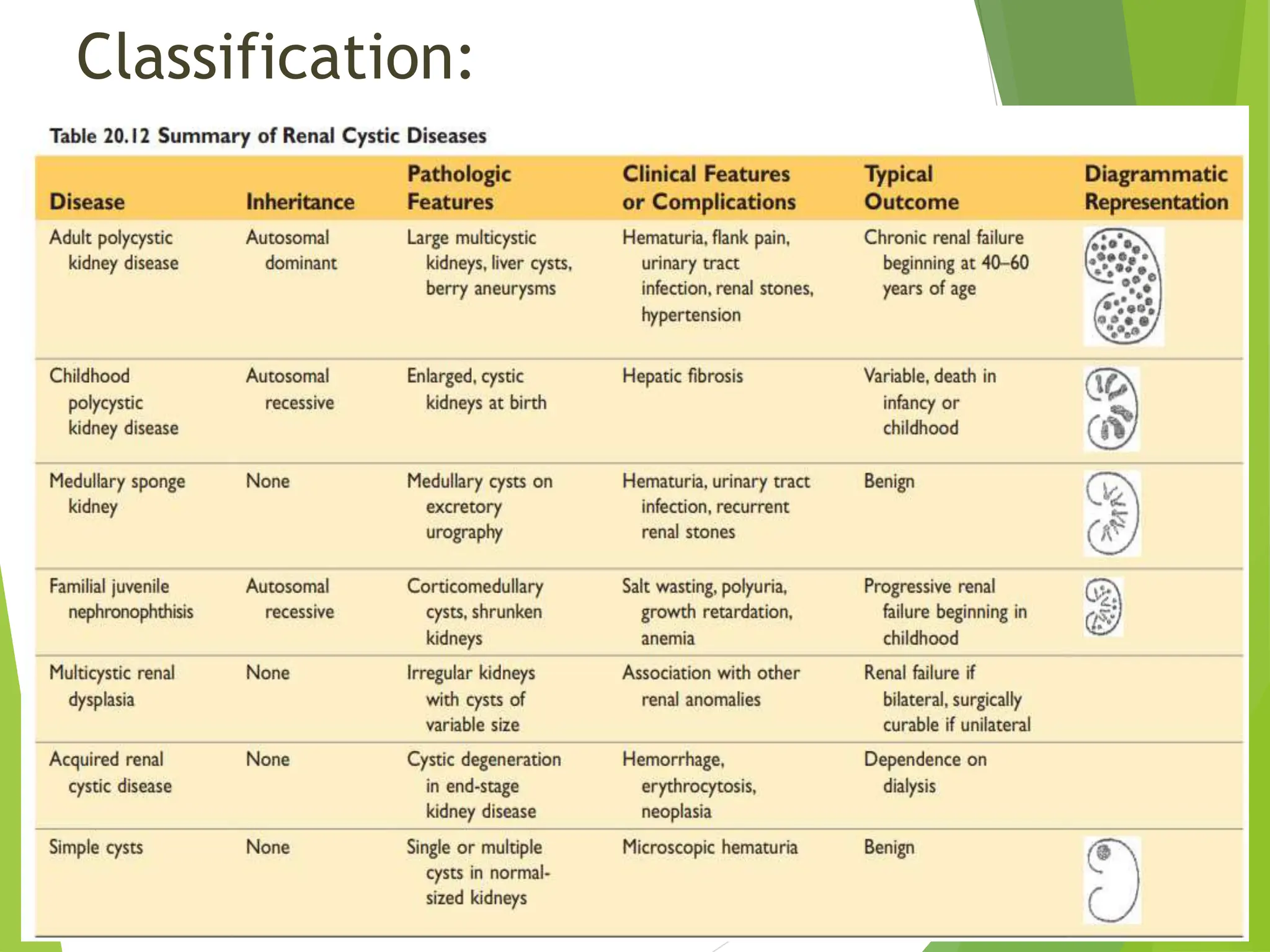
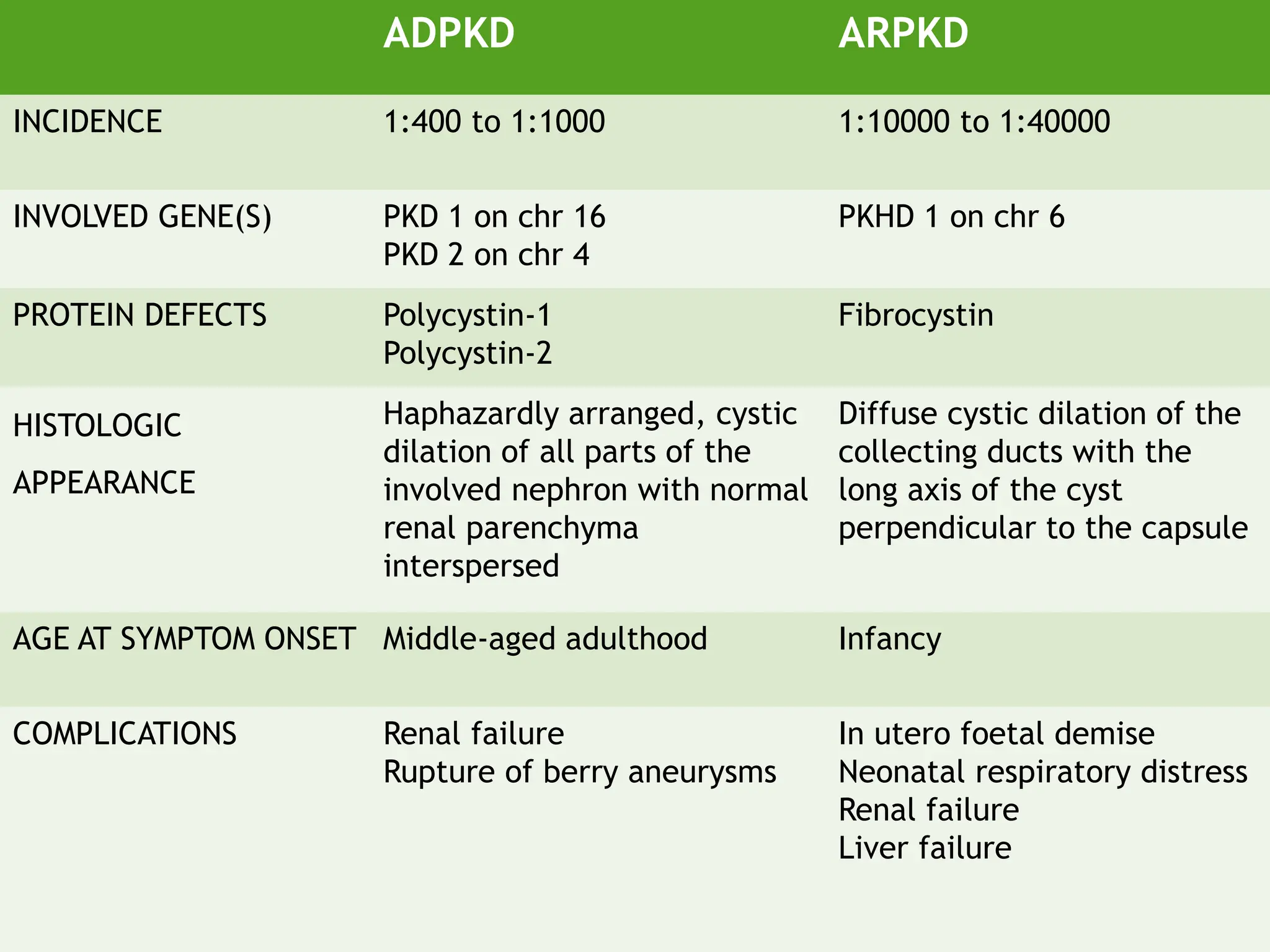
