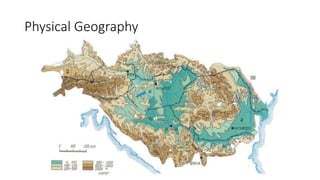
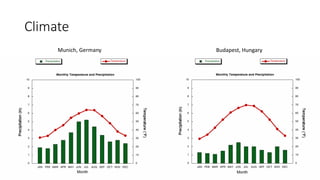
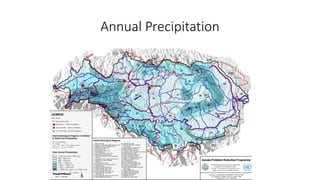
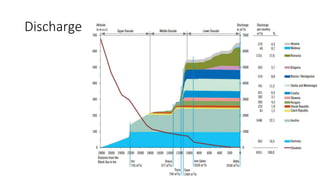
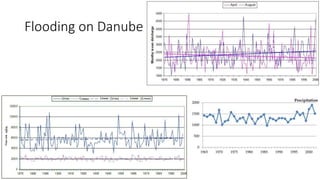
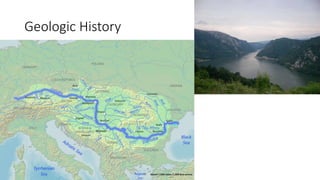
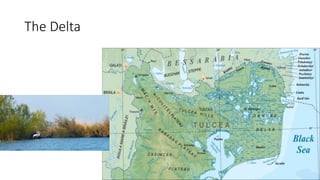
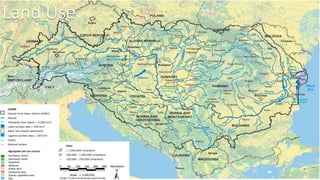
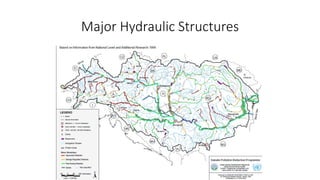
The document provides information about the Danube River Basin, including that it is the second largest river in Europe, draining an area of over 320,000 square miles across 18 countries. It describes the river's physical geography, climate, discharge, channel pattern, and geologic history. Additionally, it discusses land use and human impacts such as agriculture, municipal waste, and industry that have contributed to water quality issues. The document also briefly mentions biodiversity in the river basin and a 2010 industrial accident that released toxic sludge.