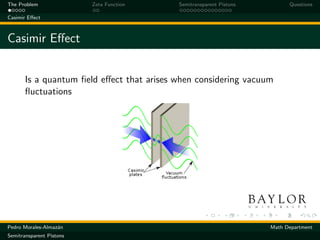
The document discusses the Casimir effect, a quantum field phenomenon arising from vacuum fluctuations, and introduces a mathematical model for calculating Casimir energy using a Riemannian manifold. It explains the definitions of the zeta function, the determination of eigenvalues, and various mathematical techniques used to analyze the Casimir force and its implications. Finally, it explores the behavior of semitransparent pistons in relation to the Casimir effect and provides insights into the stability of electrons and the significance of geometry in quantum contexts.

















![The Problem Zeta Function Semitransparent Pistons Questions
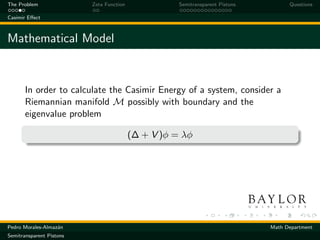
Eigenvalue Problem
Eigenvalue Problem
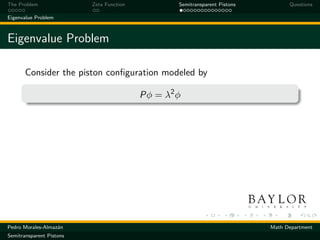
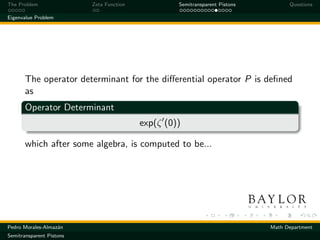
Consider the piston configuration modeled by
Pφ = λ2 φ
where P is the Laplace-type differential operator defined on
[0, L] × N
∂2
P=− − ∆N + σδ(x − a)
∂x 2
Pedro Morales-Almaz´n
a Math Department
Semitransparent Pistons](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation001-110413150356-phpapp01/85/Semitransparent-Pistons-24-320.jpg)
![The Problem Zeta Function Semitransparent Pistons Questions
Eigenvalue Problem
Eigenvalue Problem
Consider the piston configuration modeled by
Pφ = λ2 φ
where P is the Laplace-type differential operator defined on
[0, L] × N
∂2
P=− − ∆N + σδ(x − a)
∂x 2
N is a compact Riemannian manifold and we have Dirichlet
boundary conditions φ(0) = φ(L) = 0.
Pedro Morales-Almaz´n
a Math Department
Semitransparent Pistons](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation001-110413150356-phpapp01/85/Semitransparent-Pistons-25-320.jpg)

![The Problem Zeta Function Semitransparent Pistons Questions
Eigenvalue Problem
Separation of variables
Using separation of variables
λ2 = νk + η 2
k
2
where νk and η 2 are the eigenvalues for the Laplacian on [0, L] and
2
N respectively
Pedro Morales-Almaz´n
a Math Department
Semitransparent Pistons](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation001-110413150356-phpapp01/85/Semitransparent-Pistons-27-320.jpg)







![The Problem Zeta Function Semitransparent Pistons Questions
Eigenvalue Problem
Finite Part
Subtracting the asymptotic terms enlarges the convergence region
ζ(s) = ζ (f ) (s) + ζ (as) (s)
where
ζ (f ) (s) =
∞ ∞
sin(πs) d
dν (ν 2 − η 2 )−s [log F (ıν) − asymptotics]
π η dν
=1
Pedro Morales-Almaz´n
a Math Department
Semitransparent Pistons](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation001-110413150356-phpapp01/85/Semitransparent-Pistons-37-320.jpg)
![The Problem Zeta Function Semitransparent Pistons Questions
Eigenvalue Problem
Asymptotic Part
∞ ∞
sin(πs) d
ζ (as) (s) = dν (ν 2 − η 2 )−s [asymptotics]
π η dν
=1
Pedro Morales-Almaz´n
a Math Department
Semitransparent Pistons](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation001-110413150356-phpapp01/85/Semitransparent-Pistons-38-320.jpg)








![The Problem Zeta Function Semitransparent Pistons Questions
Eigenvalue Problem
Piston Behavior
Piston Behavior
Given the second order differential operator
∂2
P = − 2 − ∆N + σδ(x − a) defined on [0, L] × N with Dirichlet
∂x
boundary conditions, the piston is then attracted to the closest
wall.
Pedro Morales-Almaz´n
a Math Department
Semitransparent Pistons](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation001-110413150356-phpapp01/85/Semitransparent-Pistons-48-320.jpg)