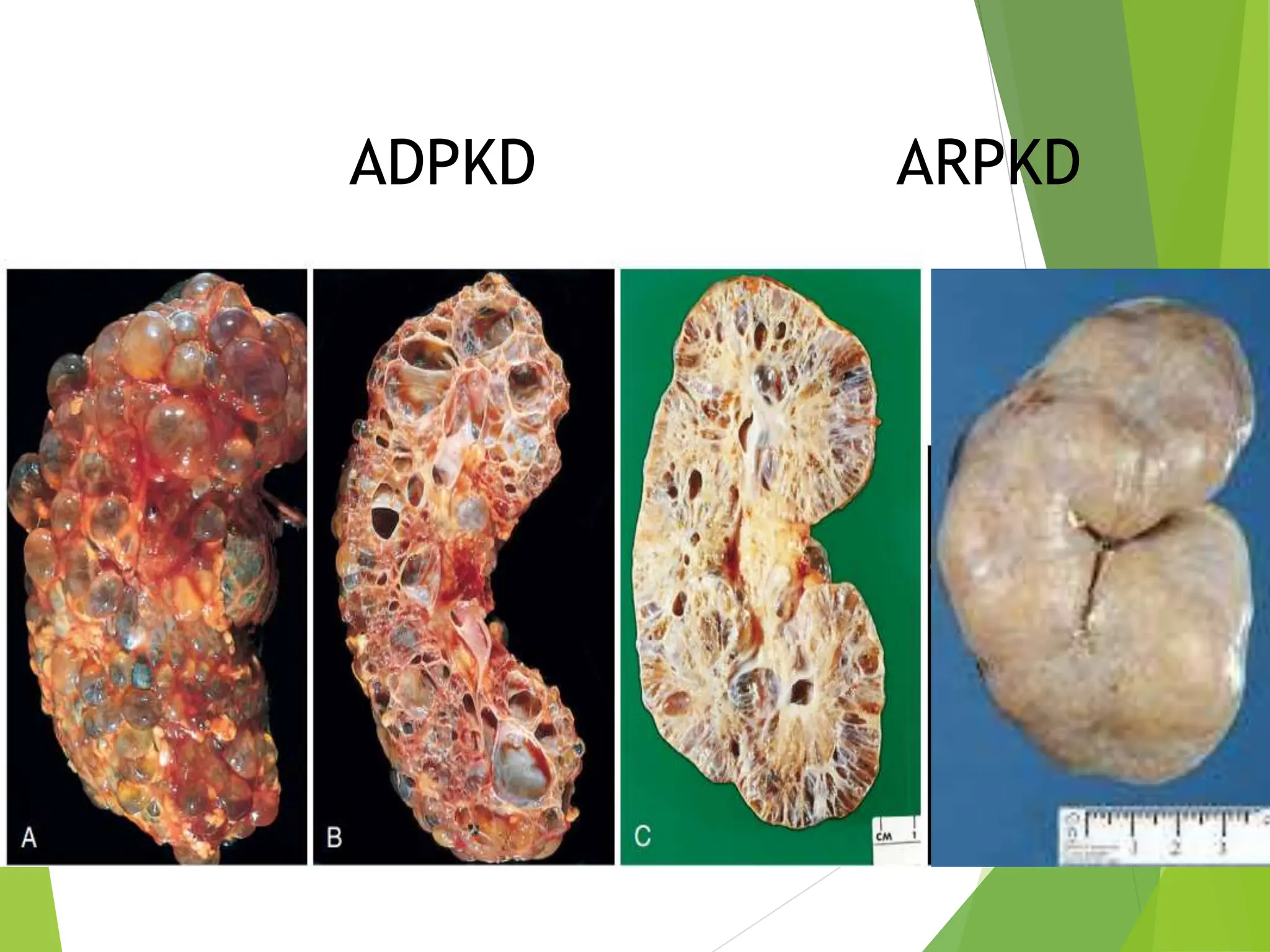
