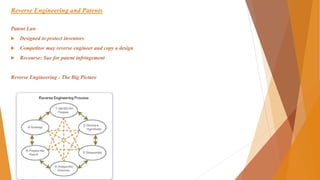
Reverse engineering is the process of taking something apart and analyzing its components and workings in detail. It is an important step in the design process that involves analyzing a product's function and features. The goals are to develop replacement parts, documentation to manufacture old products, and to gain a new understanding. It can also be used for research, failure analysis, and continuous improvement. The process involves identifying the purpose, developing a hypothesis, carefully disassembling the product, analyzing the elements through various tests, and documenting findings in a report.