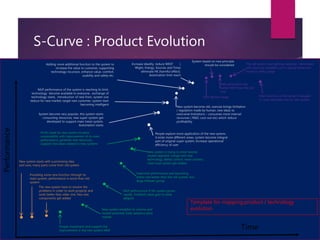
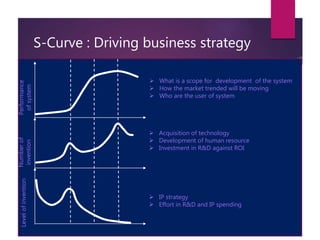
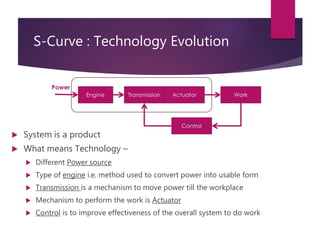
The document discusses S-curves and how they can be used to evaluate technology opportunities and support investment decisions. It explains that S-curves show how technologies evolve over time, with performance initially increasing slowly, then rapidly as the technology matures and is adopted more widely, before reaching a limit and declining. The document provides templates and questions to help map the evolution of products and technologies onto S-curves to understand the current stage and guide business strategies around R&D, IP, acquisitions, and other factors.