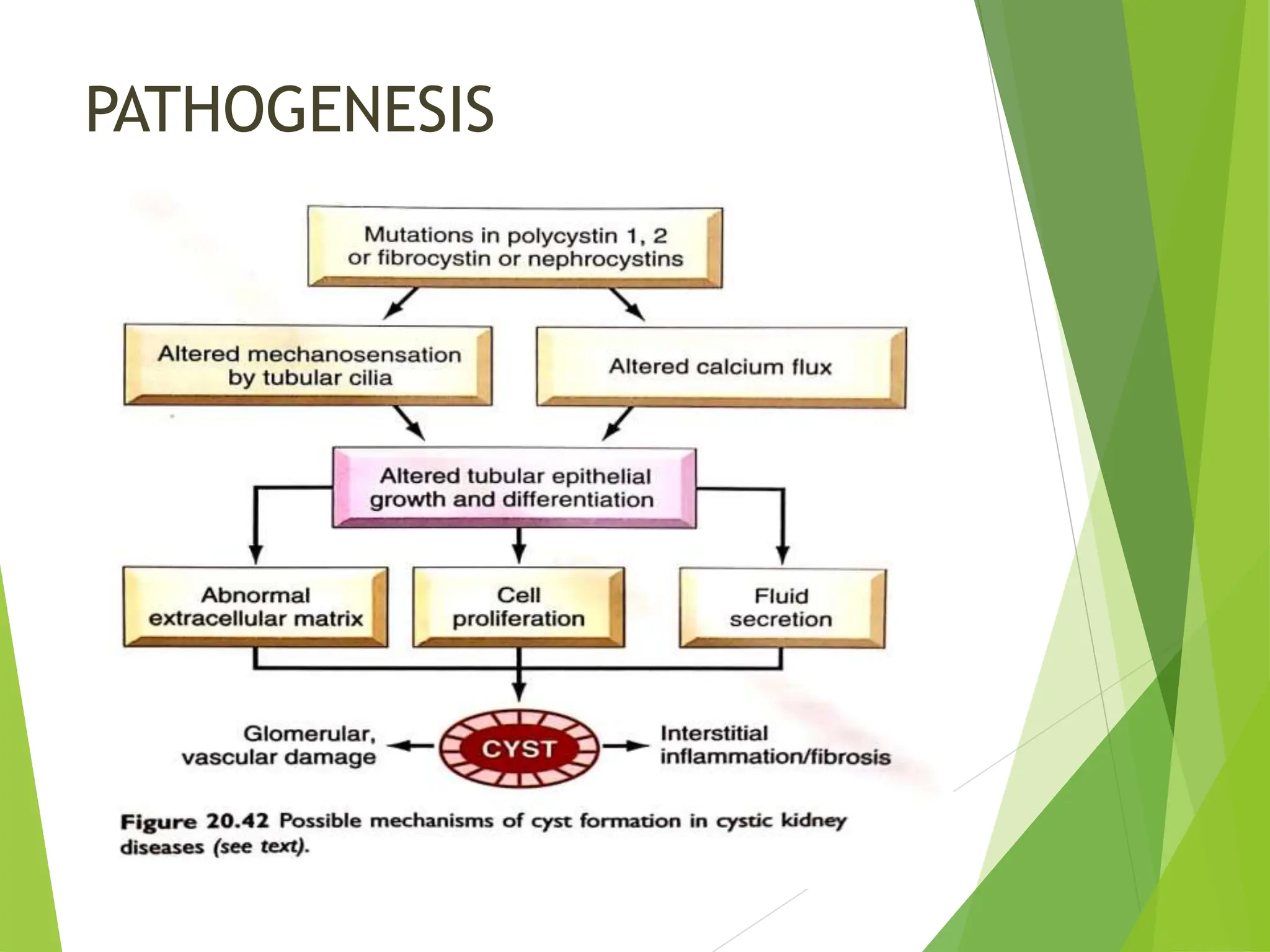
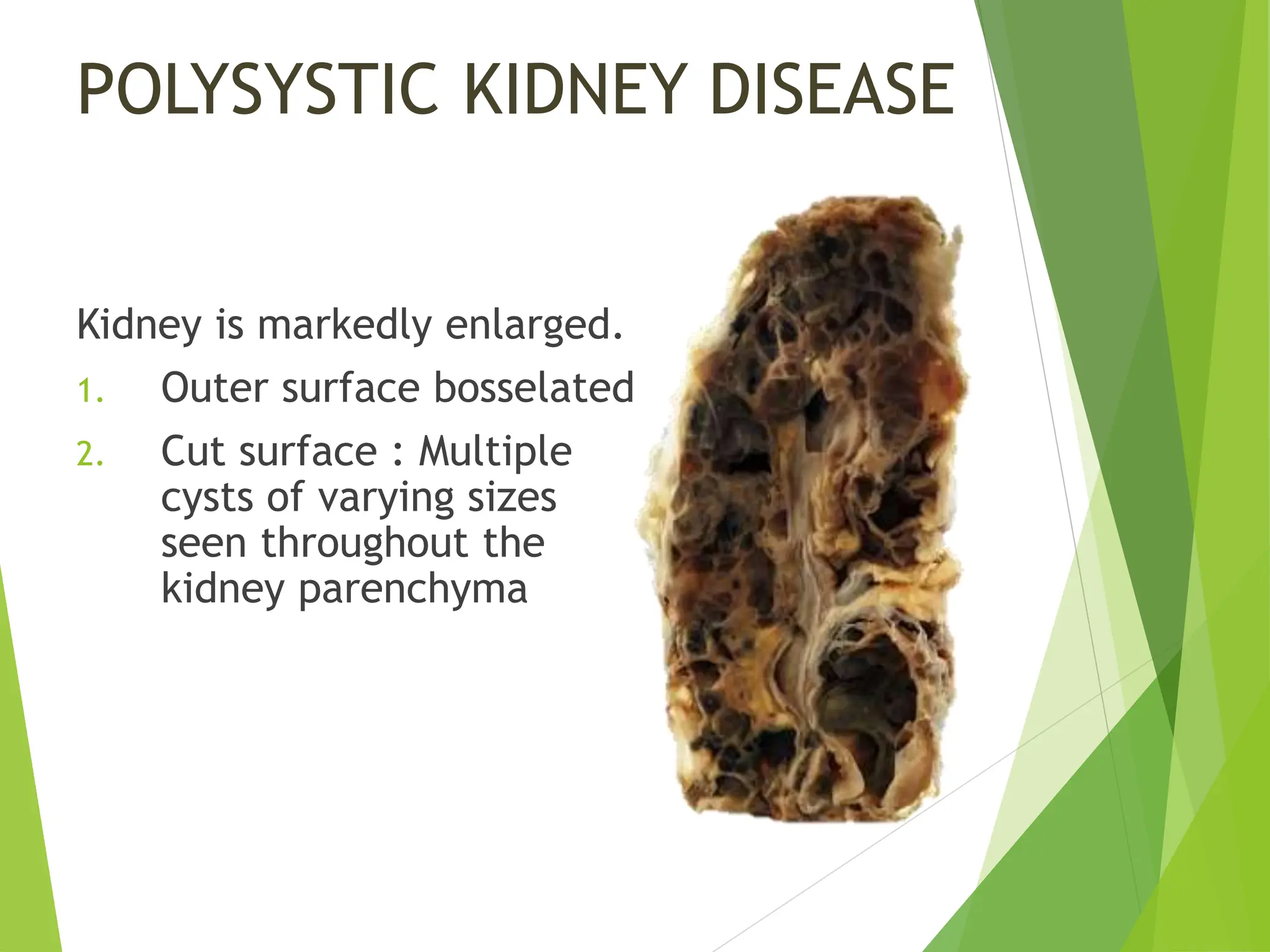
