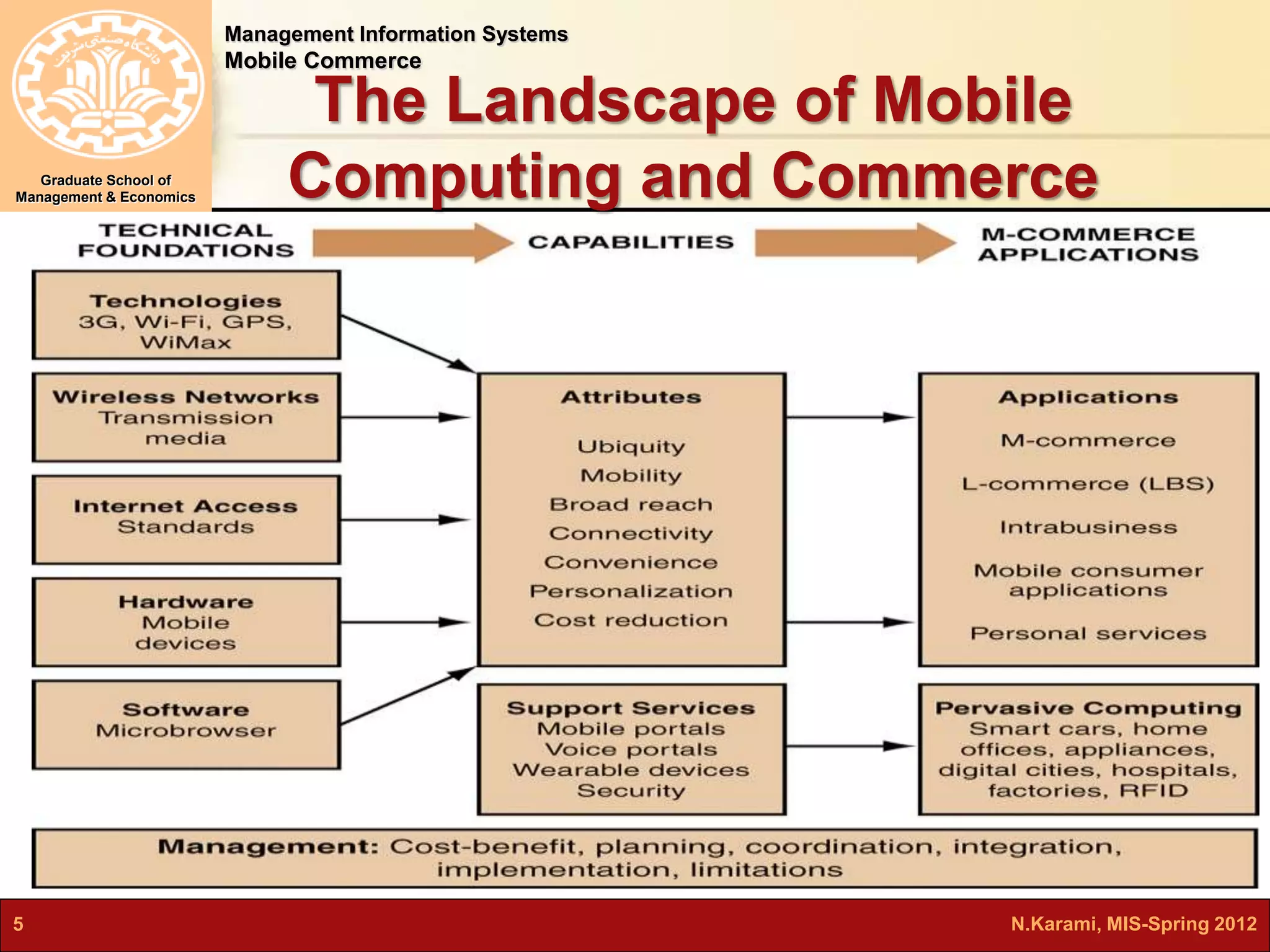
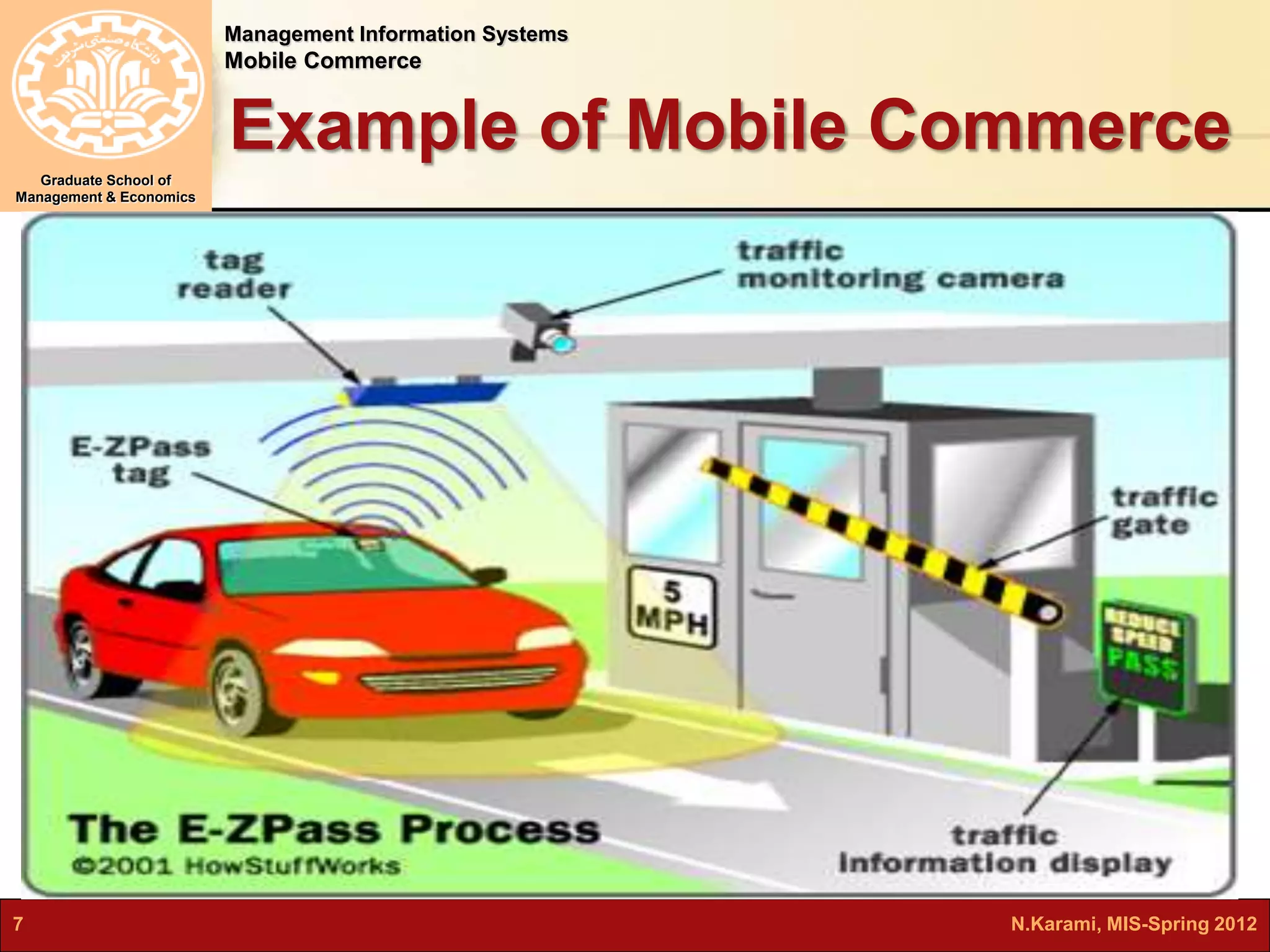
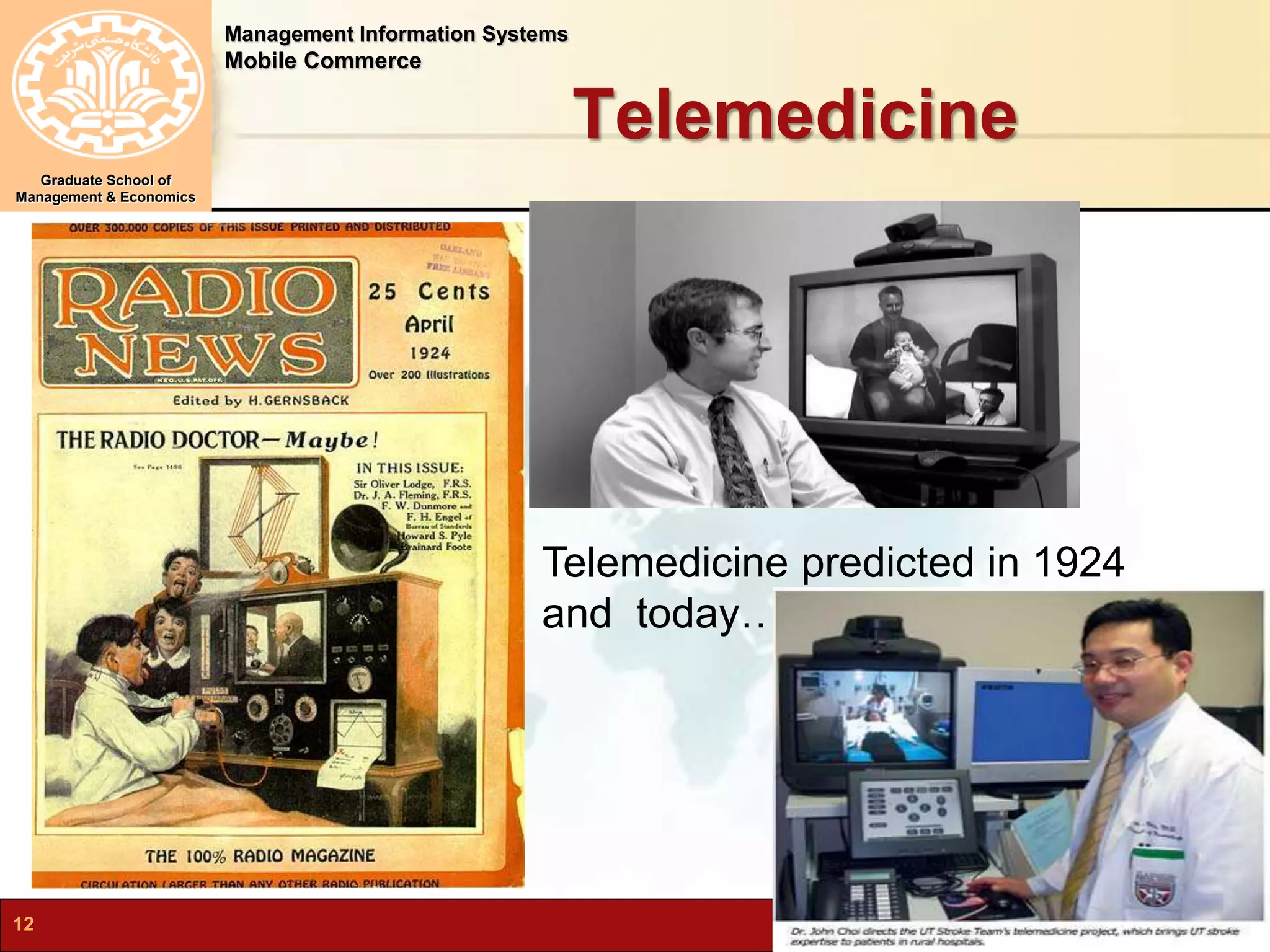
