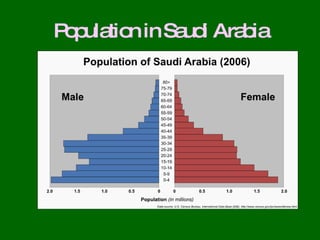
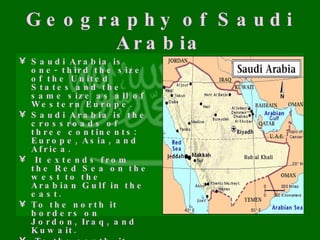
The document outlines the history, demographics, geography, government, culture, human rights, holidays, and religious practices in Saudi Arabia. It covers key historical events, including the establishment of the Saudi dynasty, the discovery of oil, and the country's modernization efforts. Additionally, it highlights cultural aspects and human rights issues, particularly regarding women and religious freedoms.