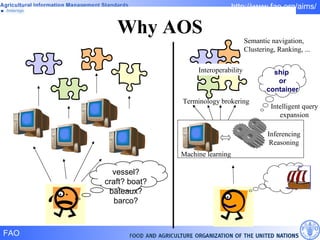
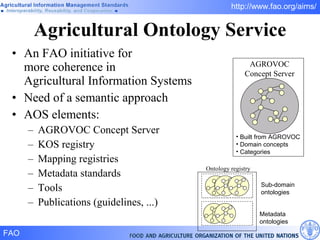
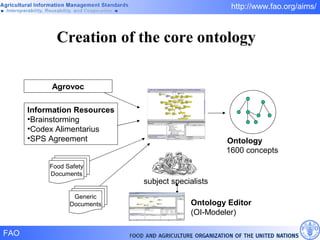
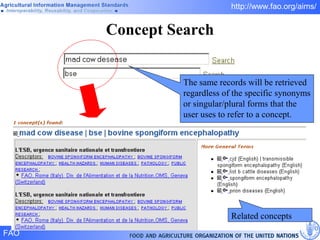
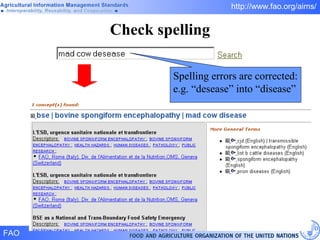
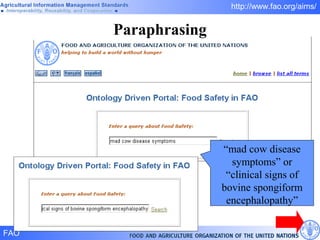
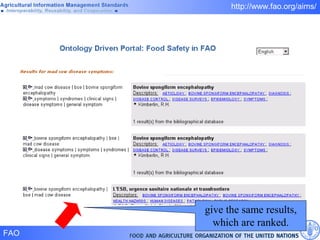
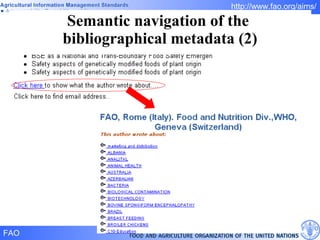
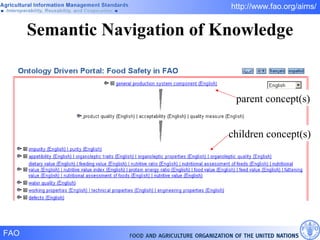
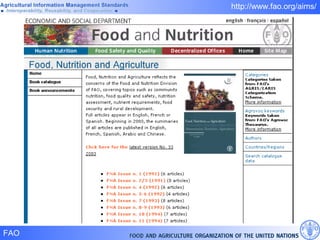
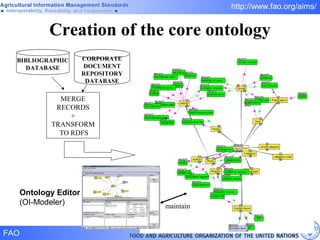
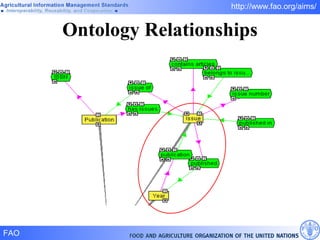
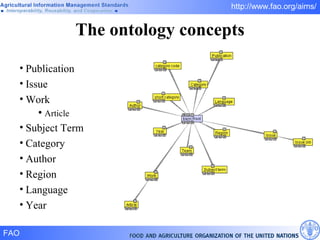
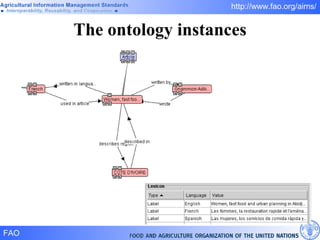
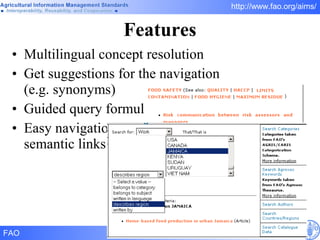
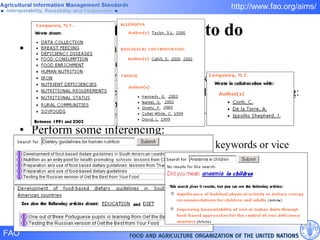
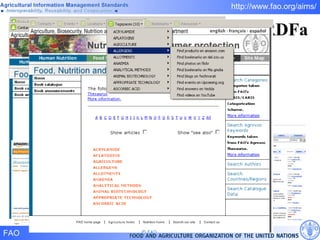
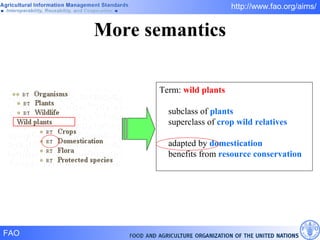
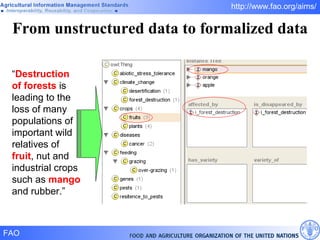
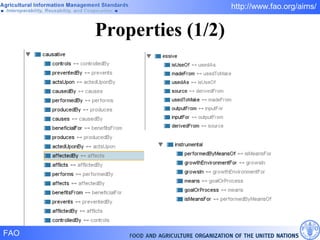
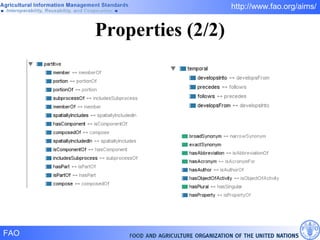
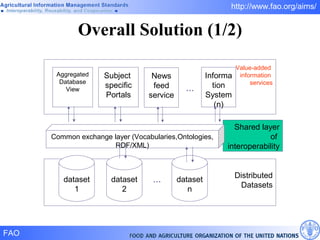
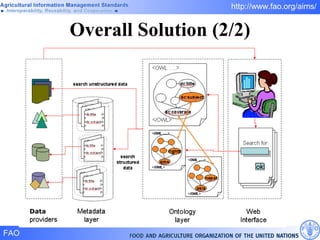
