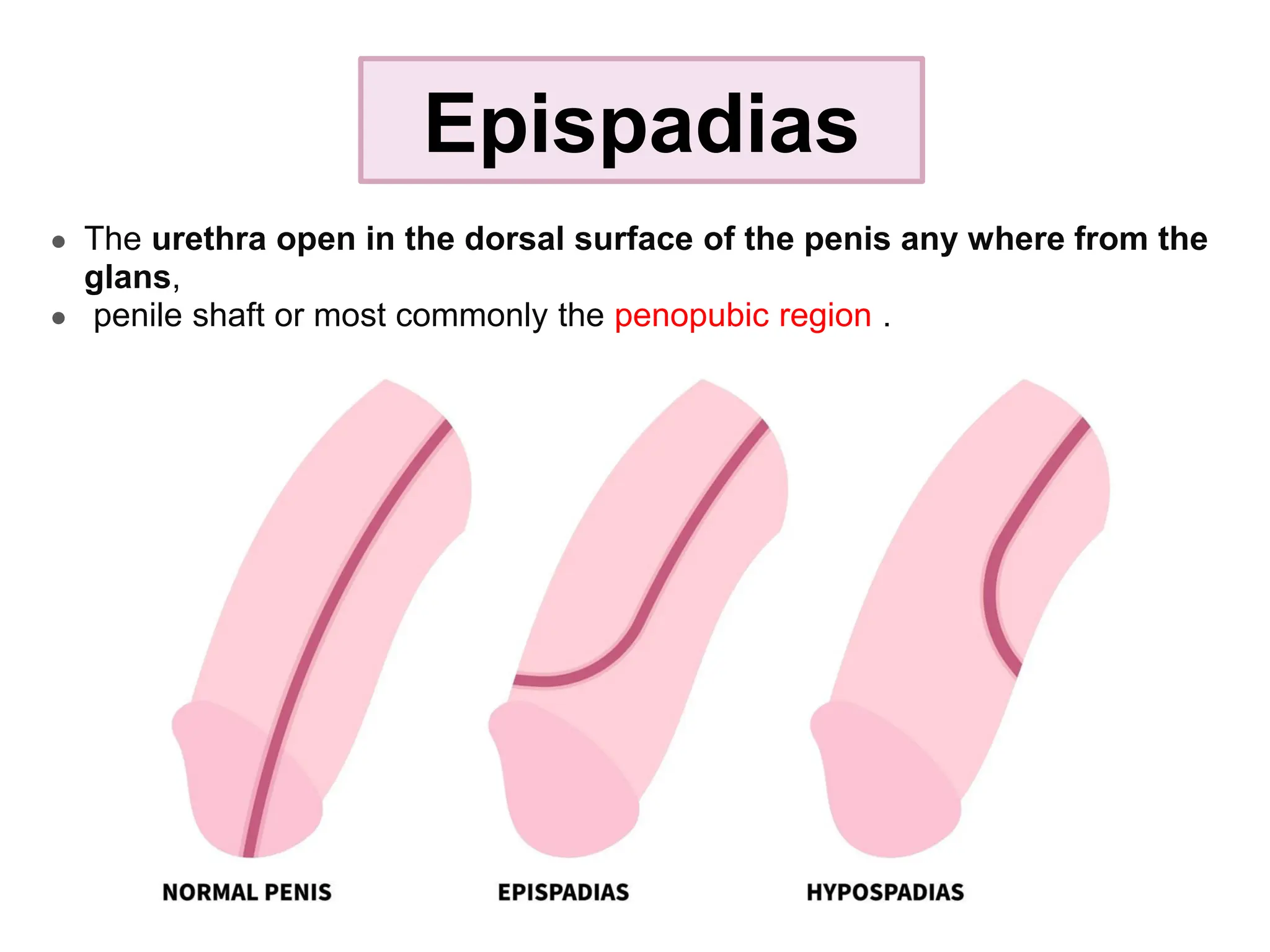
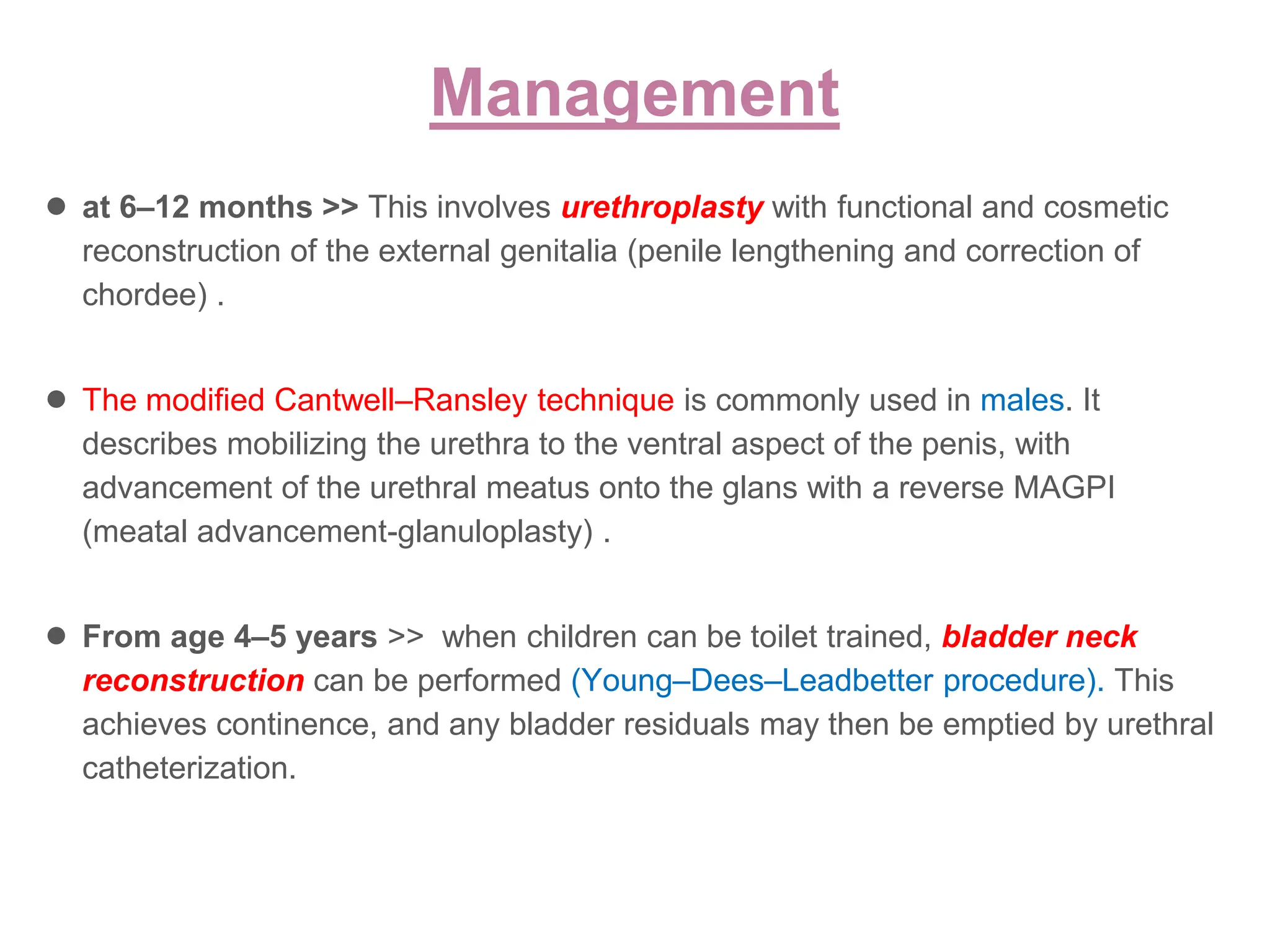
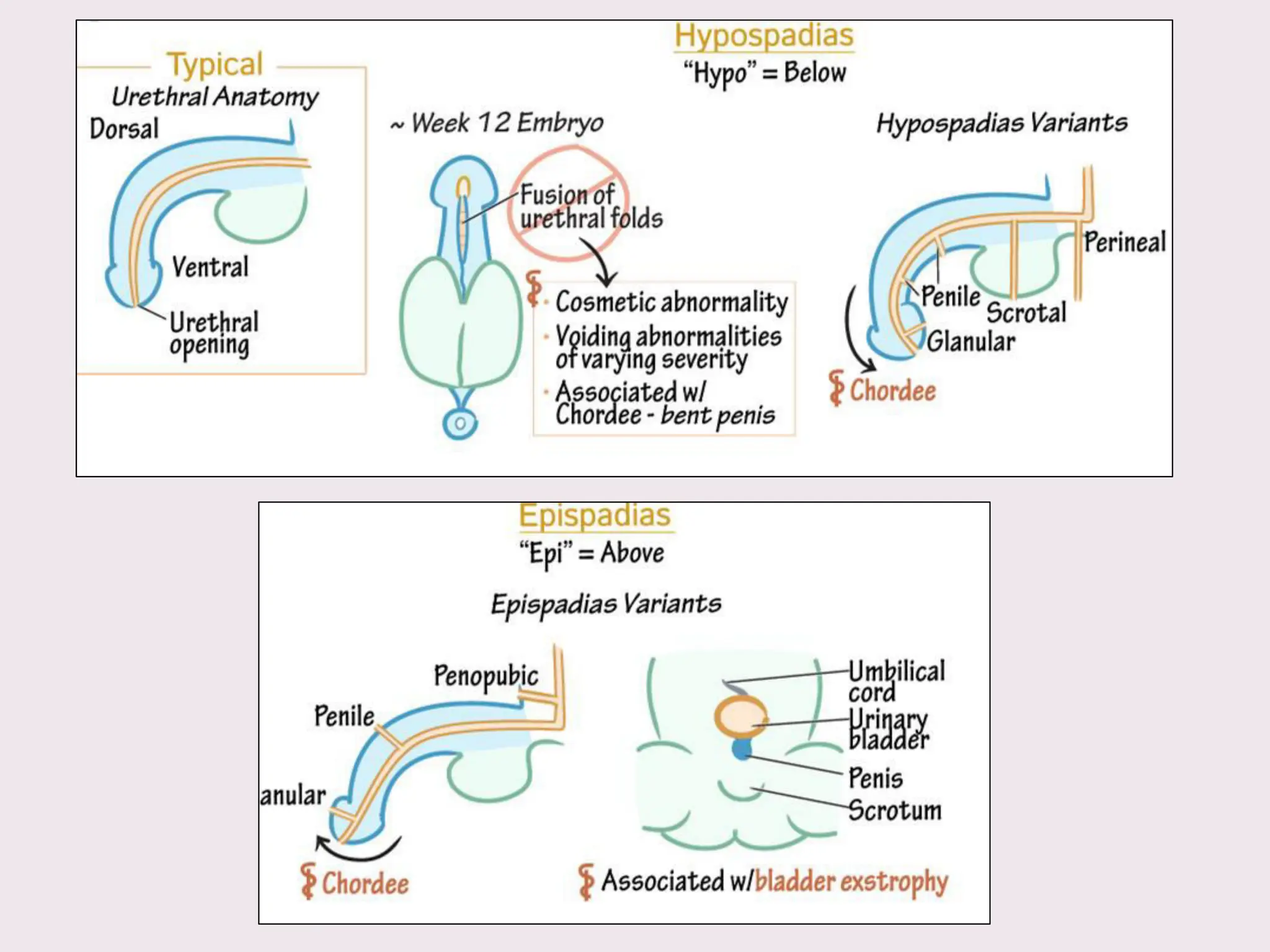
