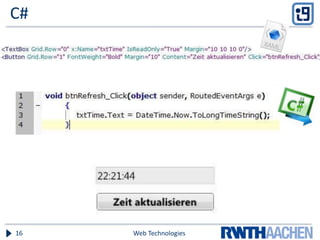
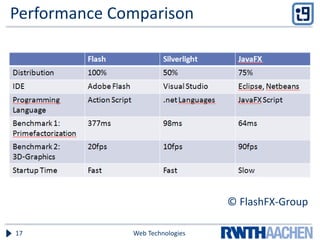
Silverlight is a Microsoft technology that allows creation of rich interactive applications that run in a web browser. It uses XAML for user interface design and C# or VB.NET for functionality. Applications are rendered using the Silverlight plugin and integrate multimedia, graphics and interactivity. Silverlight is based on .NET and a subset of Windows Presentation Foundation, allowing development of applications with a professional IDE like Visual Studio. While it provides powerful capabilities, Silverlight does have limitations around cross-browser compatibility and lack of development tools on non-Windows platforms.