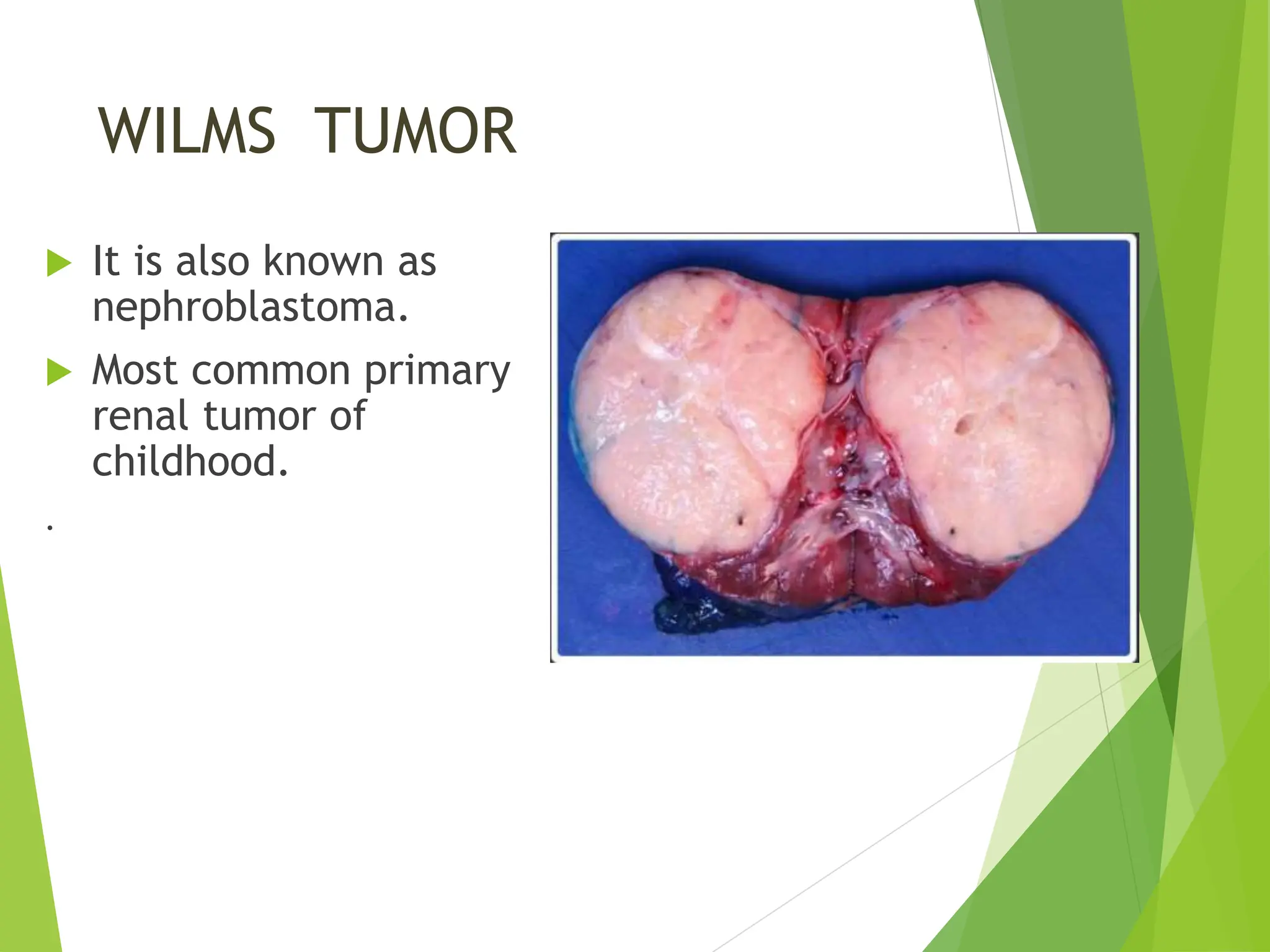
