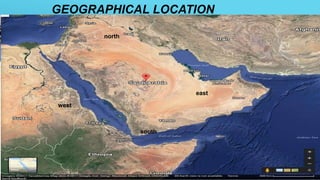
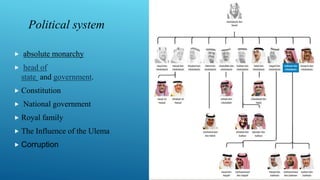
This document provides information about Saudi Arabia. It discusses the country's founding, location, demographics, culture, education system, political system based on absolute monarchy, economy which is largely based on oil exports, and legal system based on Sharia law. It also lists group members and their student IDs for a project on Saudi Arabia.