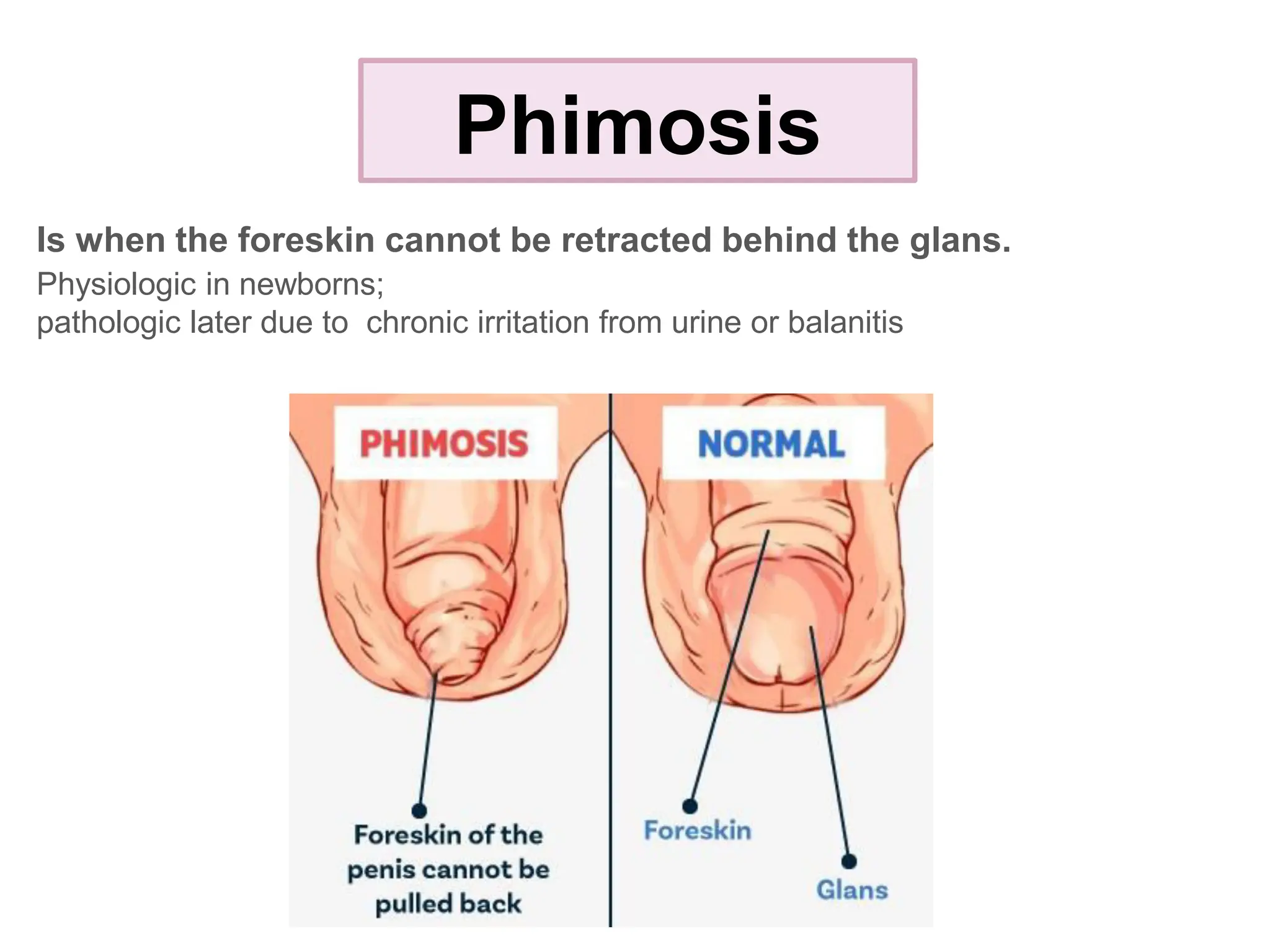
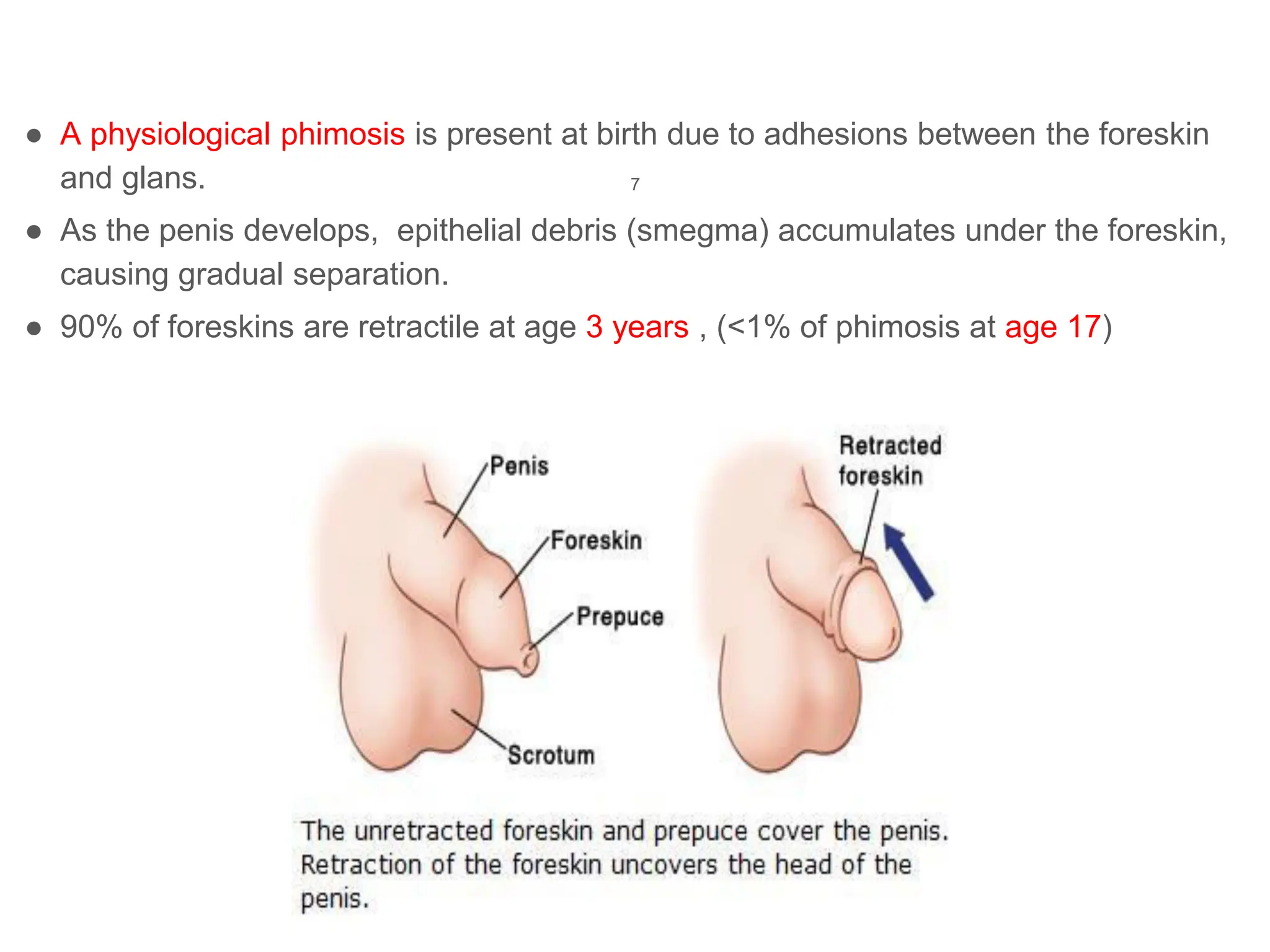
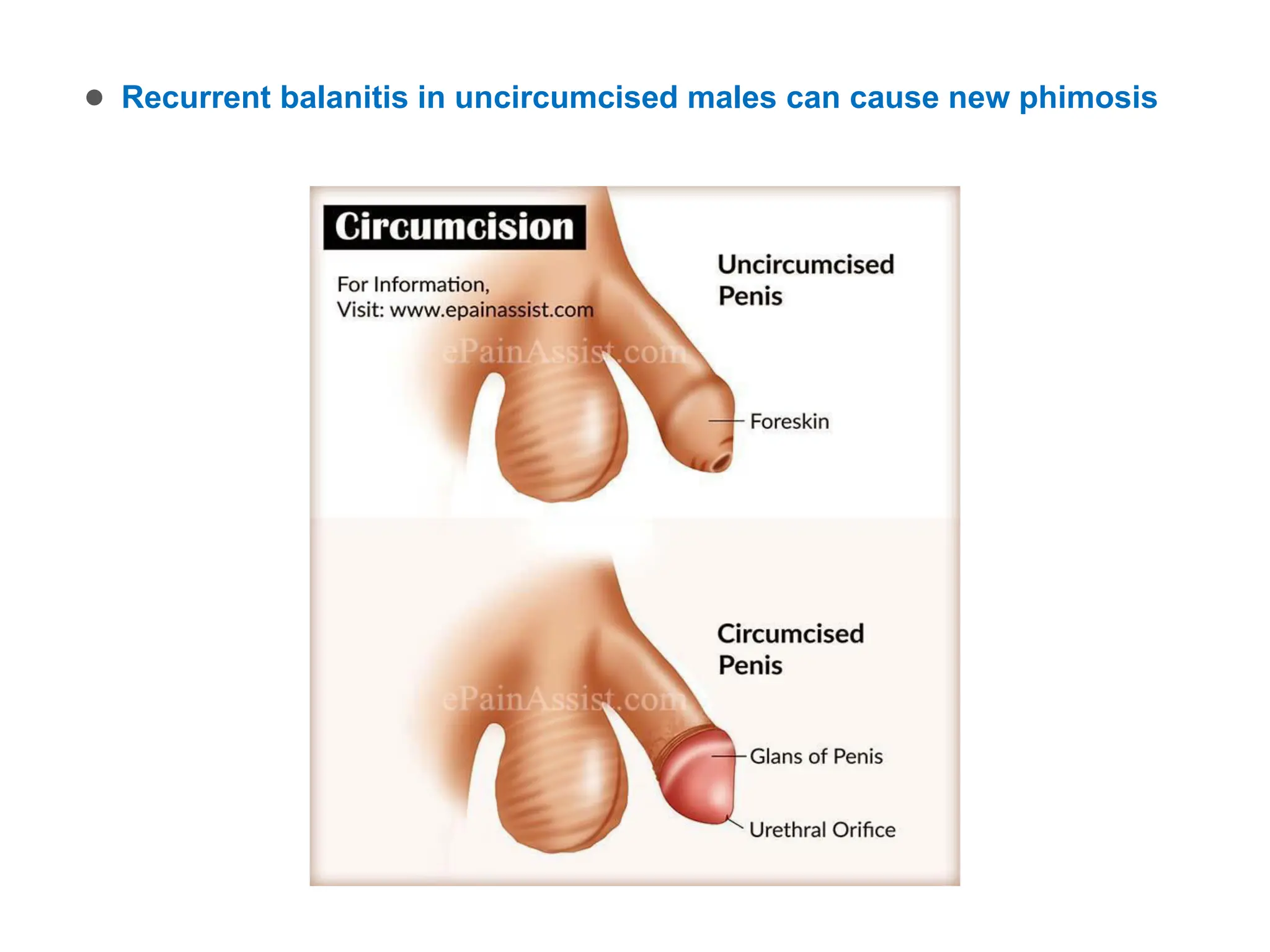
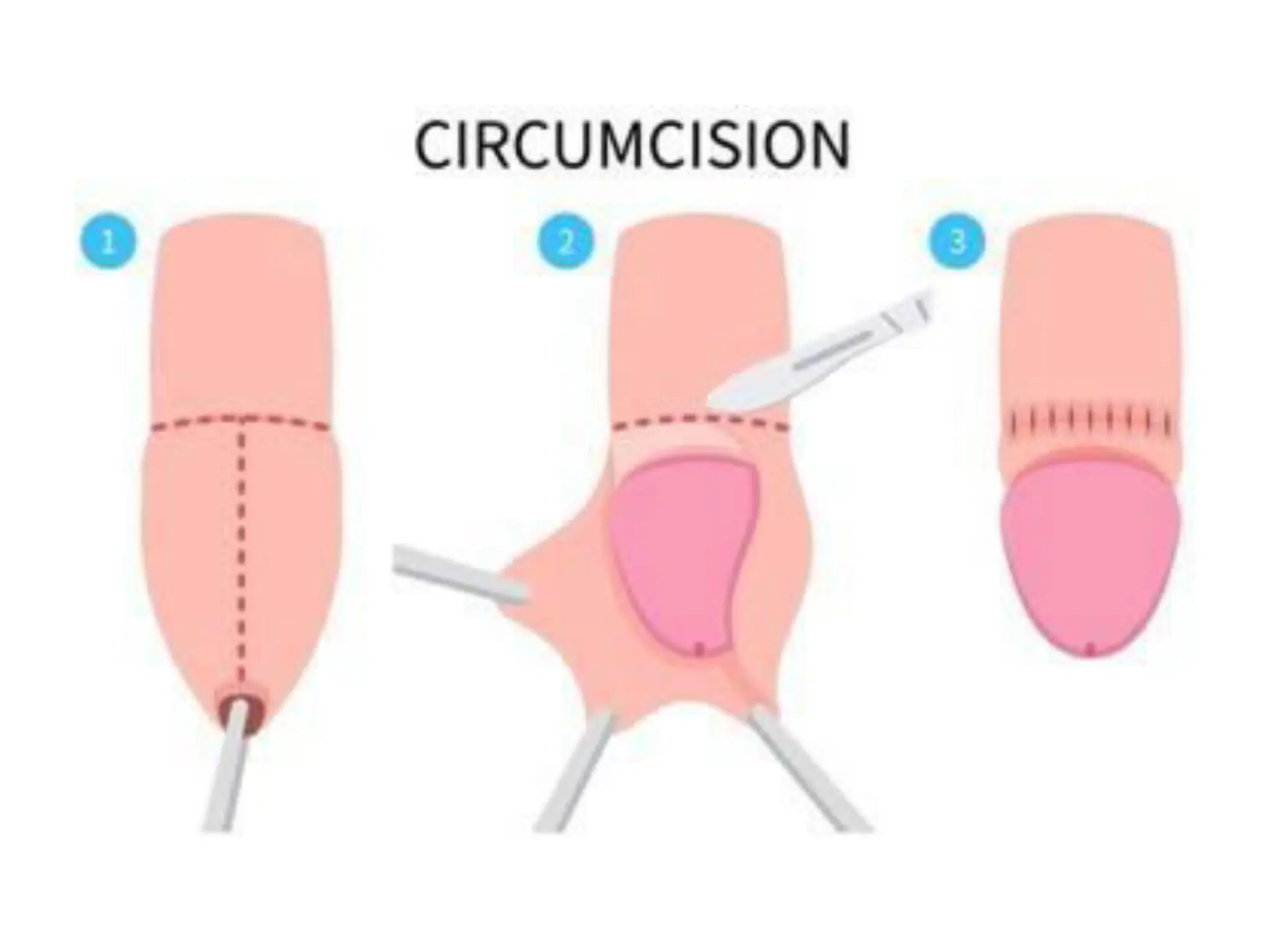