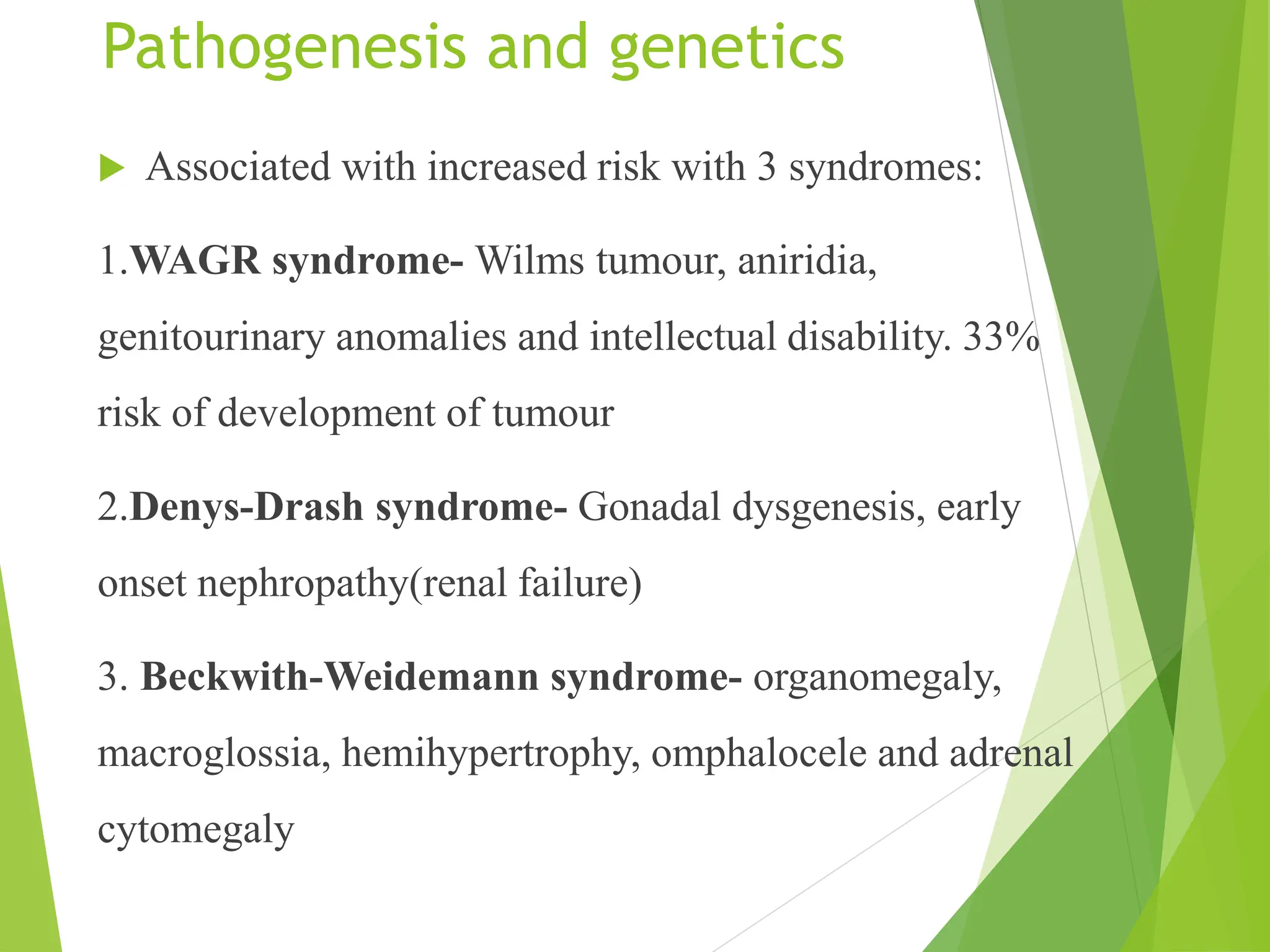
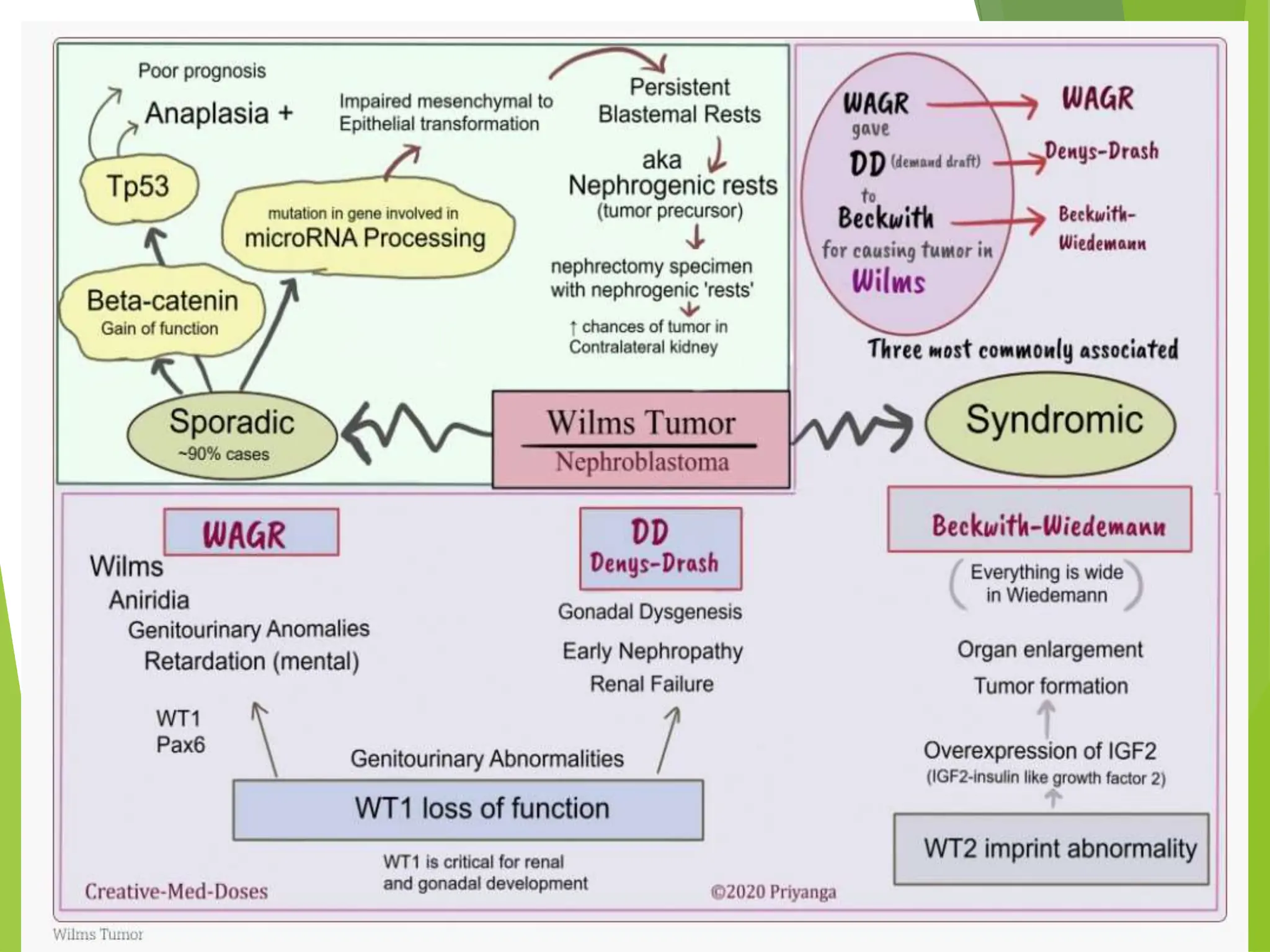
