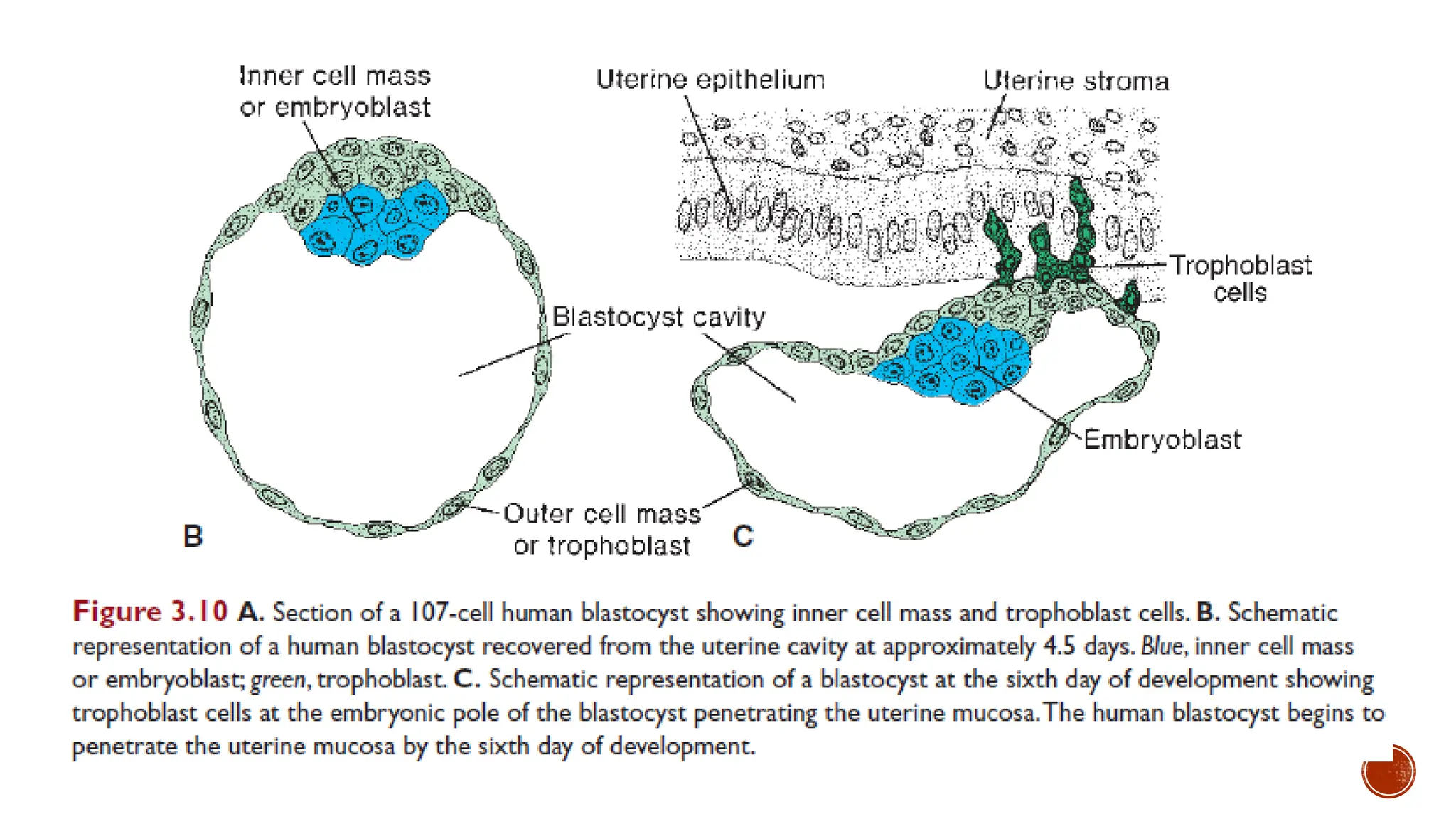
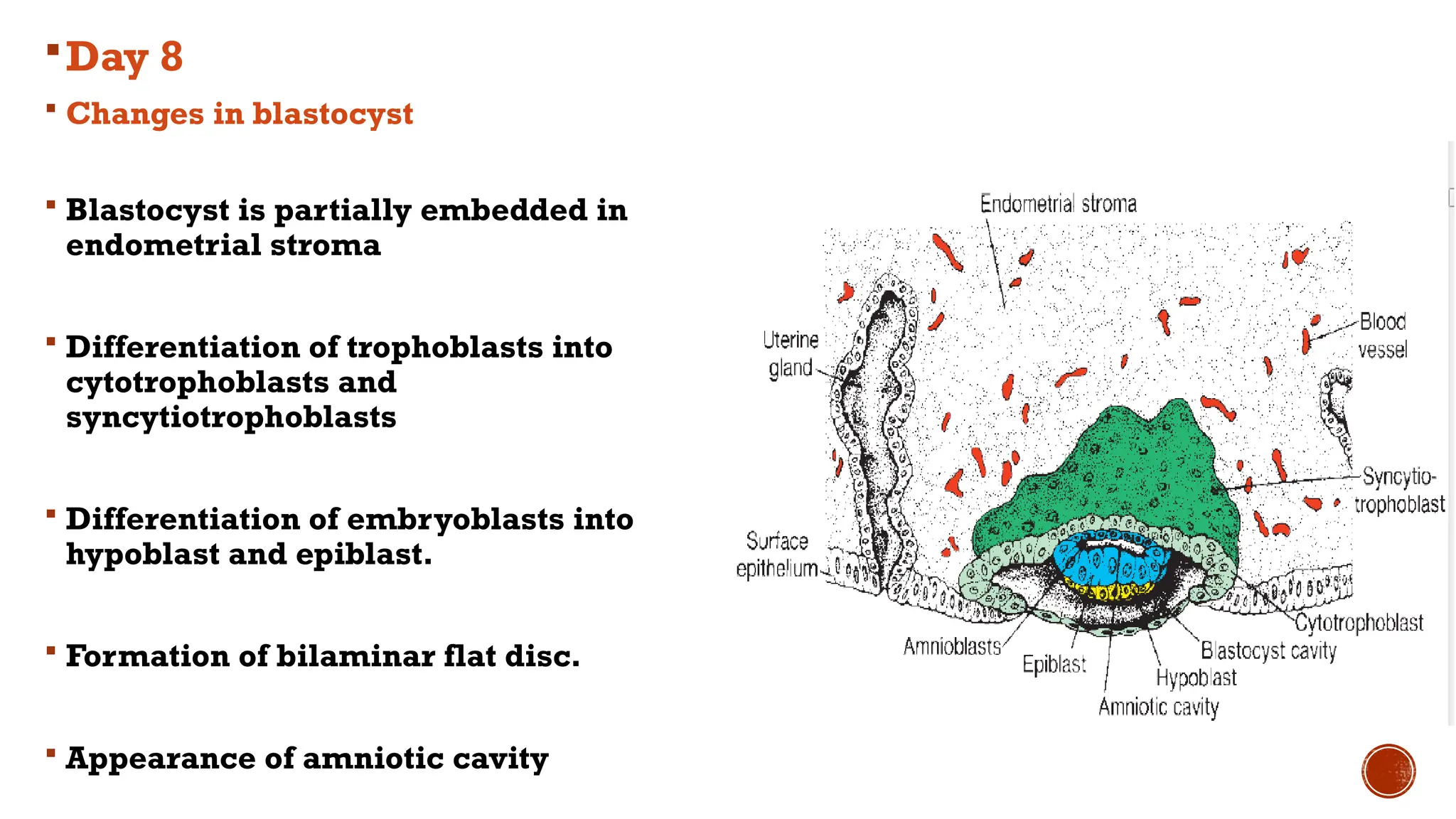
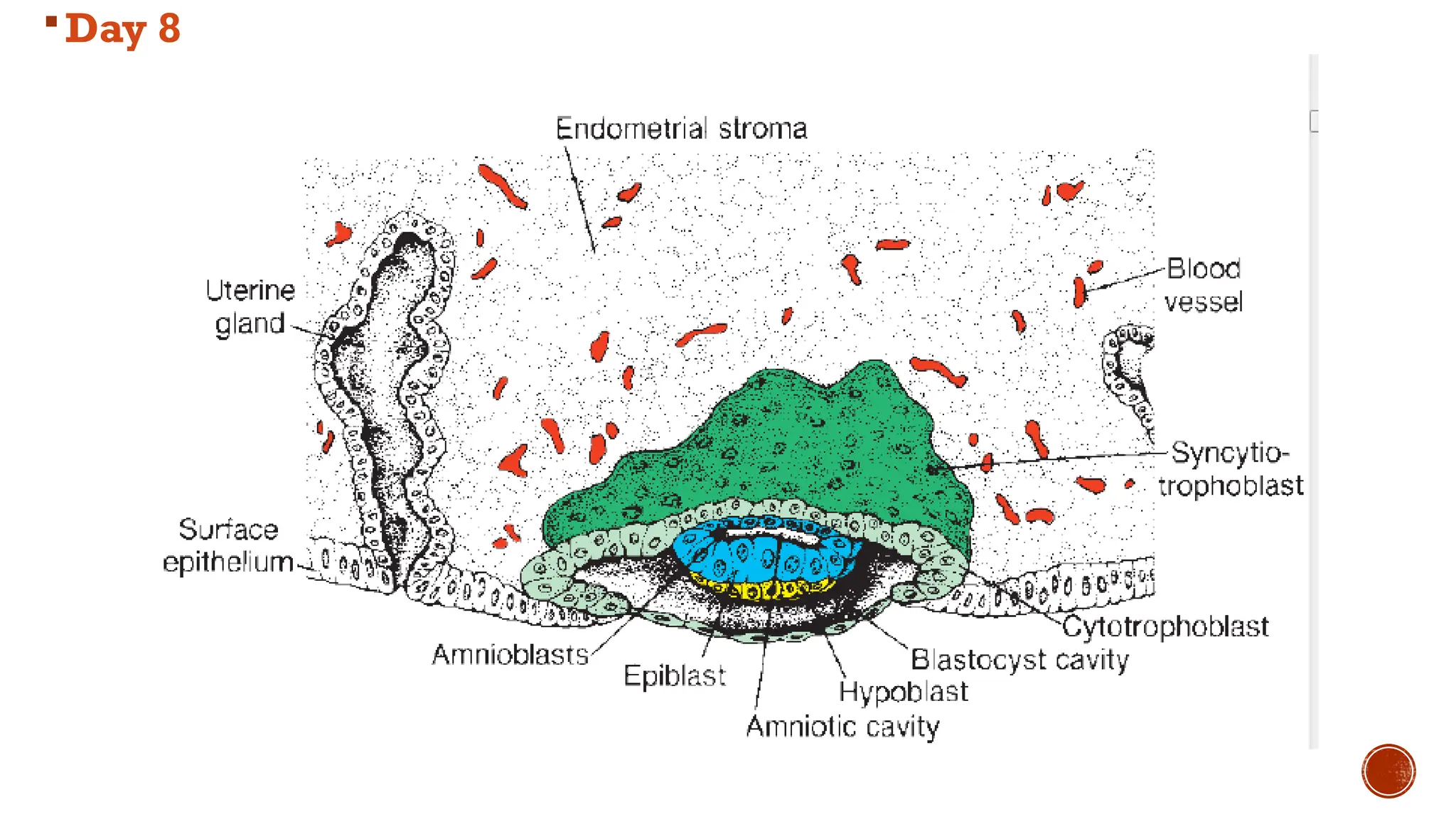