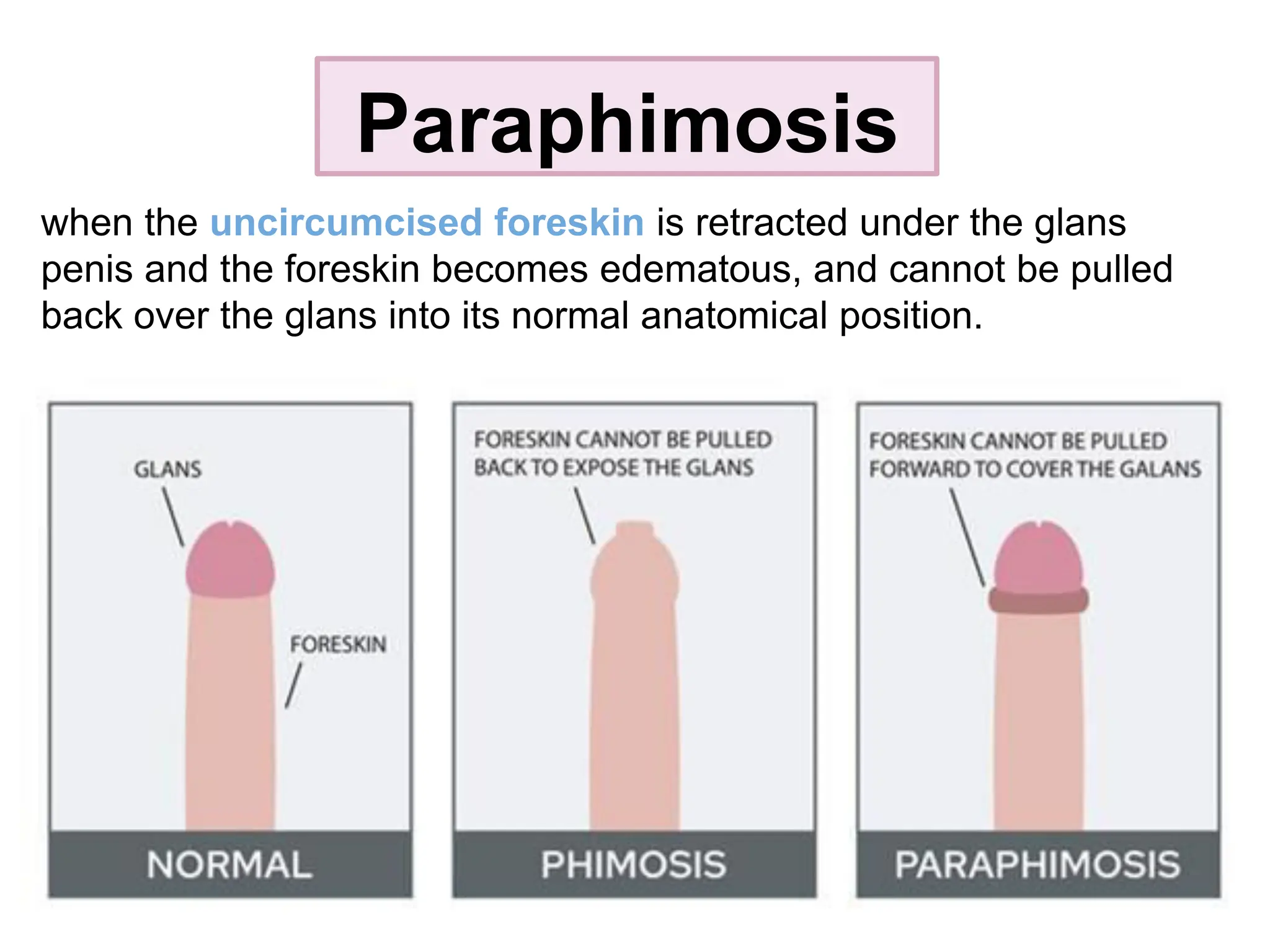
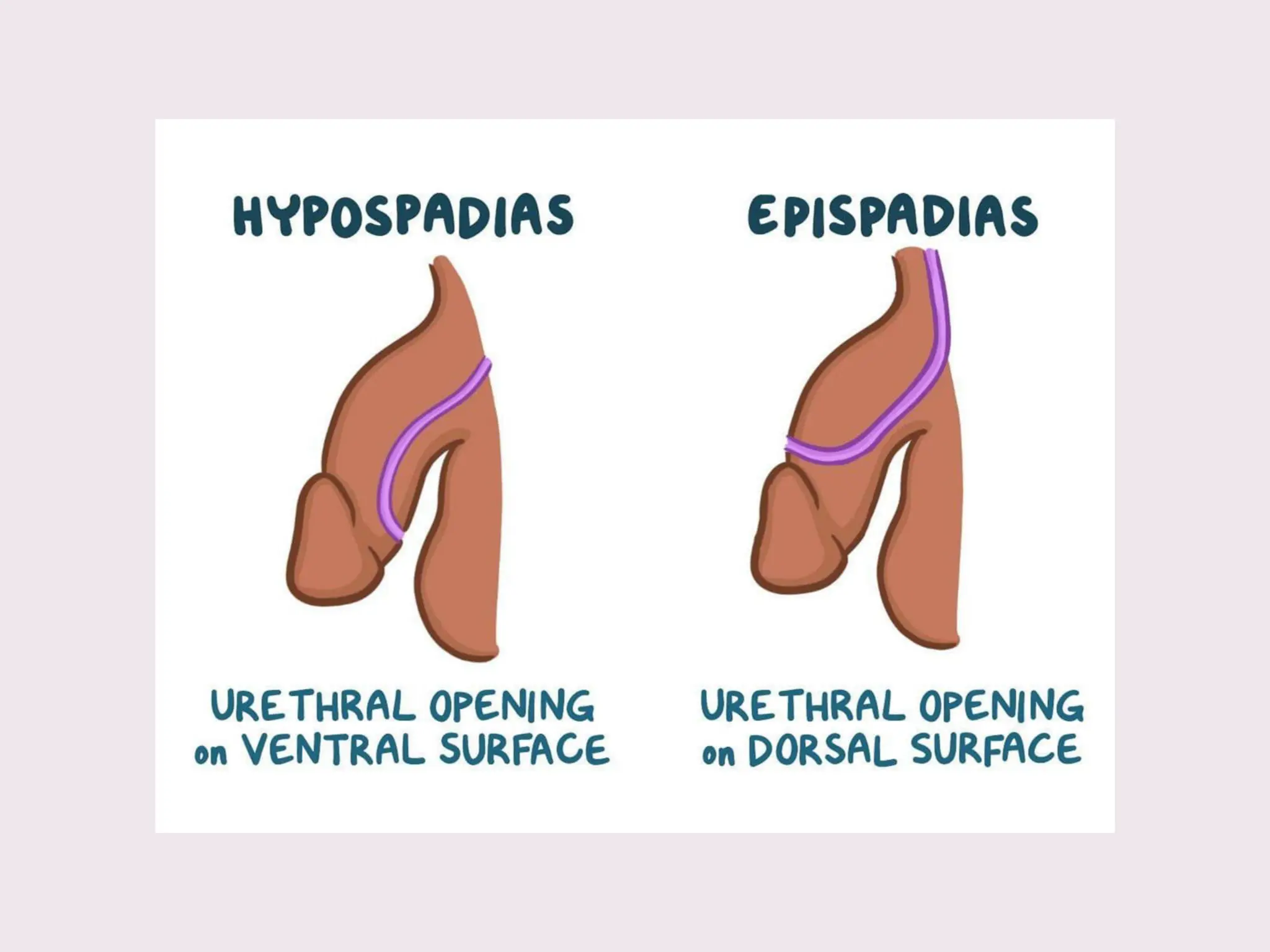
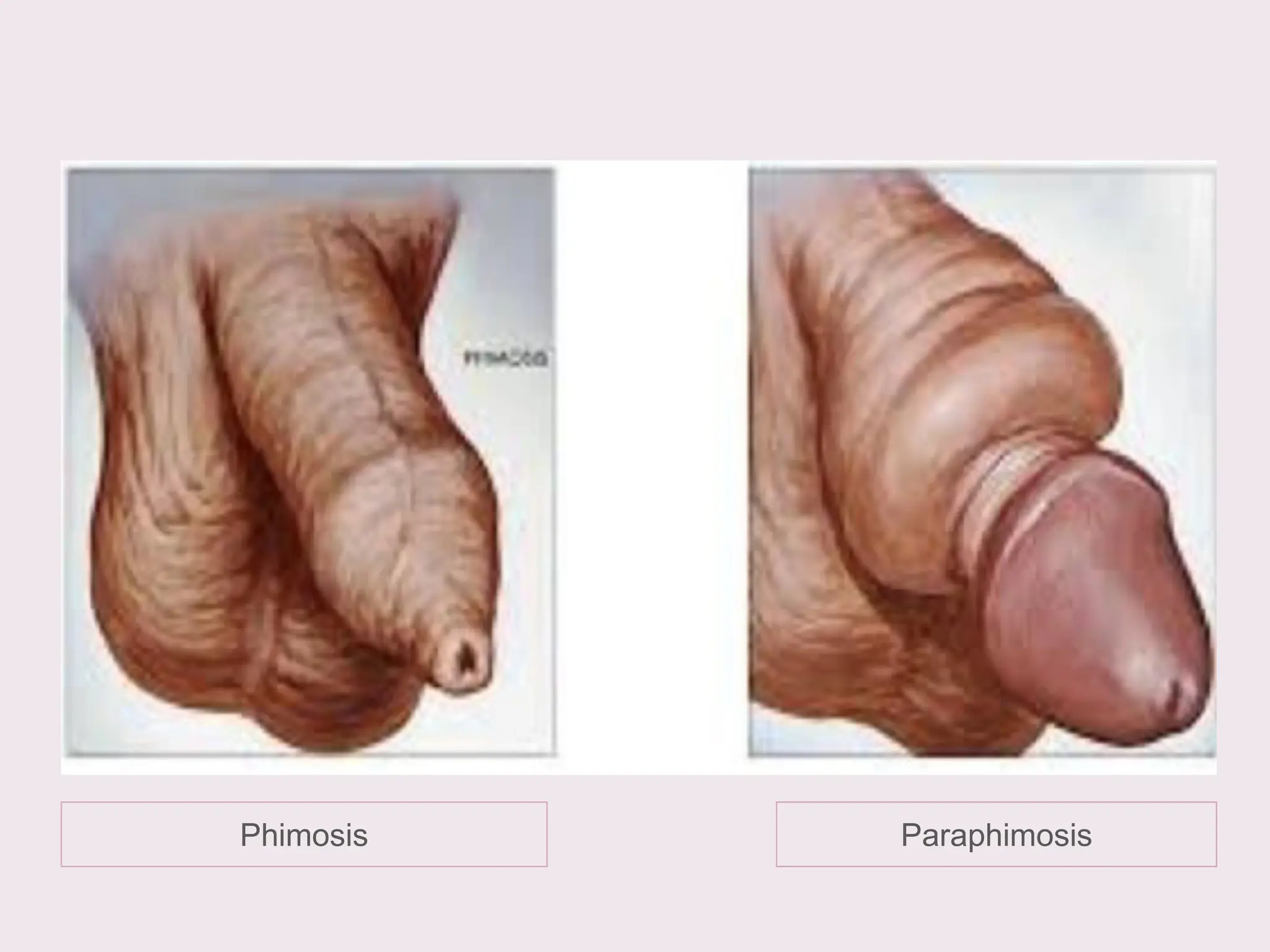