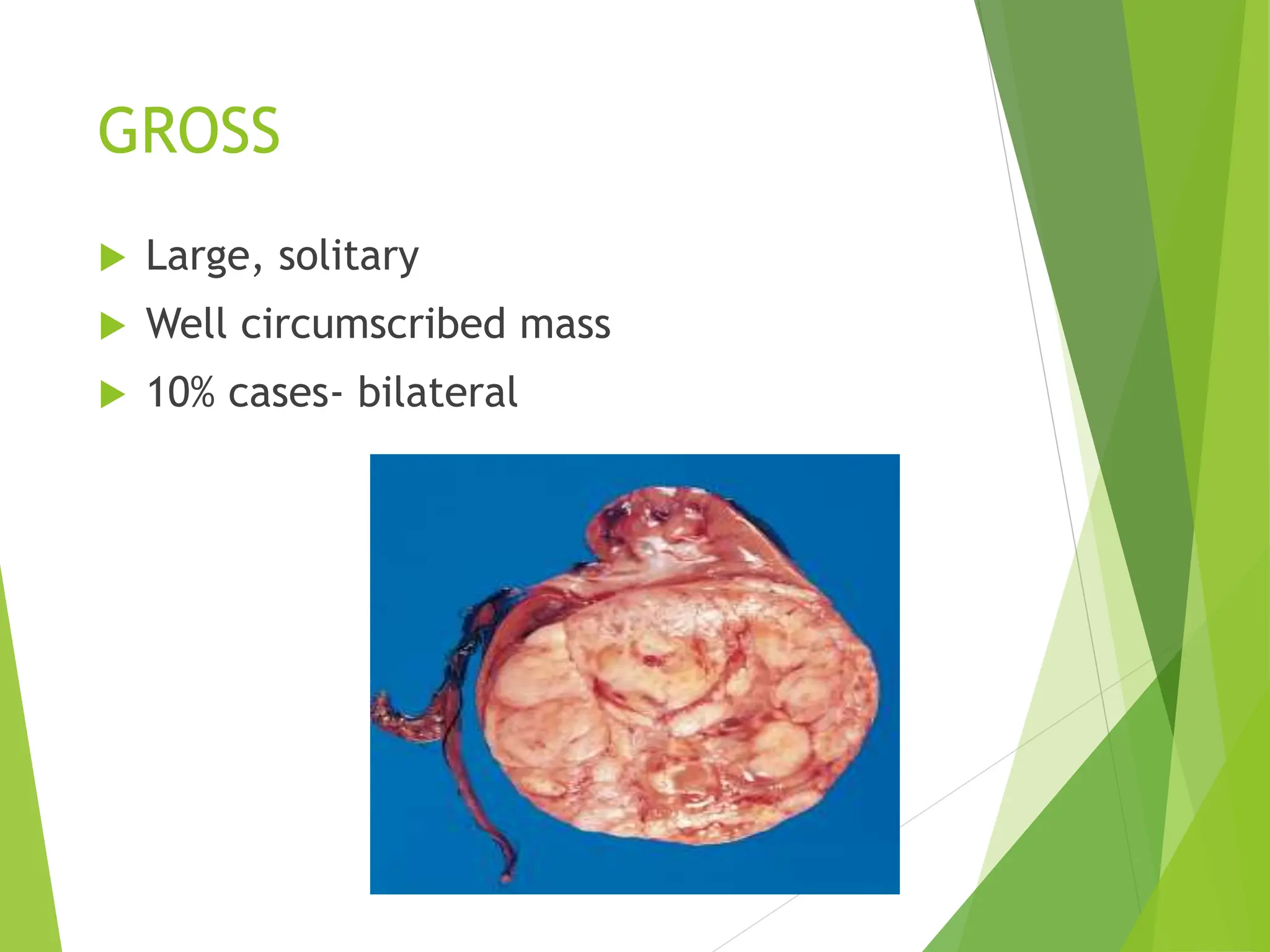
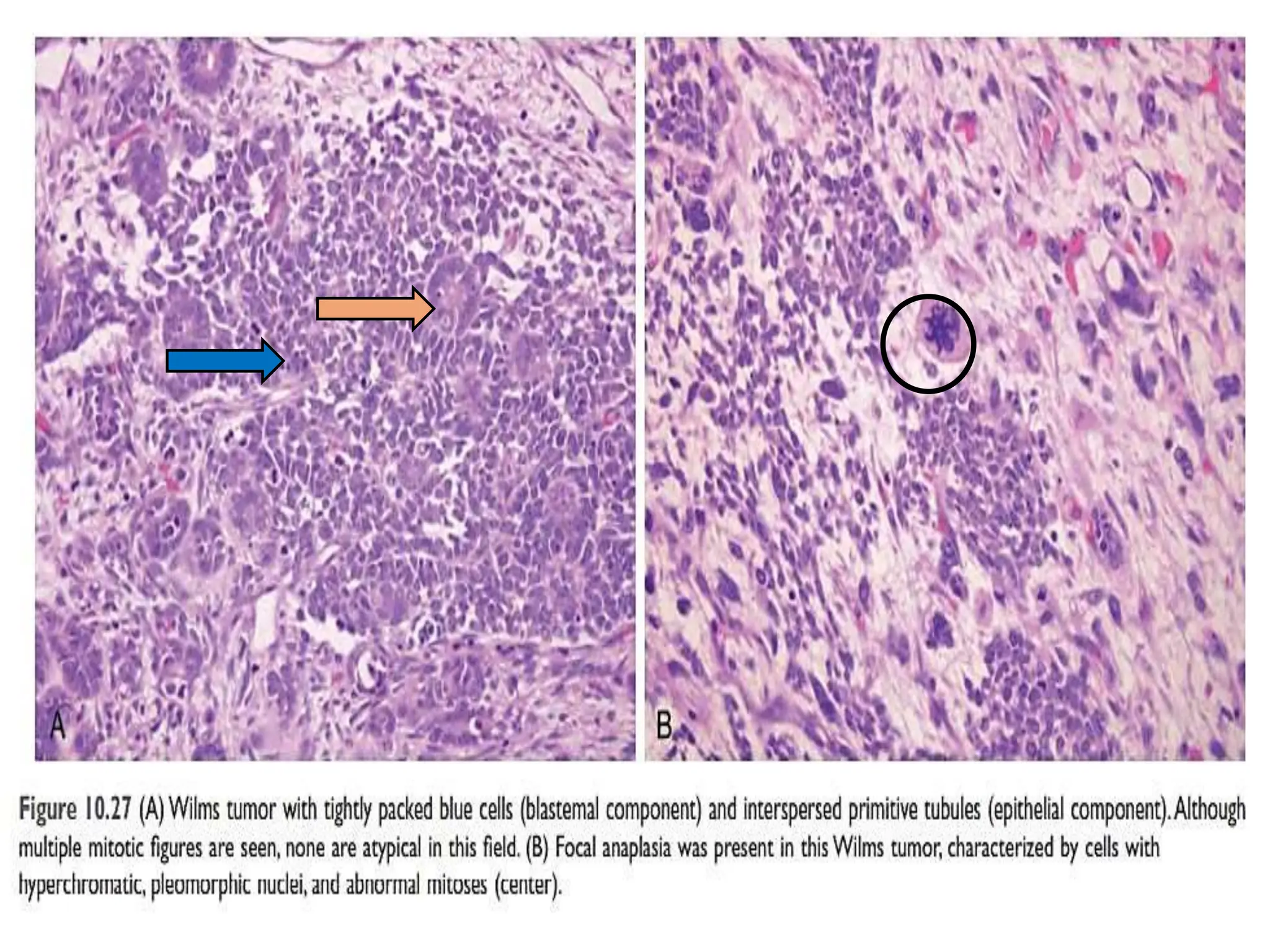