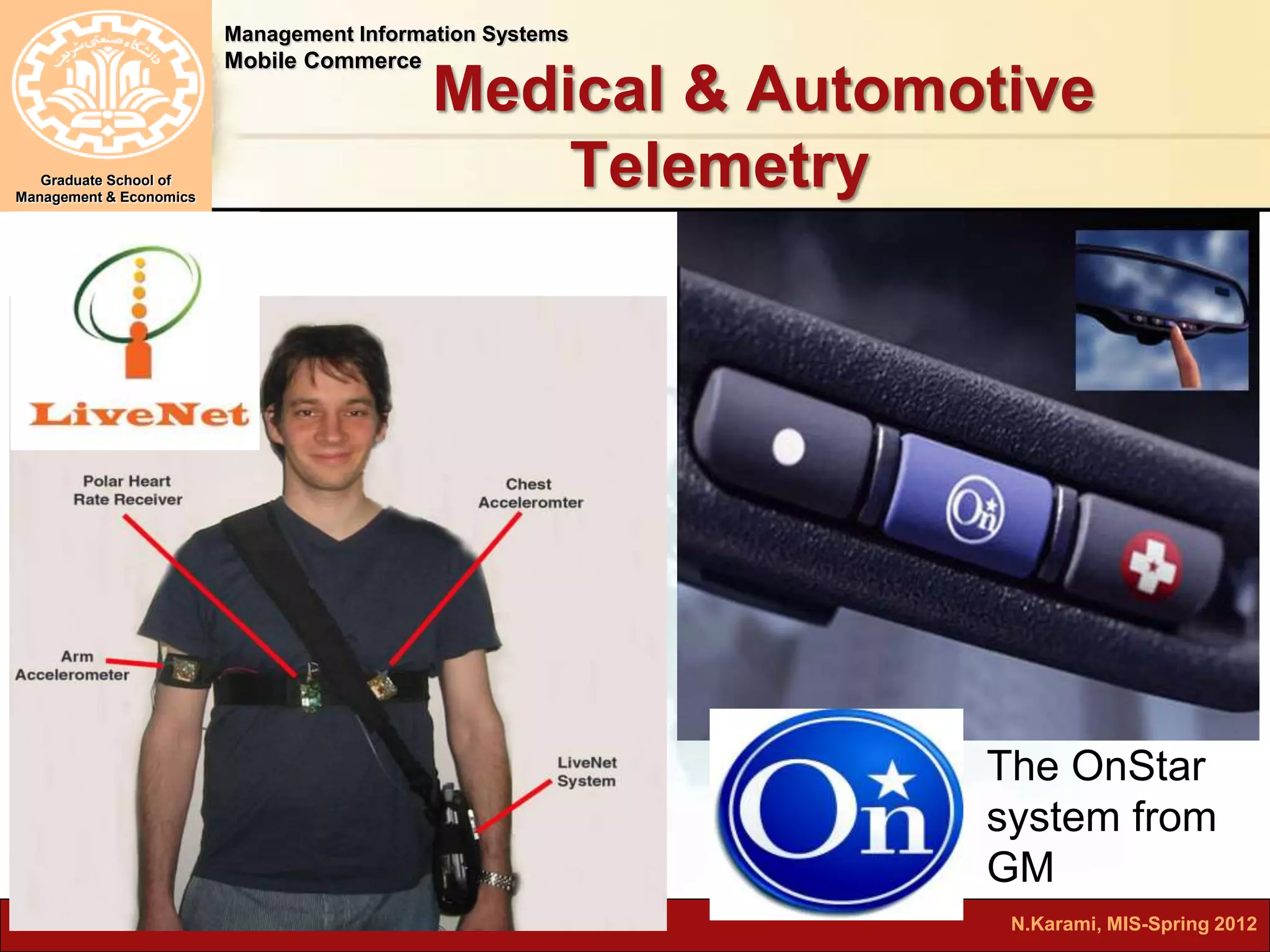
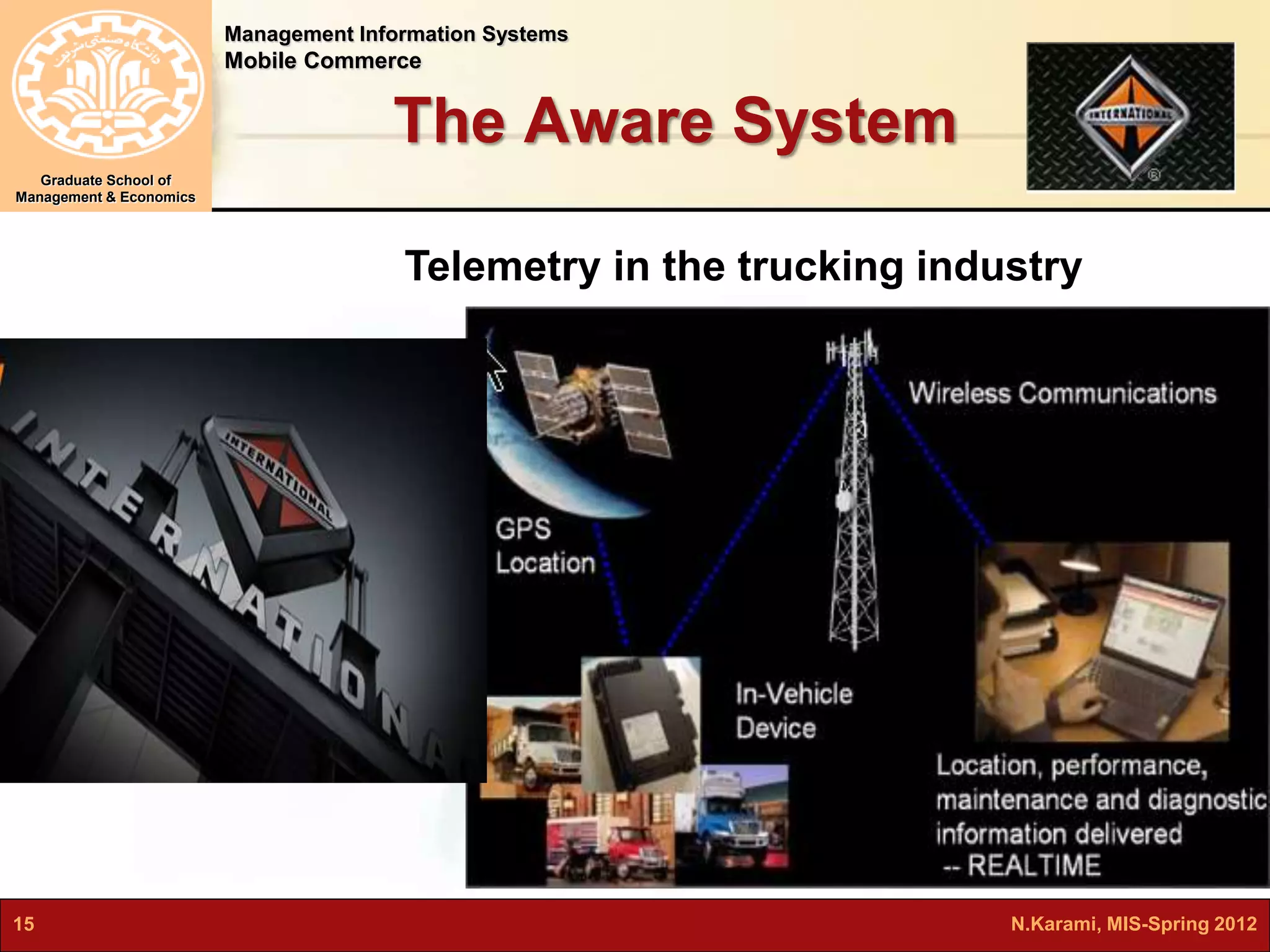
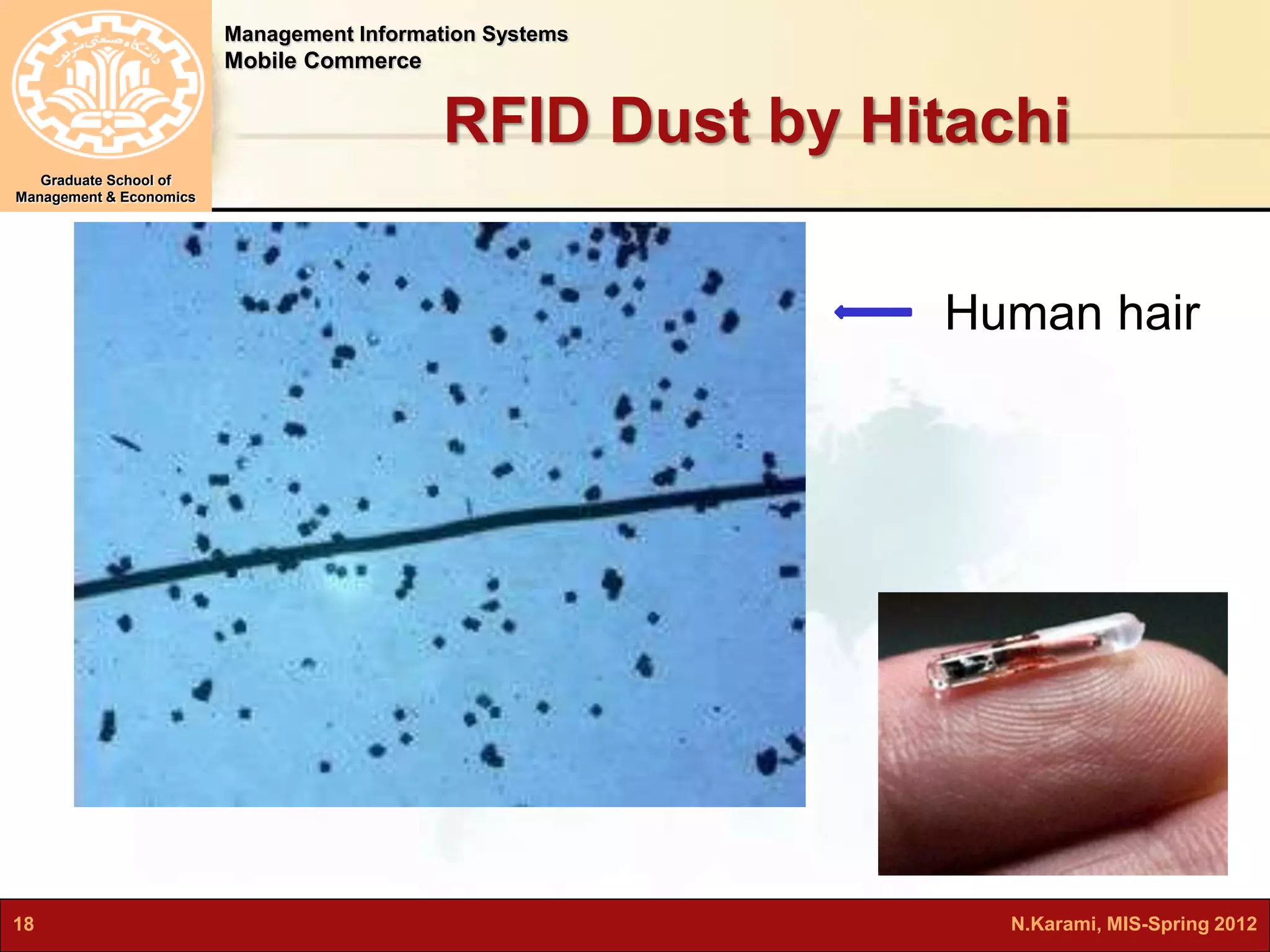
