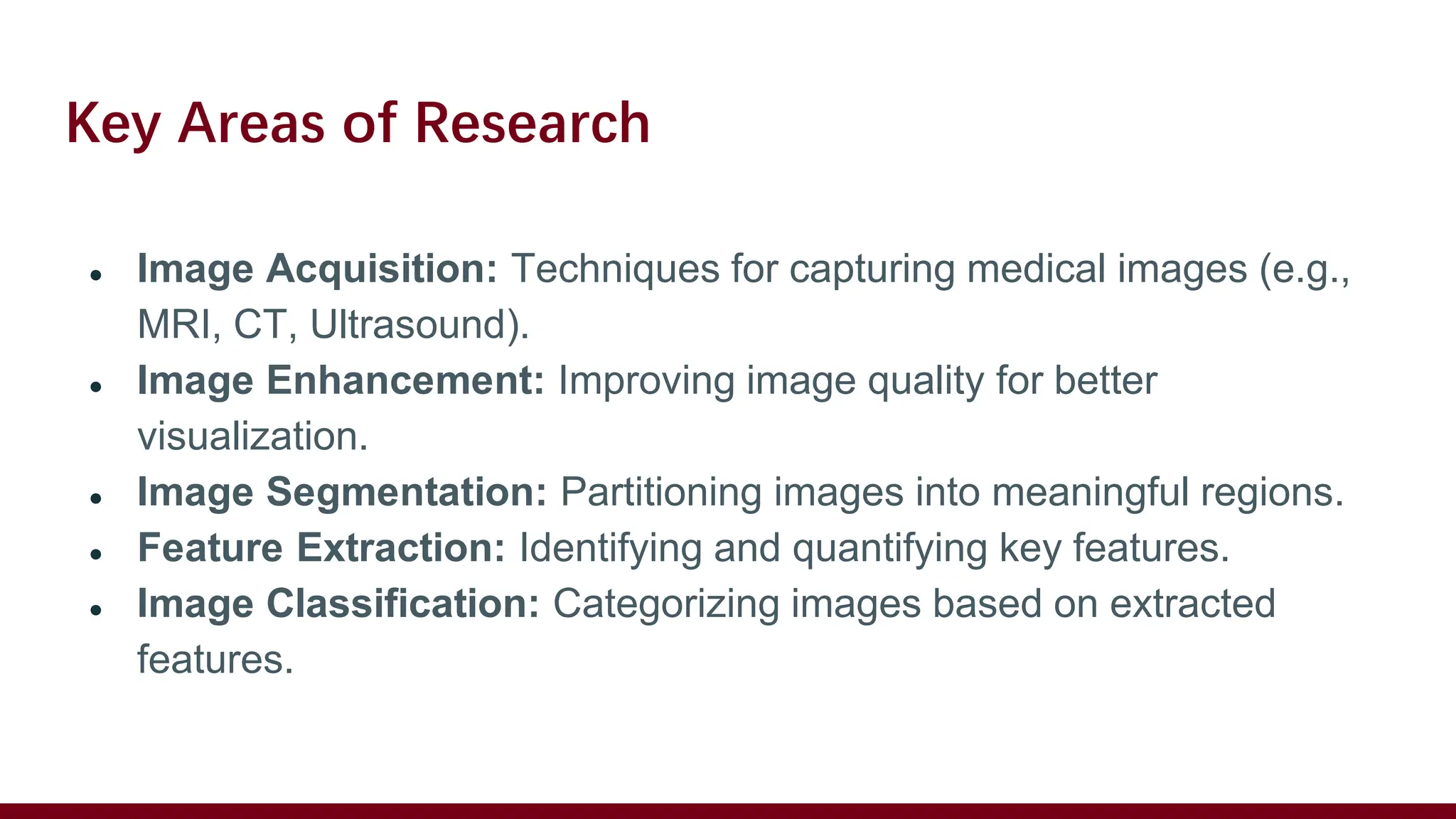
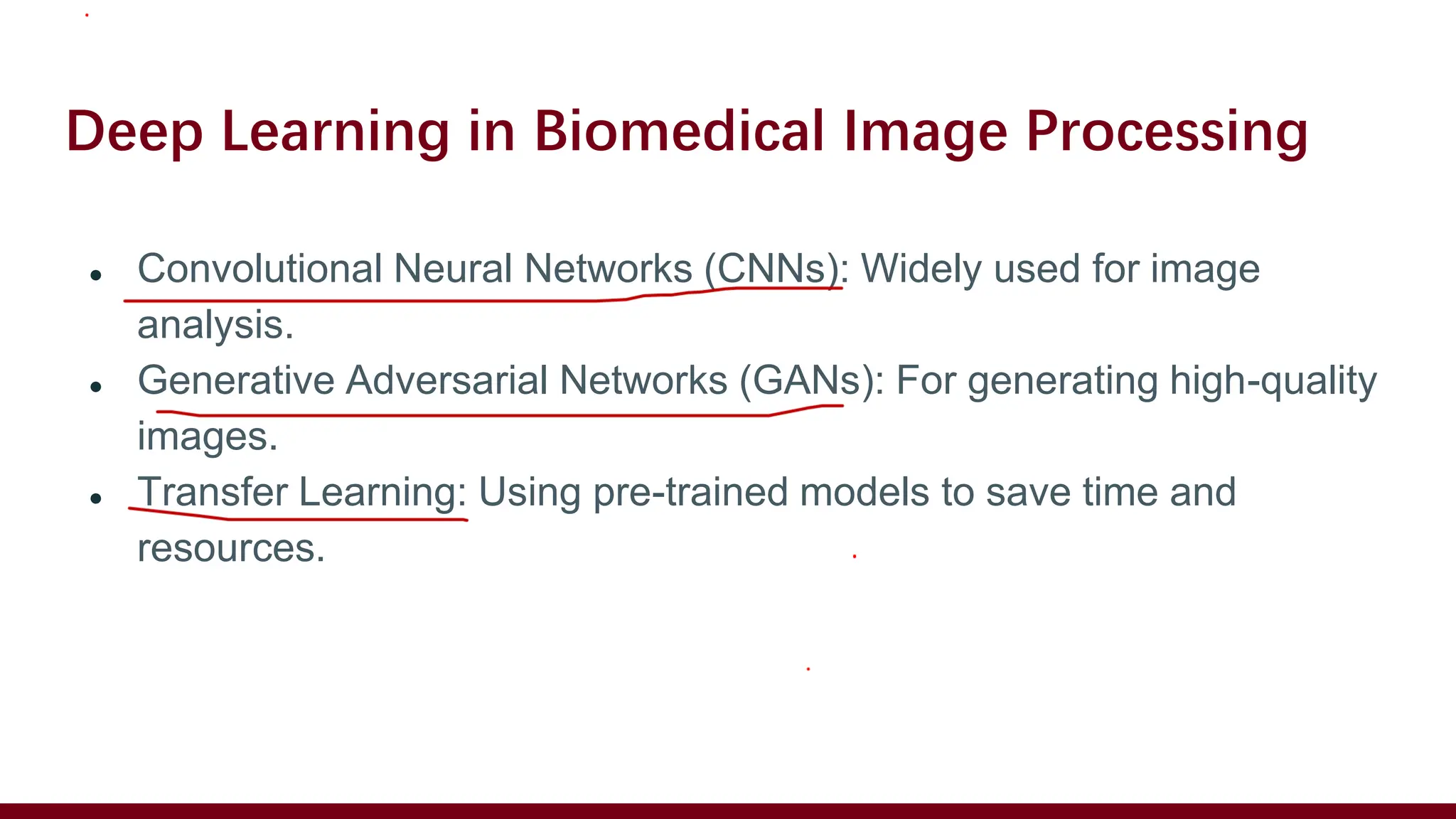
The document discusses biomedical image processing, focusing on techniques for analyzing and enhancing medical images to improve diagnostic and treatment outcomes. Key research areas include image acquisition, enhancement, segmentation, feature extraction, and classification, with an emphasis on using software and techniques such as machine learning and deep learning. It also addresses challenges in the field, future directions for AI integration, and provides resources for further learning.