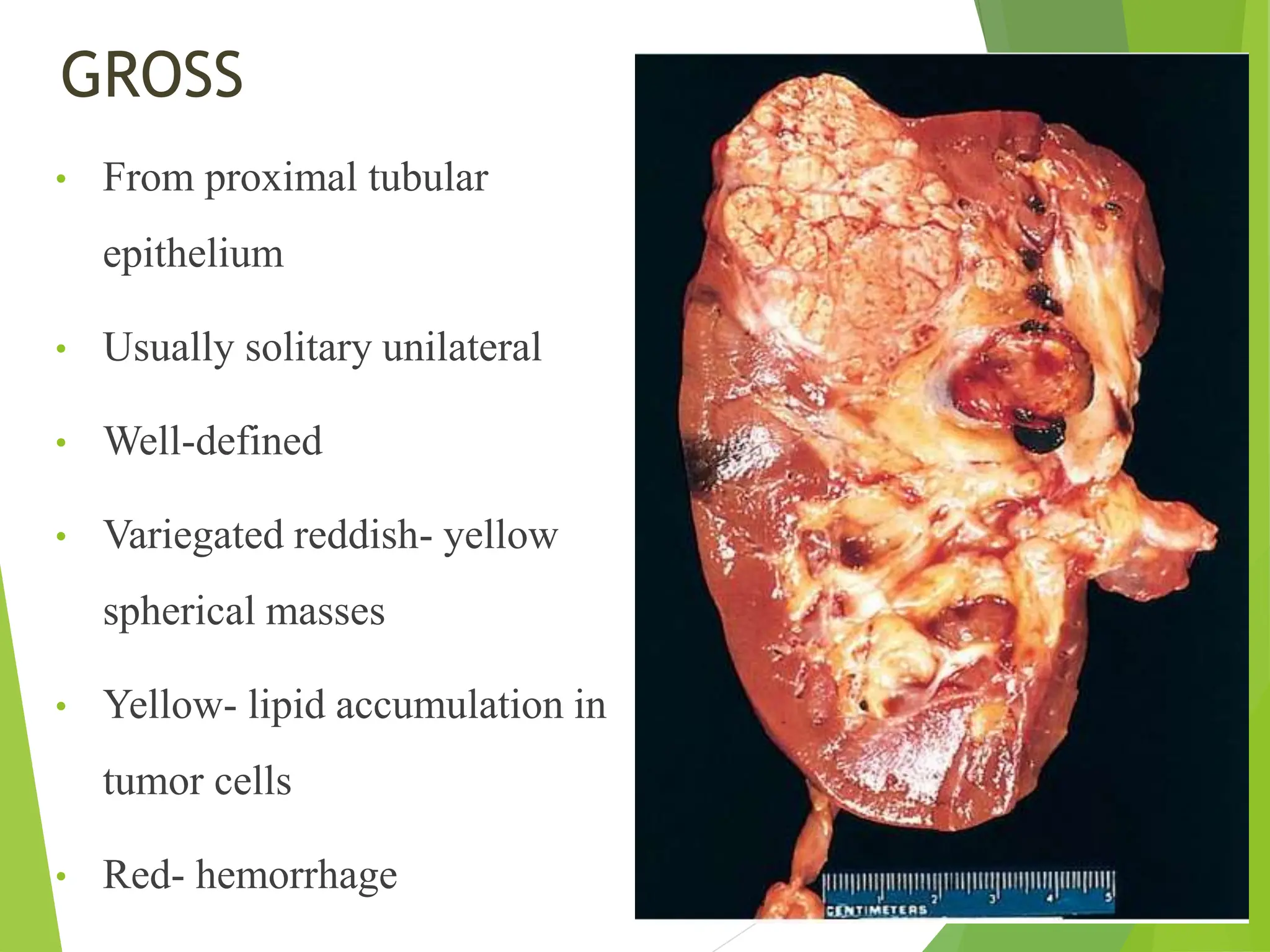