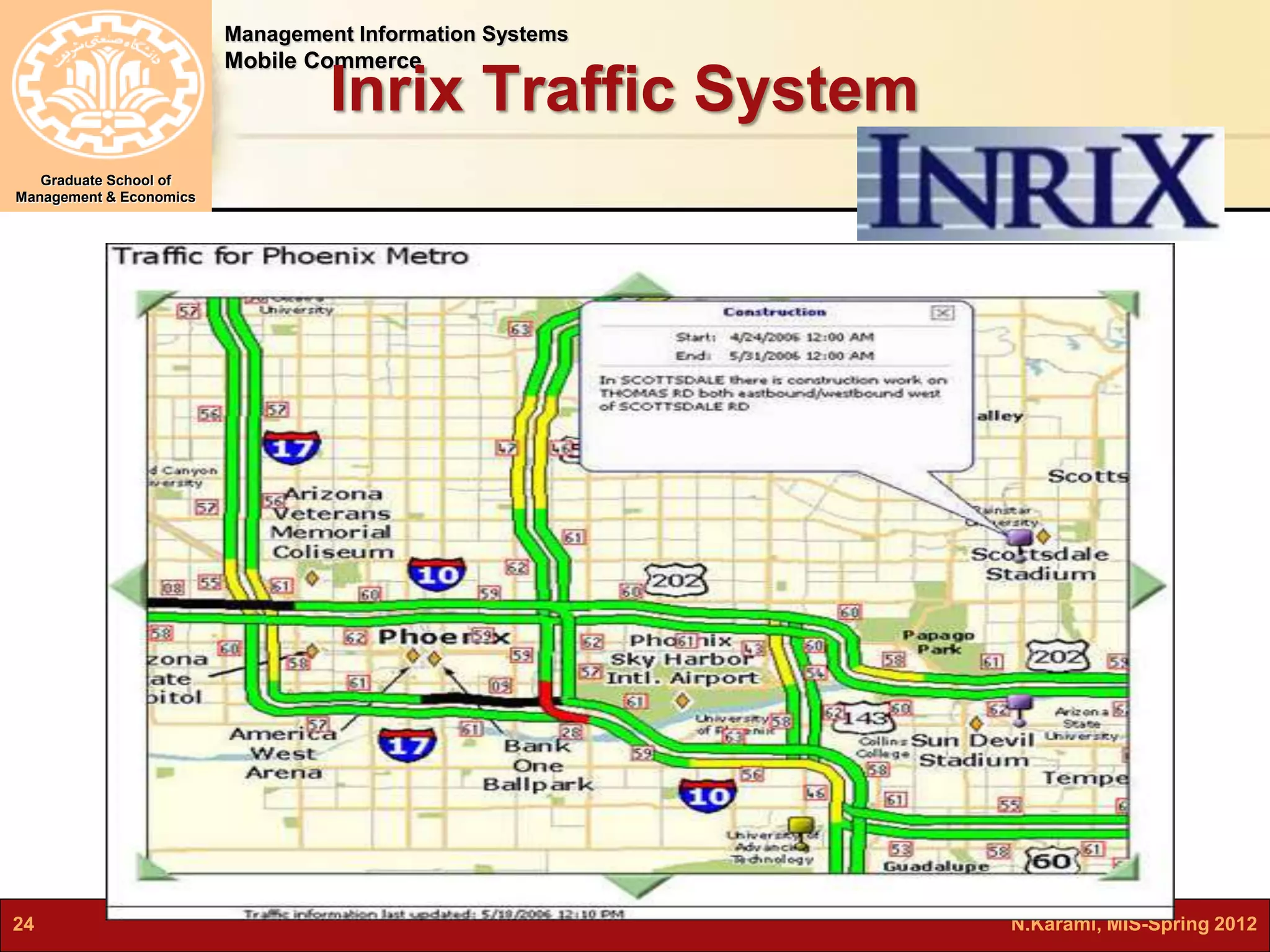
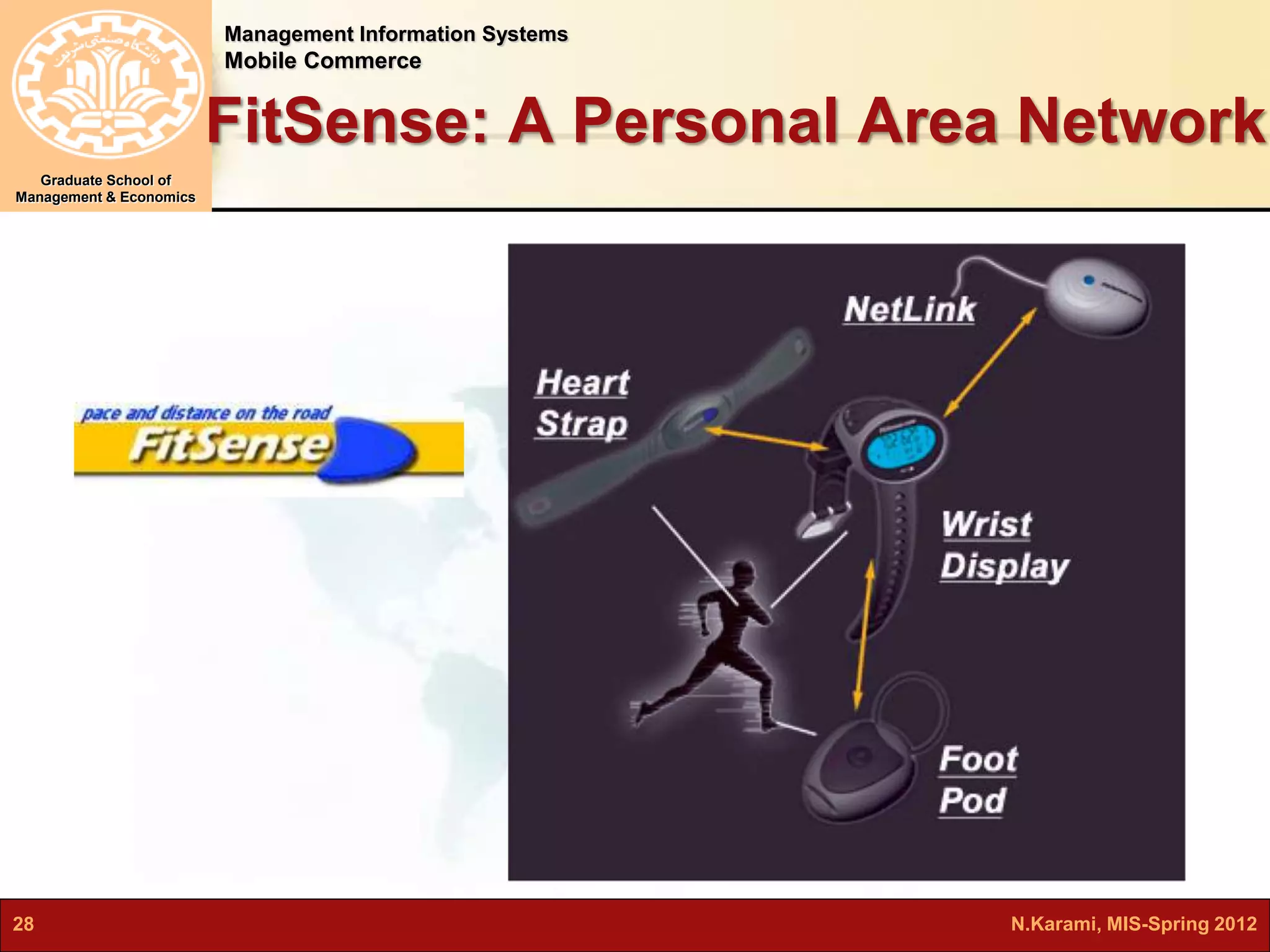
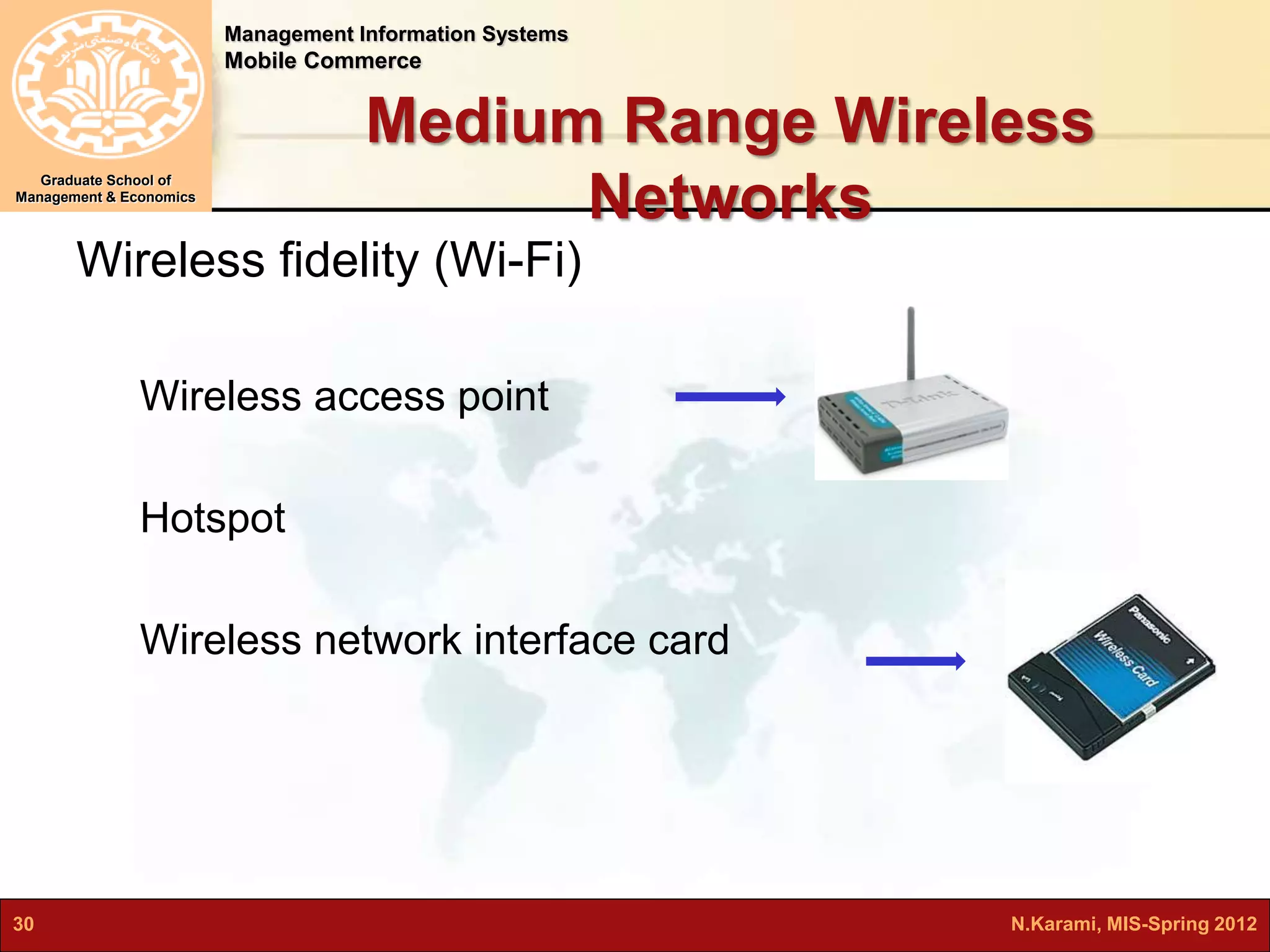