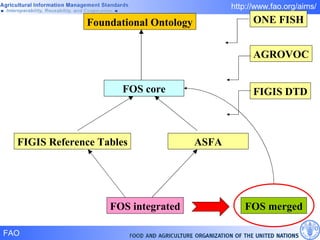
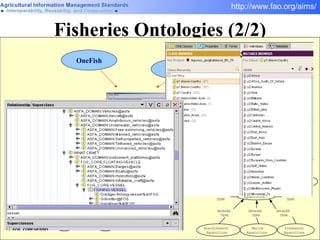
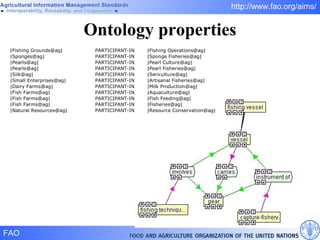
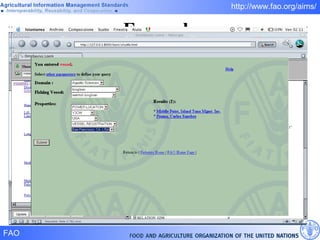
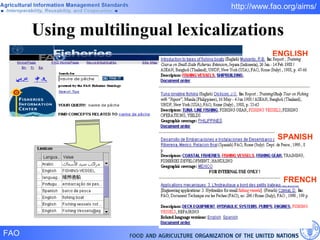
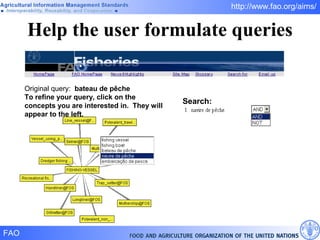
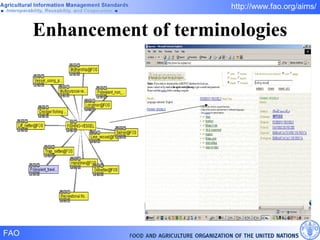
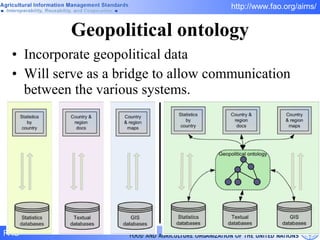
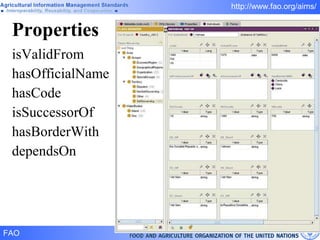
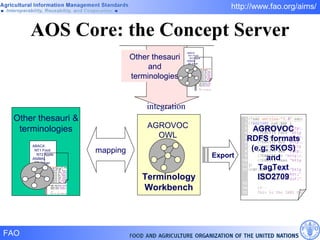
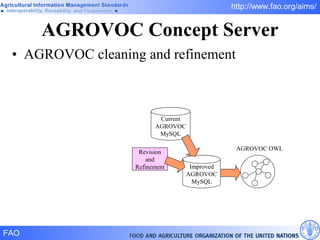
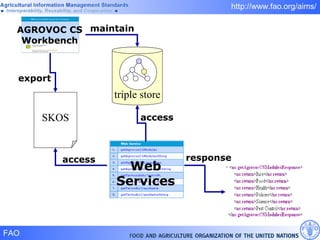
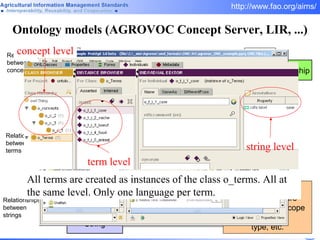
FAO has developed several semantic technologies and ontologies to improve information sharing and interoperability across different knowledge domains, including AGROVOC, the Agricultural Ontology Service, ontologies for fisheries, crops, nutrition, and geopolitics. These projects use techniques such as concept mapping, multilingual support, and semantic search to facilitate knowledge organization and exchange.