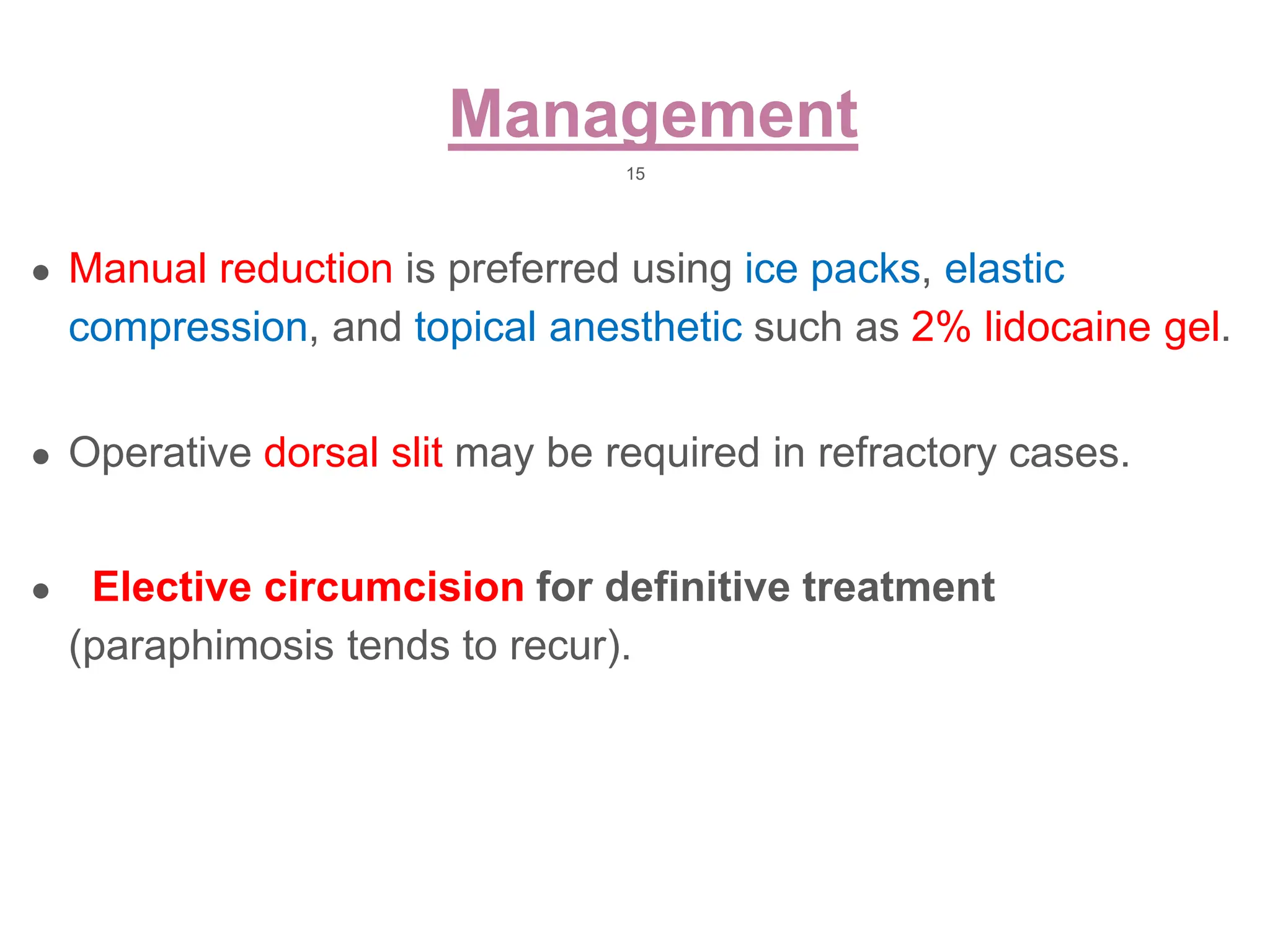
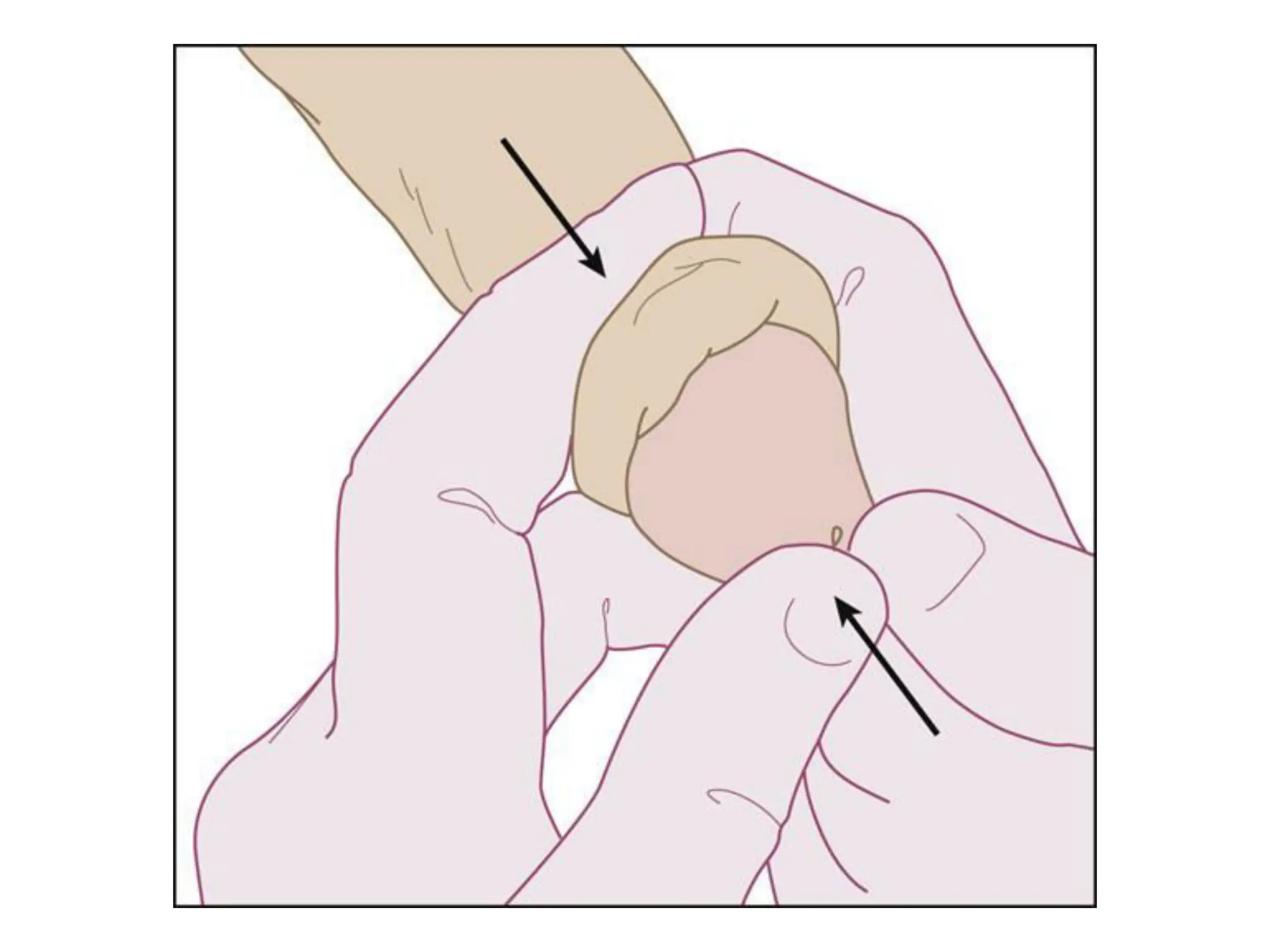
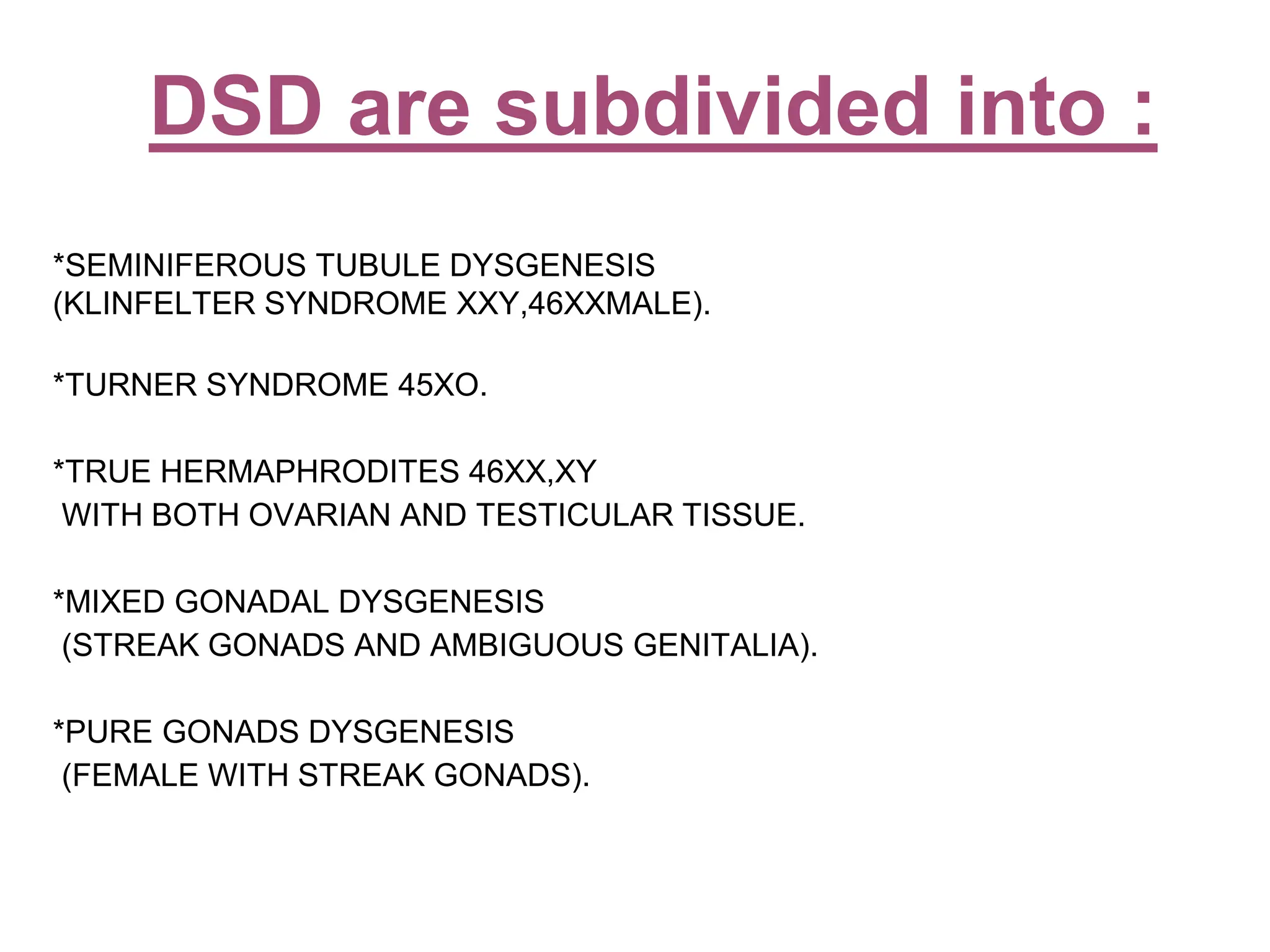
The document discusses conditions related to abnormalities in urethral development, including epispadias and hypospadias, as well as management strategies for phimosis and paraphimosis. It covers treatment options for various disorders of sexual differentiation (DSDs) and stresses a multidisciplinary approach for diagnosis and management, ensuring optimal psychosocial outcomes and monitoring for potential malignancies. Key treatment interventions include surgical reconstruction, hormonal therapy, and monitoring depending on the specific condition and age of the patient.