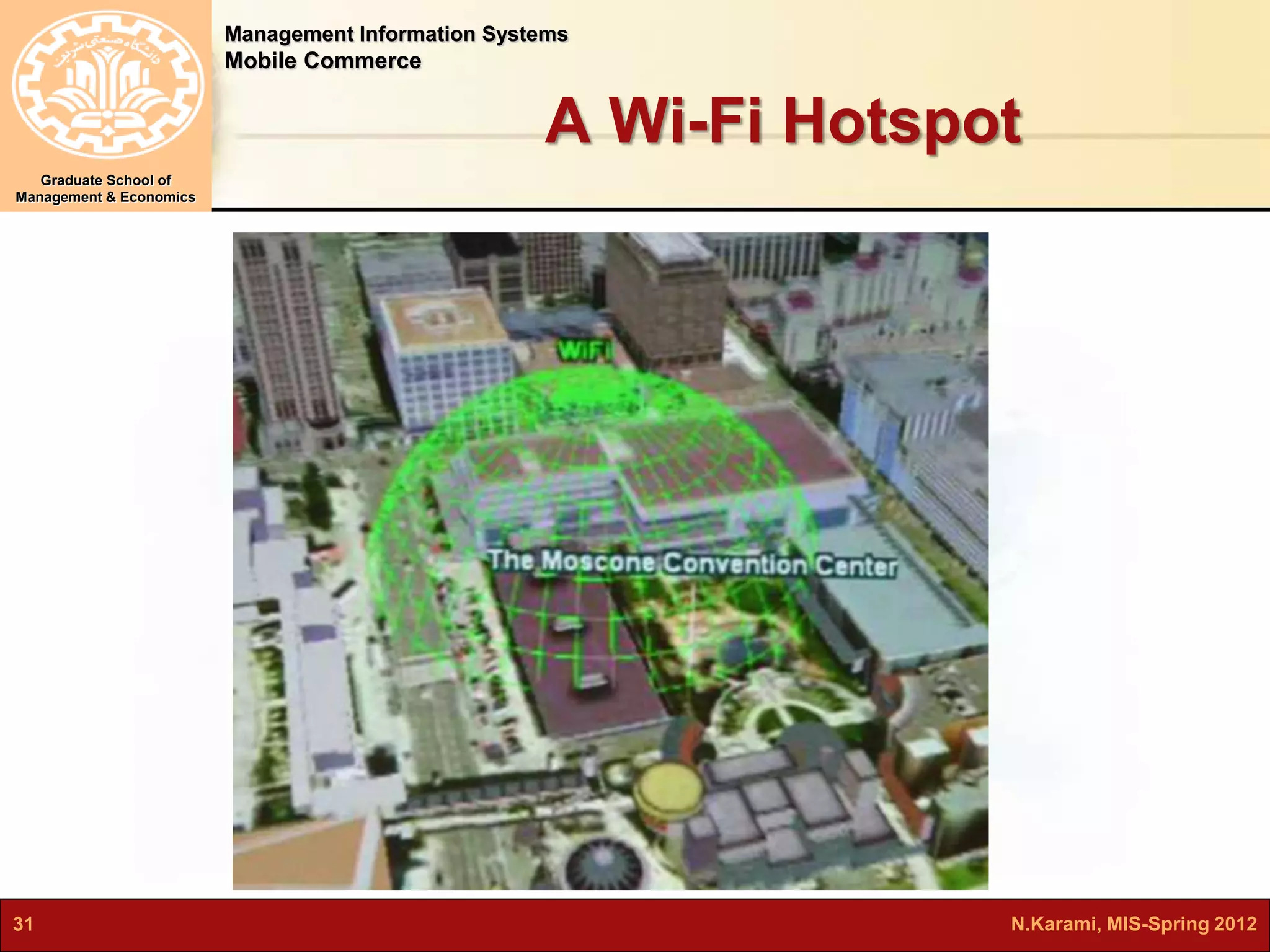
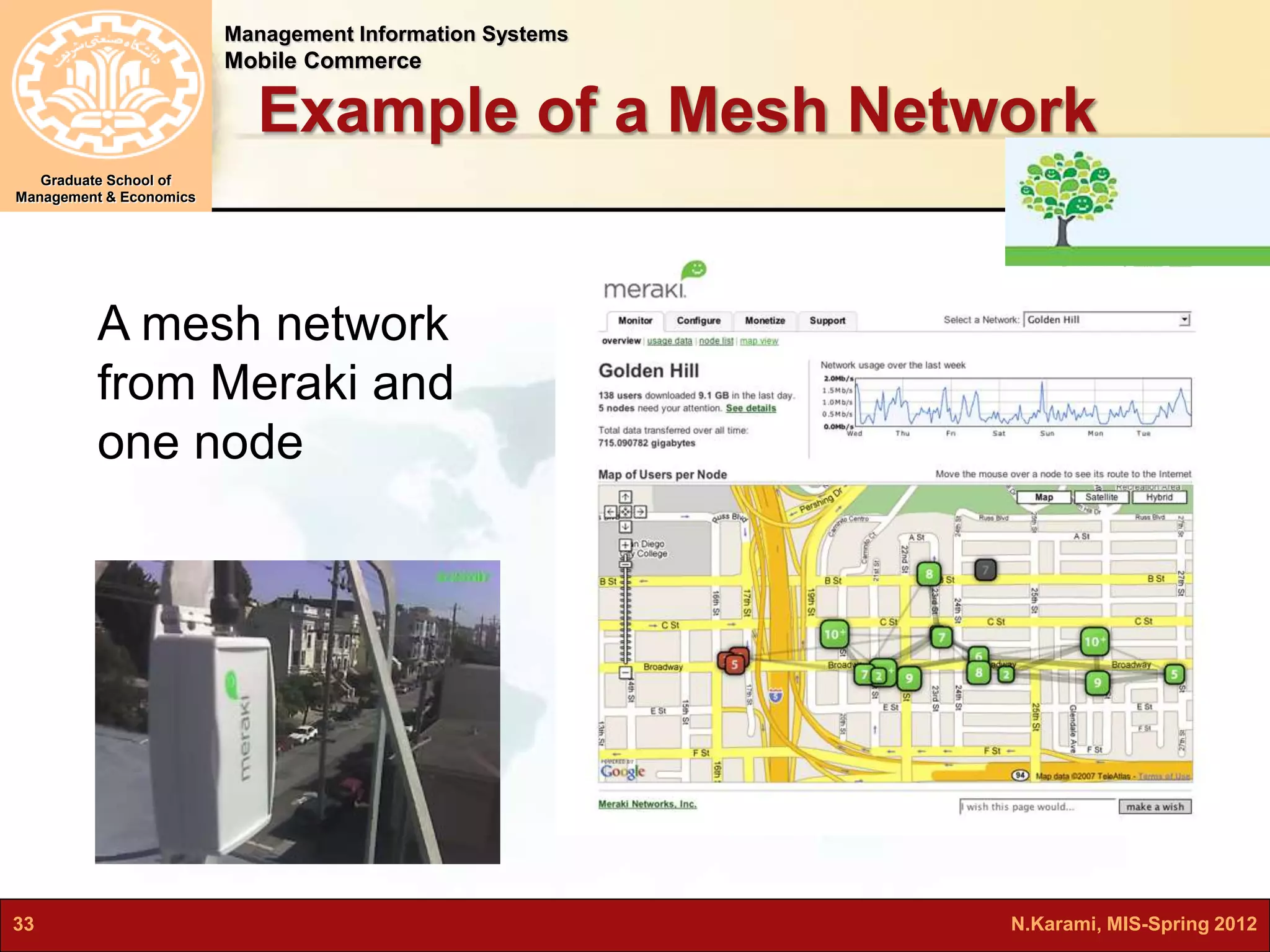
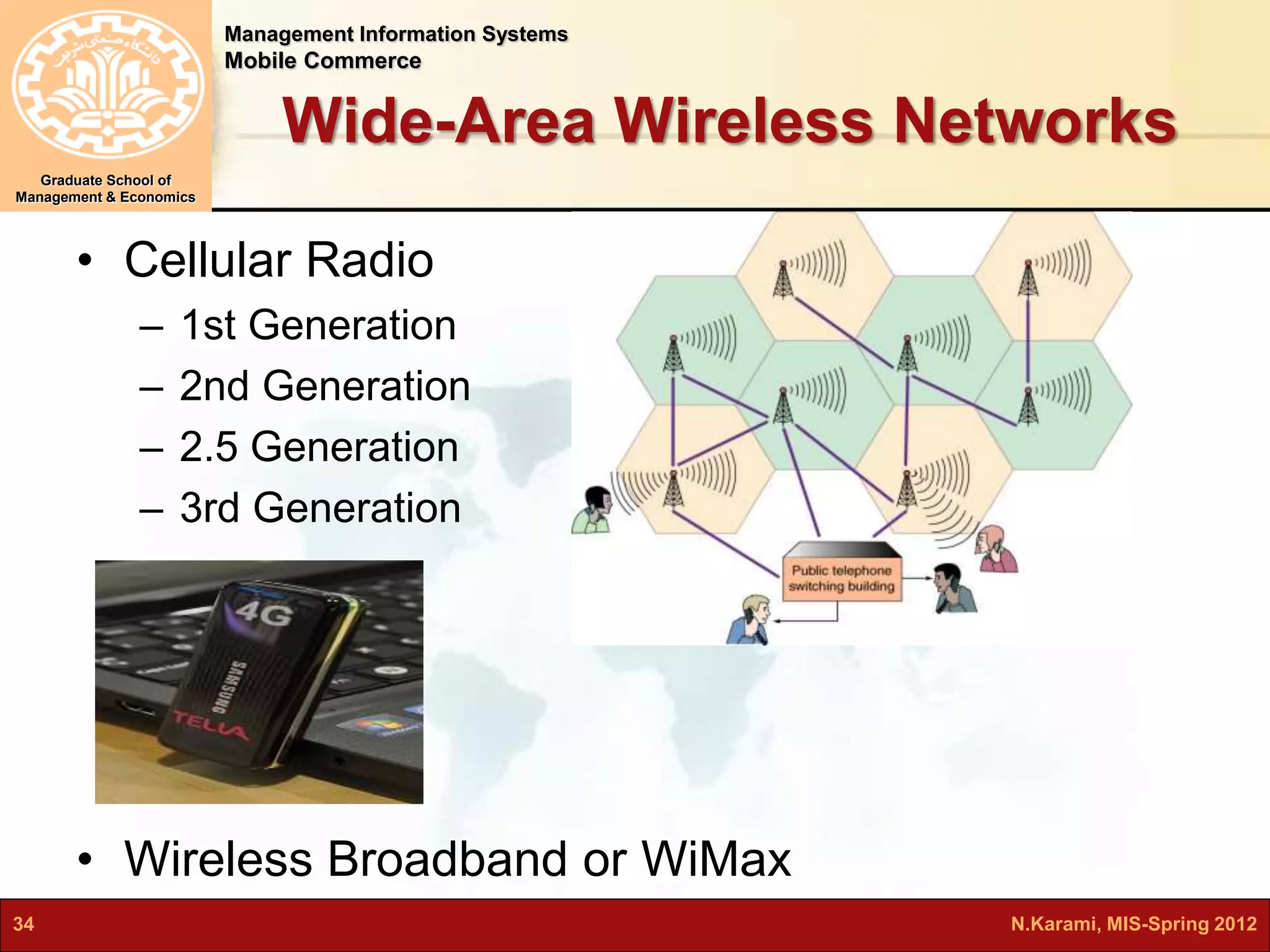
