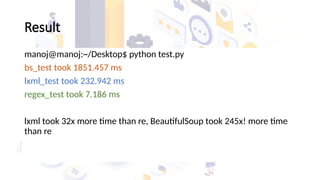
The document discusses web scraping, a technique for automatically extracting data from websites, detailing its workflow and the useful libraries available such as BeautifulSoup, lxml, and Selenium. It highlights the legal considerations surrounding web scraping, emphasizing that while the action itself isn't illegal, extracting non-public data is against the law. Additionally, it explores the pros and cons of different parsing libraries, providing benchmarks on their performance.













![Comparison
import re
import time
import urllib2
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from lxml import html as lxmlhtml
def timeit(fn, *args):
t1 = time.time()
for i in range(100):
fn(*args)
t2 = time.time()
print '%s took %0.3f ms' % (fn.func_name, (t2-t1)*1000.0)
def bs_test(html):
soup = BeautifulSoup(html)
return soup.html.head.title
def lxml_test(html):
tree = lxmlhtml.fromstring(html)
return tree.xpath('//title')[0].text_content()
def regex_test(html):
return re.findall('', html)[0]
if __name__ == '__main__':
url = 'http://pydelhi.org'
html = urllib2.urlopen(url).read()
for fn in (bs_test, lxml_test, regex_test):
timeit(fn, html)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesi8scrapingapi-241224002547-327abe6a/85/Sesi-8_Scraping-API-for-really-bnegineer-pptx-14-320.jpg)