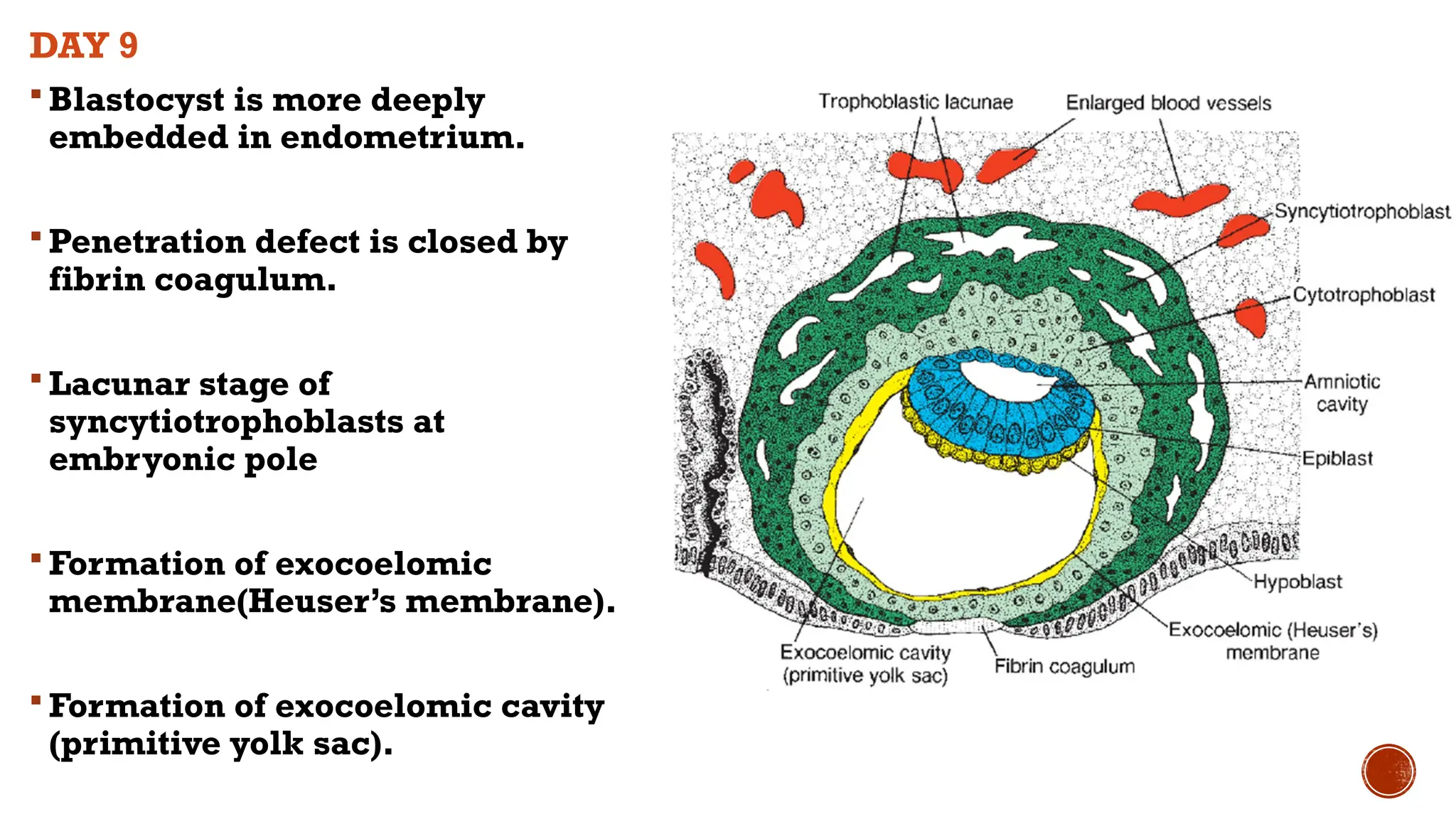
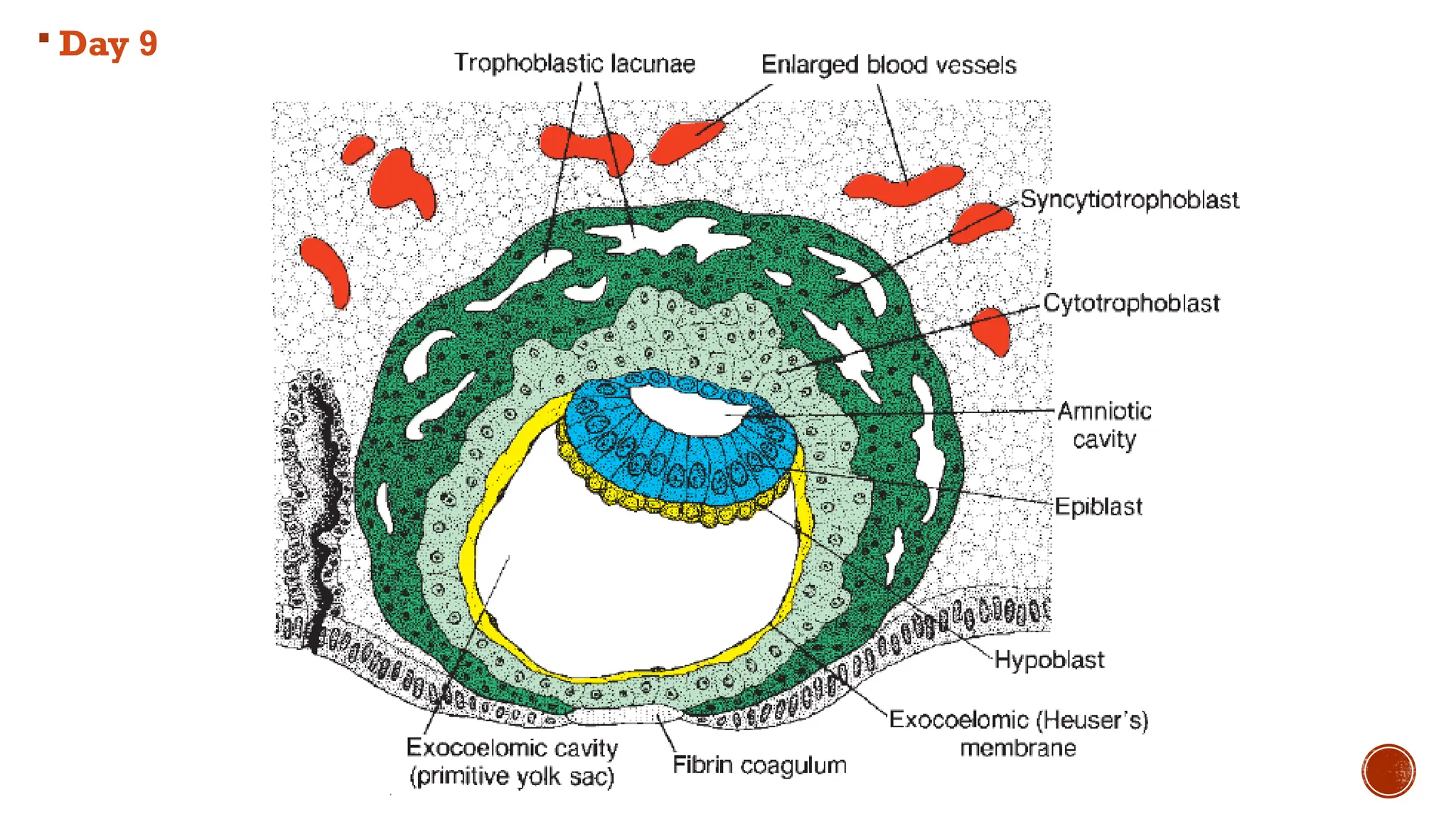