![Procedure =CONCATENATE("<owl:Class rdf:ID=""",J2,"""><rdfs:subClassOf><owl:Class rdf:ID=""c_",B2,"""/></rdfs:subClassOf><rdfs:label xml:lang=""en""><![CDATA[",D2,"]]></rdfs:label><code><![CDATA[",J2,"]]></code><TAGNAME><![CDATA[",J2,"]]></TAGNAME>",S2, T2,"</owl:Class>") <?xml version="1.0"?> <rdf:RDF xmlns="http://www.fao.org/aos/infoods#" xmlns:protege="http://protege.stanford.edu/plugins/owl/protege#" xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#" xmlns:rdfs="http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#" xmlns:owl="http://www.w3.org/2002/07/owl#" xmlns:daml="http://www.daml.org/2001/03/daml+oil#" xmlns:dc="http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/" xml:base="http://www.fao.org/aos/infoods"> <owl:Ontology rdf:about=""> <owl:imports rdf:resource="http://protege.stanford.edu/plugins/owl/protege"/> <owl:versionInfo rdf:datatype="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string" >Revision 4.0</owl:versionInfo> <protege:defaultLanguage rdf:datatype="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string" >en</protege:defaultLanguage> <rdfs:comment rdf:datatype="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string" >International Network of Food Data Systems (INFOODS) was established in 1984 on the basis of the recommendations of an international group convened under the auspices of the United Nations University (UNU). Its goal was to .....</rdfs:comment> </owl:Ontology> <owl:Class rdf:ID="c_0413"> <code rdf:datatype="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string" >0413</code> <rdfs:subClassOf> <owl:Class rdf:ID="c_041"/> </rdfs:subClassOf> <rdfs:label xml:lang="en">Vitamin D</rdfs:label> </owl:Class>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/faoisko-090402100539-phpapp01/85/Semantic-Technologies-at-FAO-59-320.jpg)




![Methods Concepts from descriptors Synonym <owl:DatatypeProperty rdf:ID="synonym"> Acronyms <owl:AnnotationProperty rdf:about="http://www.fao.org/aos/agrovoc/2005#acronym"> < owl:Class rdf:about=" http://www.fao.org/aos/agrovoc/2005 #c_3"> <rdfs:label xml:lang="en">ABA</rdfs:label> <rdfs:label xml:lang="fr">ABA</rdfs:label> <rdfs:label xml:lang="es">ABA</rdfs:label> <rdfs:label xml:lang="ar">آبا</rdfs:label> <rdfs:label xml:lang="zh">脱è½é…¸</rdfs:label> <synonym xml:lang="en">[8565] Abscisic acid</synonym> <rdfs:subClassOf rdf:resource=" http://www.fao.org/aos/agrovoc/2005 #c_3397"/> <rdfs:subClassOf rdf:resource=" http://www.fao.org/aos/agrovoc/2005 #c_32543"/> </owl:Class>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/faoisko-090402100539-phpapp01/85/Semantic-Technologies-at-FAO-66-320.jpg)










![Questions? Thanks Margherita Sini: margherita.Sini@fao.org Johannes Keizer: Johannes.Keizer@fao.org Dagobert Soergel: dsoergel@umd.edu Asanee Kawtrakul: [email_address] But Also: Gudrun Johannsen, Boris Lauser, Claudio Baldassarre, Gauri Salokhe, Marta Iglesias, Caterina Caracciolo, Sachit Rajbhandari, Jeetendra Singh, Mary Redahan, Shrestha, Prashanta, Ton, Imm, Thanapth, Trakul, and many others...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/faoisko-090402100539-phpapp01/85/Semantic-Technologies-at-FAO-79-320.jpg)