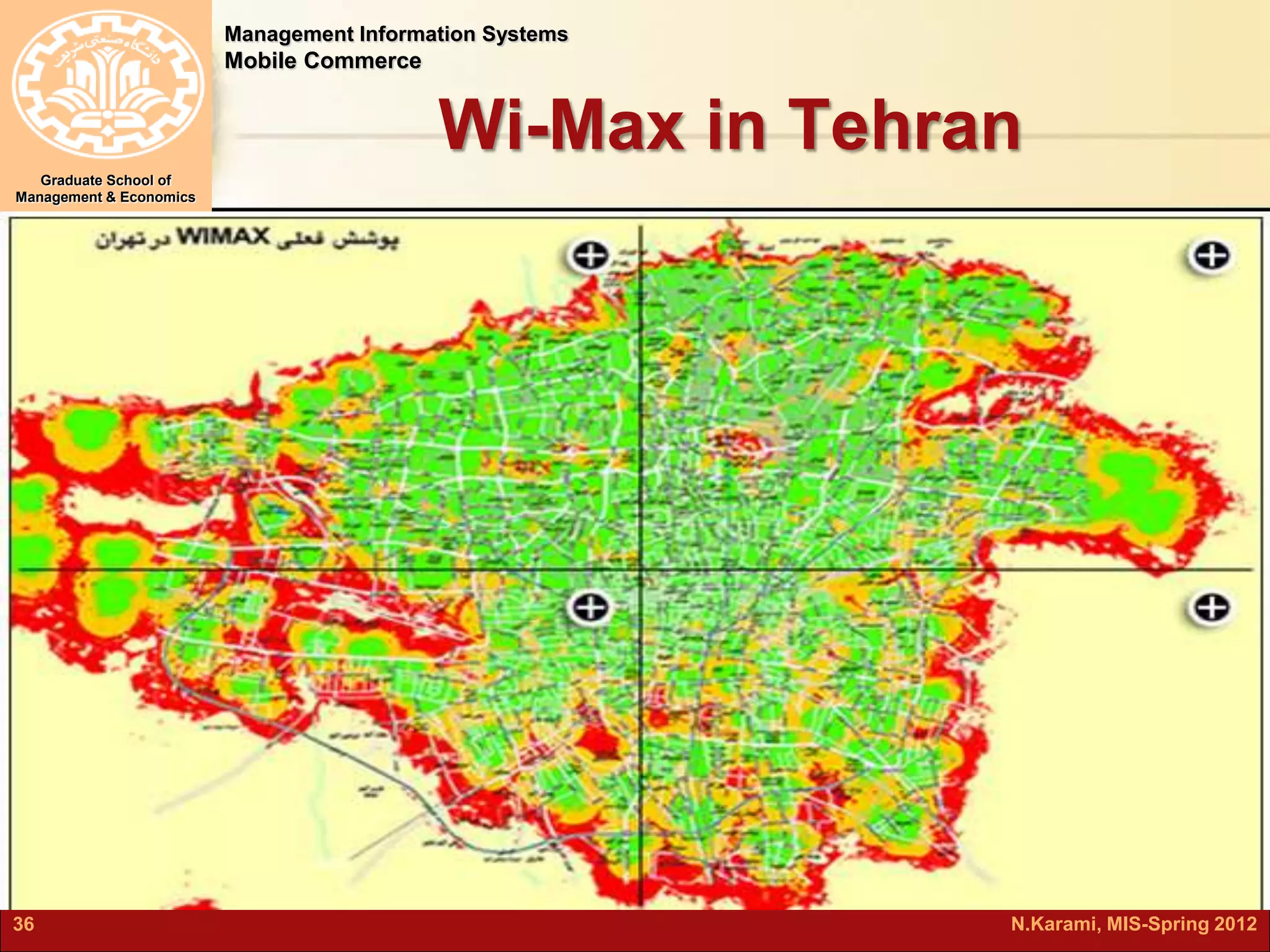
This document discusses mobile computing and commerce. It defines mobile computing and commerce, describes major applications of mobile commerce including financial services and location-based services. It also discusses technologies underlying pervasive/ubiquitous computing such as RFID and wireless sensor networks. The document outlines different types of wireless networks from short to long range and highlights security threats to wireless networks.