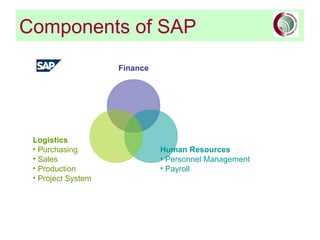
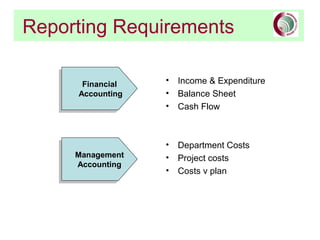
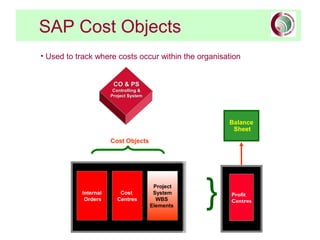
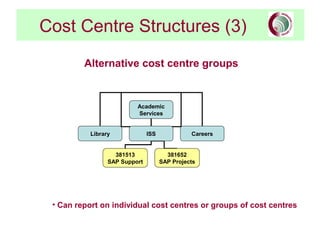
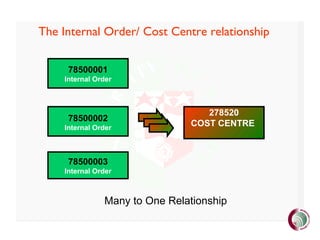
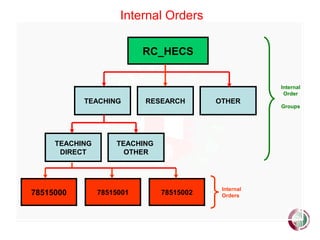
This document provides an overview of SAP financial modules and reporting at the University of Leeds. It describes the objectives of SAP financial reporting, the SAP modules used, key SAP concepts like cost objects and cost centres, and the types of reports available for income/expenditure, balance sheet, costs vs. budget, and department/project costs. Cost objects like cost centres, internal orders, and cost elements are explained and examples are provided.