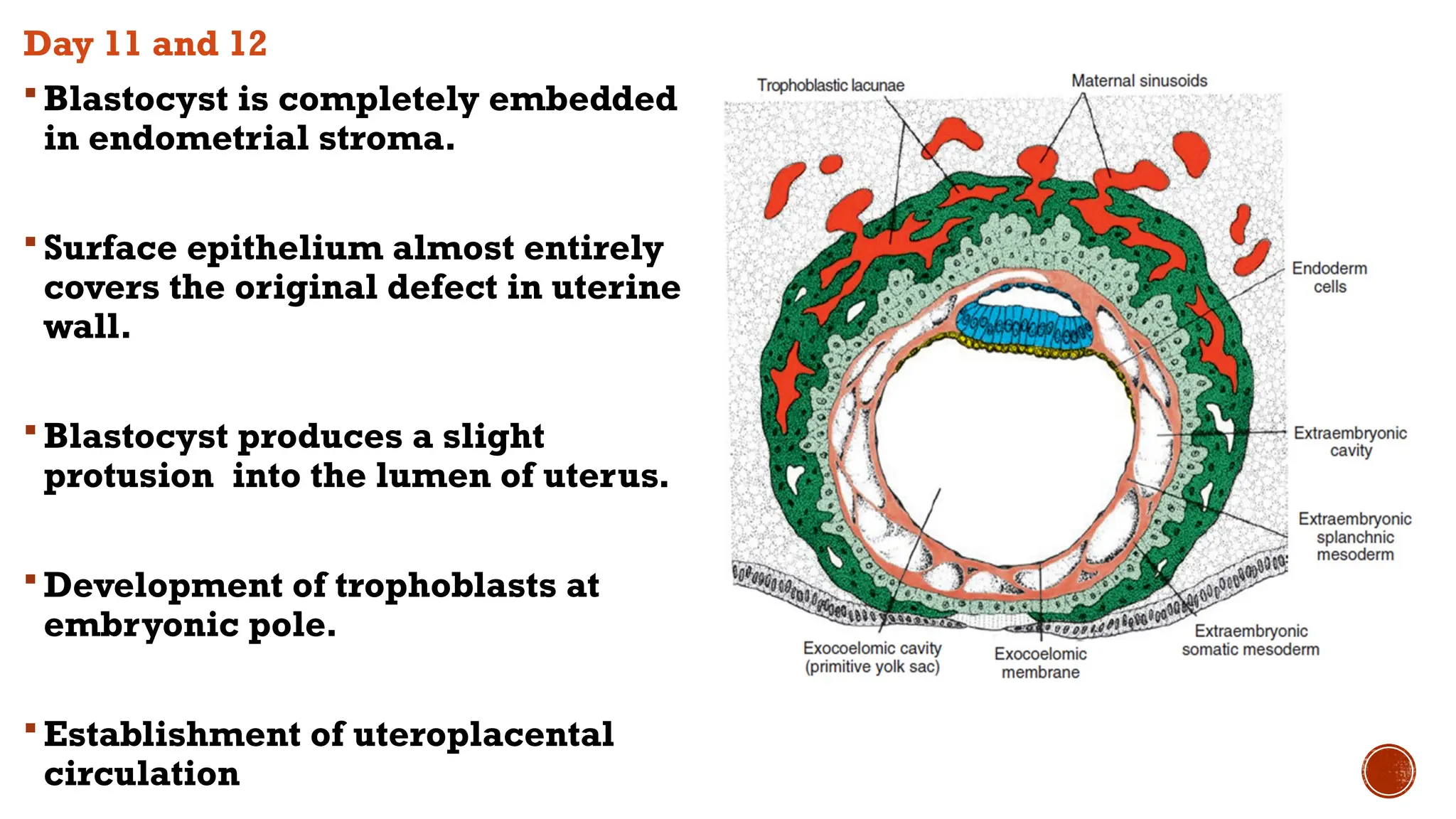
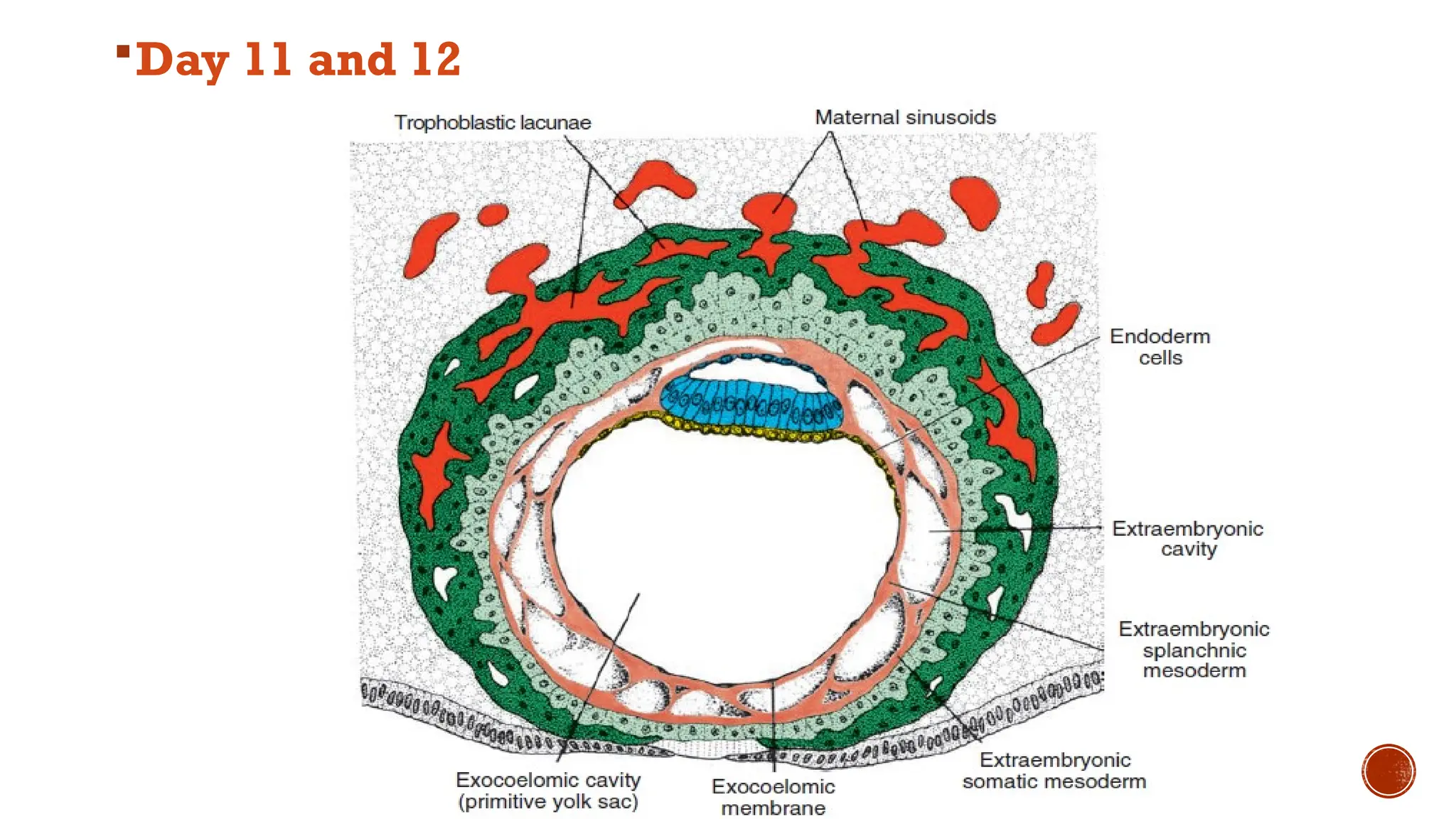
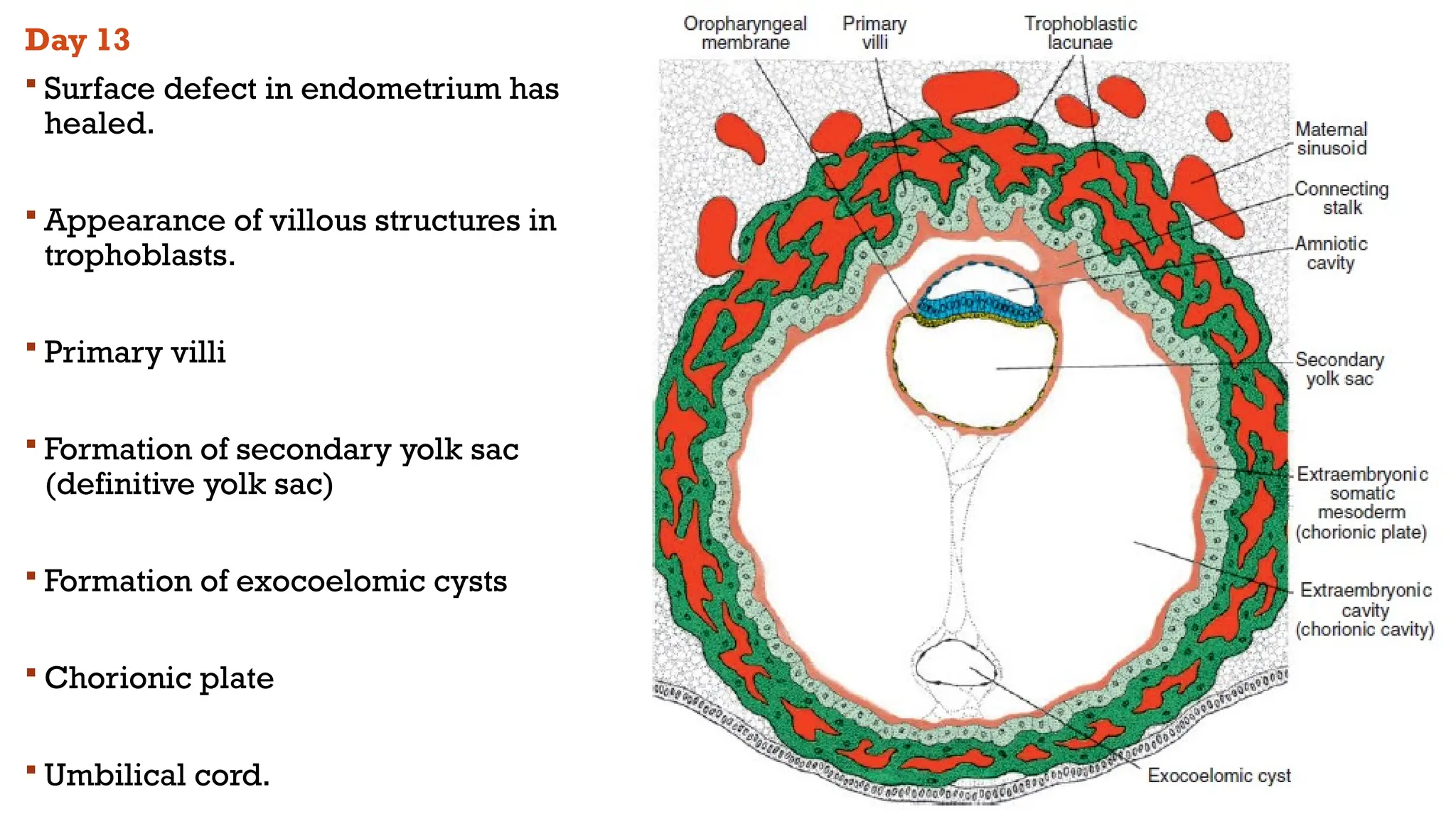
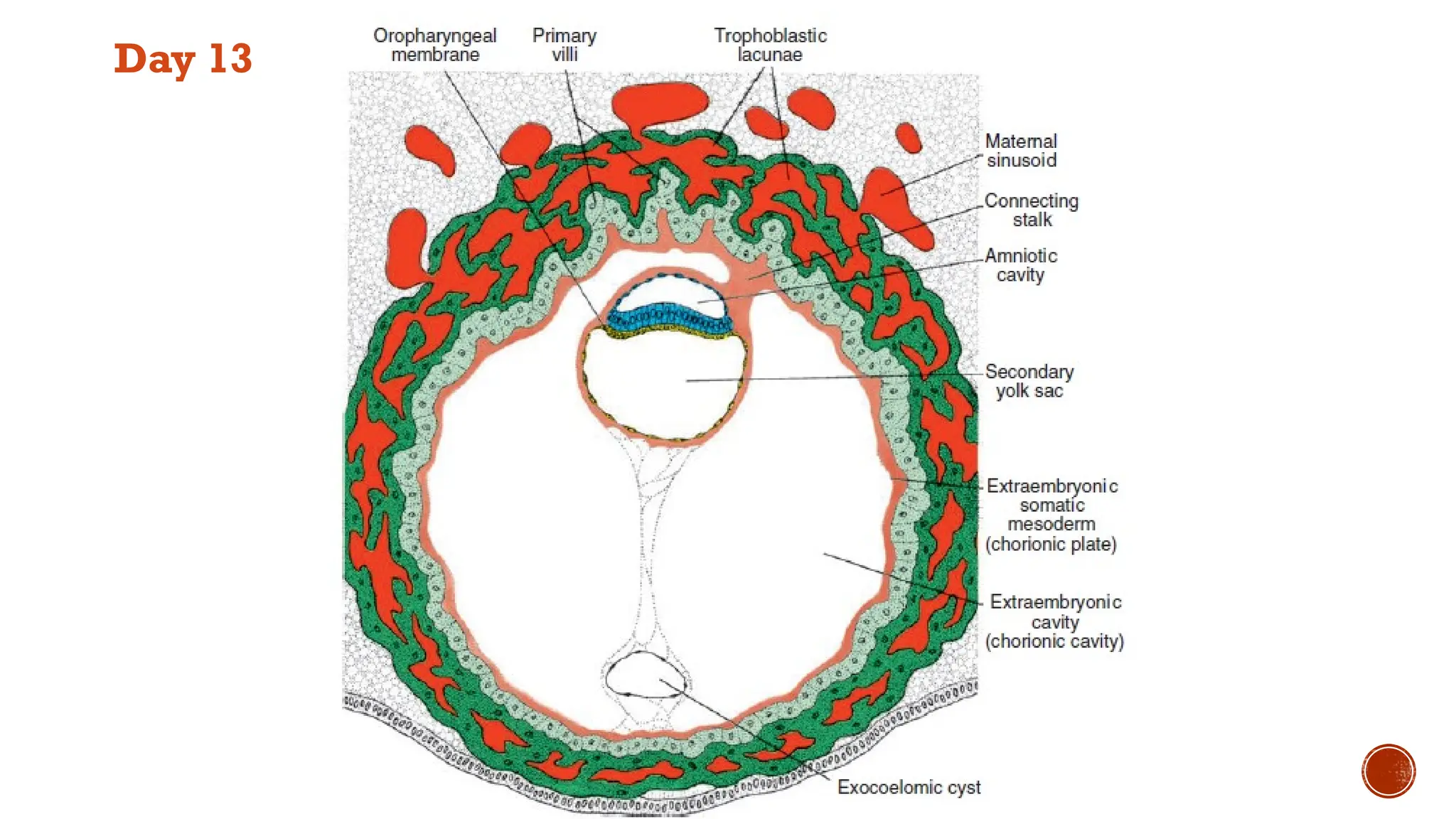
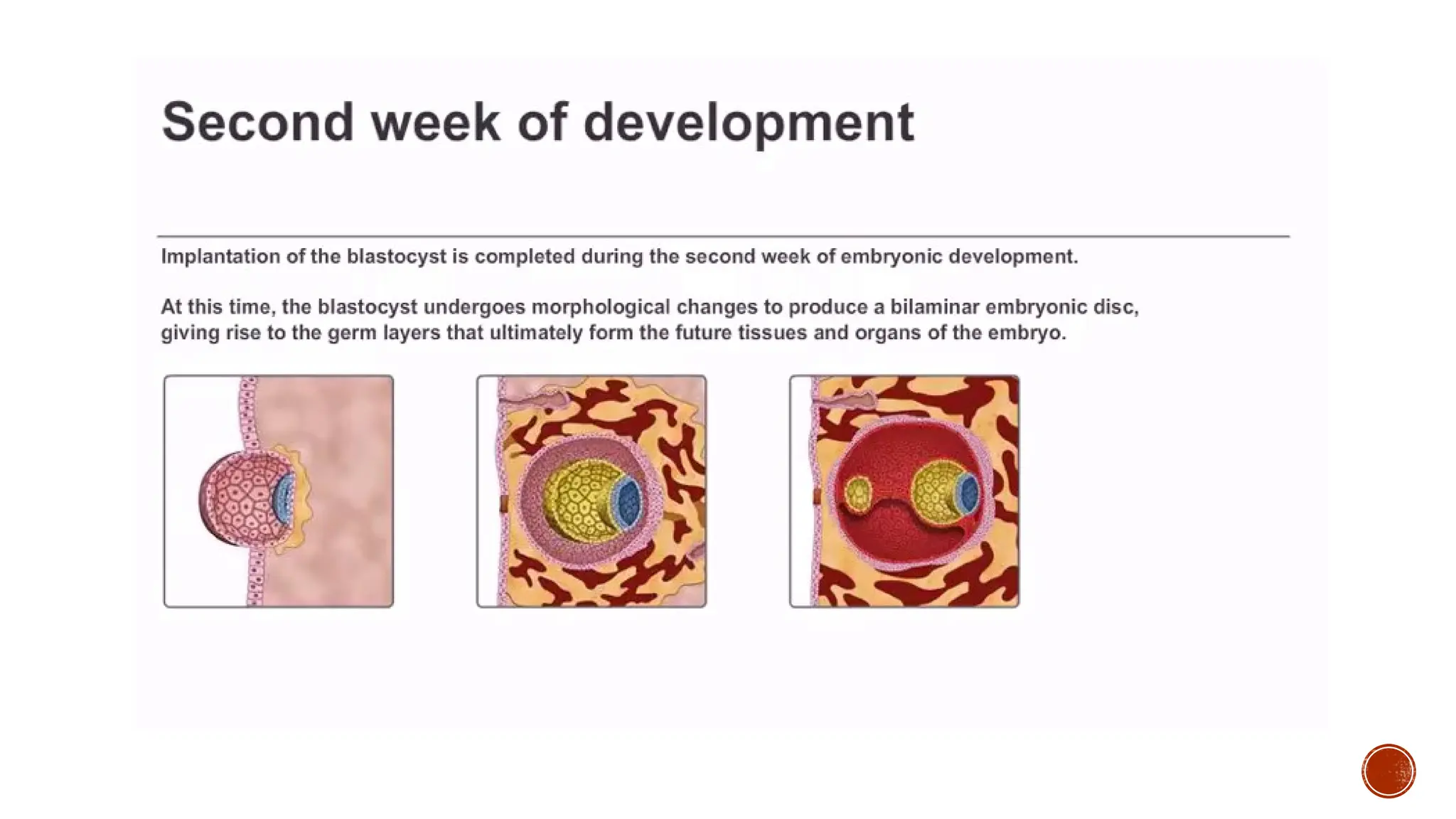
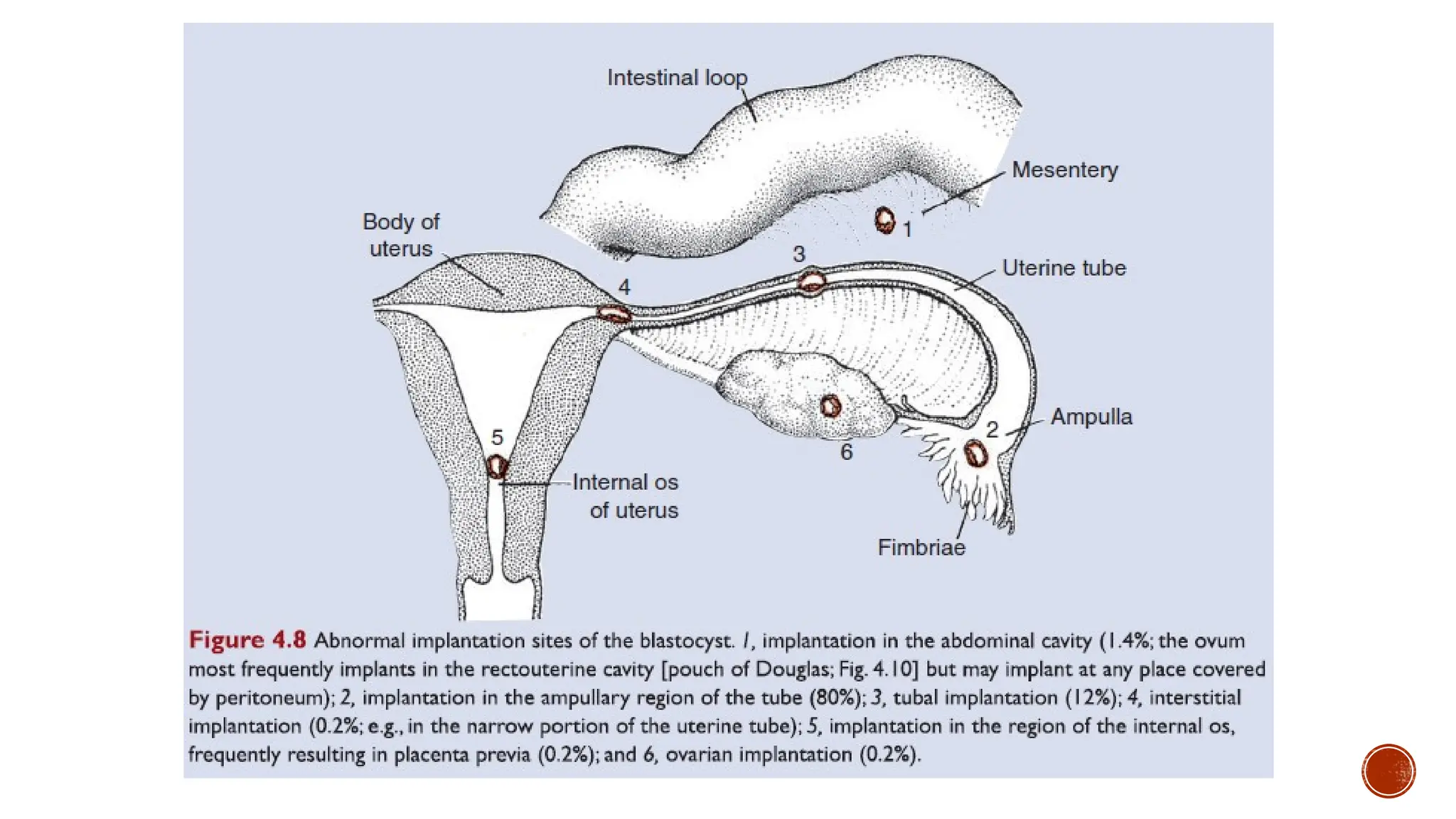
The document outlines the developmental changes occurring in the blastocyst and endometrial stroma during the second week of embryonic development. Key stages include the differentiation of trophoblasts and embryoblasts, embedding of the blastocyst within the endometrium, and the formation of various embryonic and extraembryonic structures. It also addresses clinical implications of abnormal implantation and related conditions.