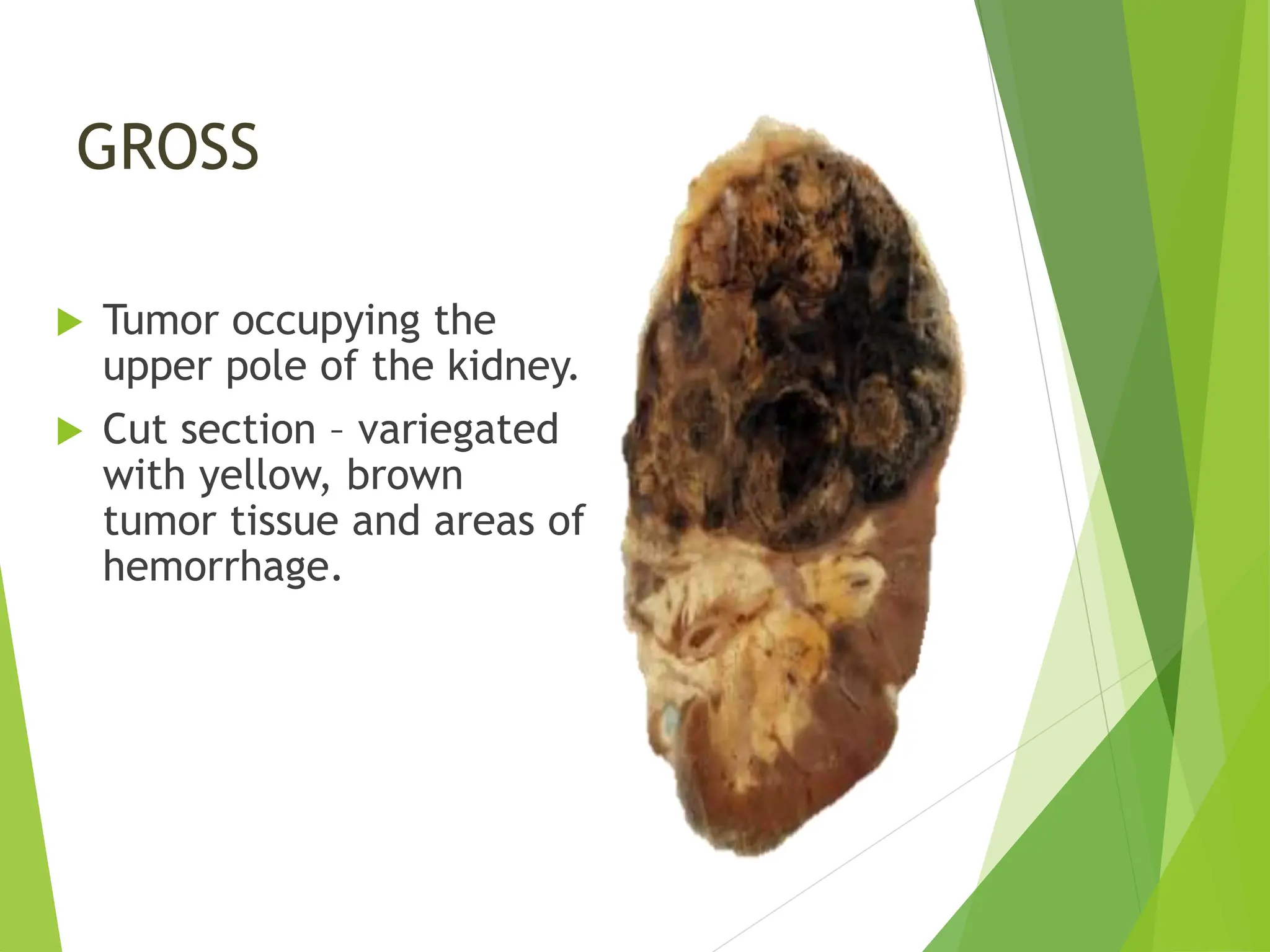
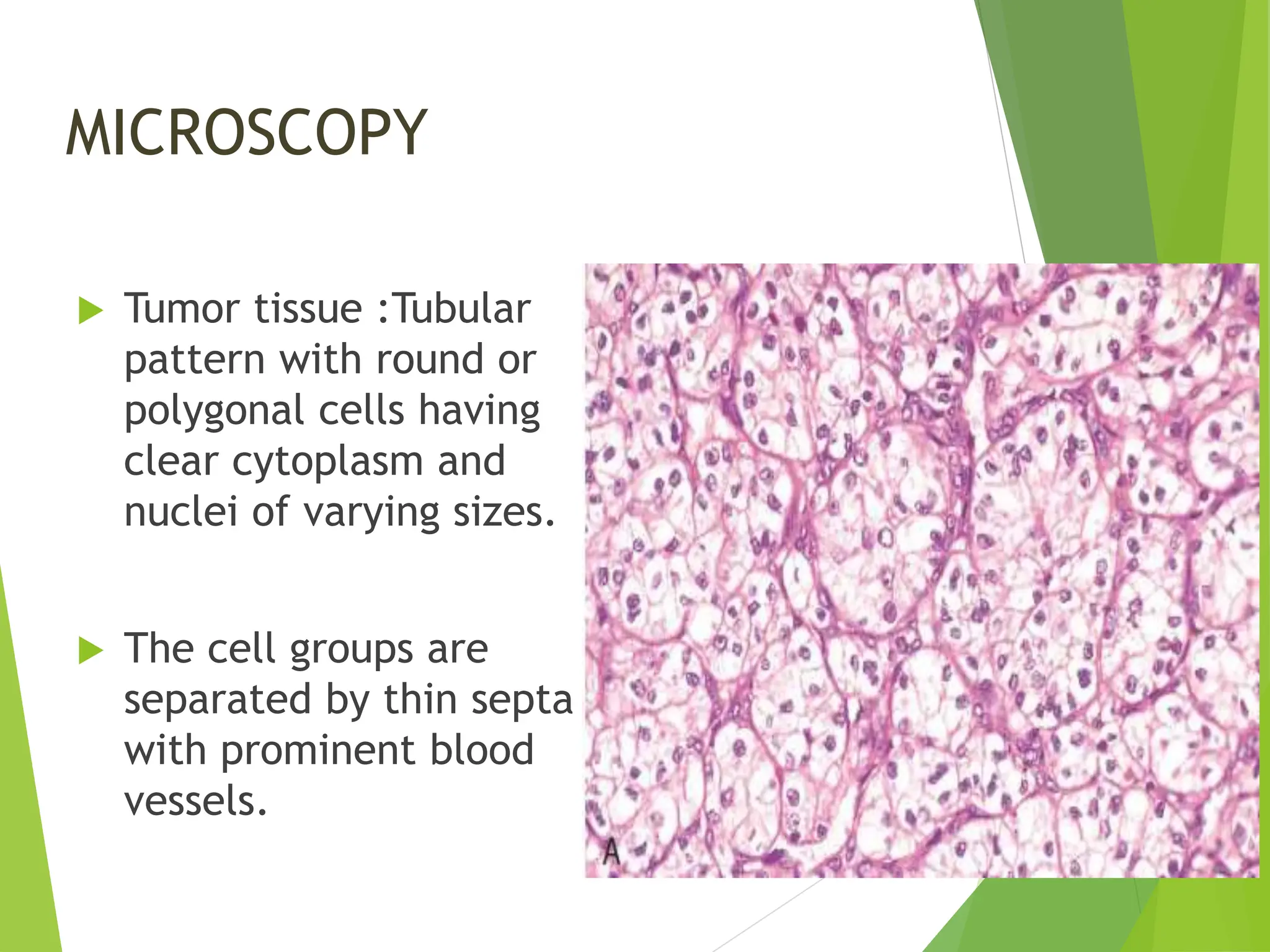
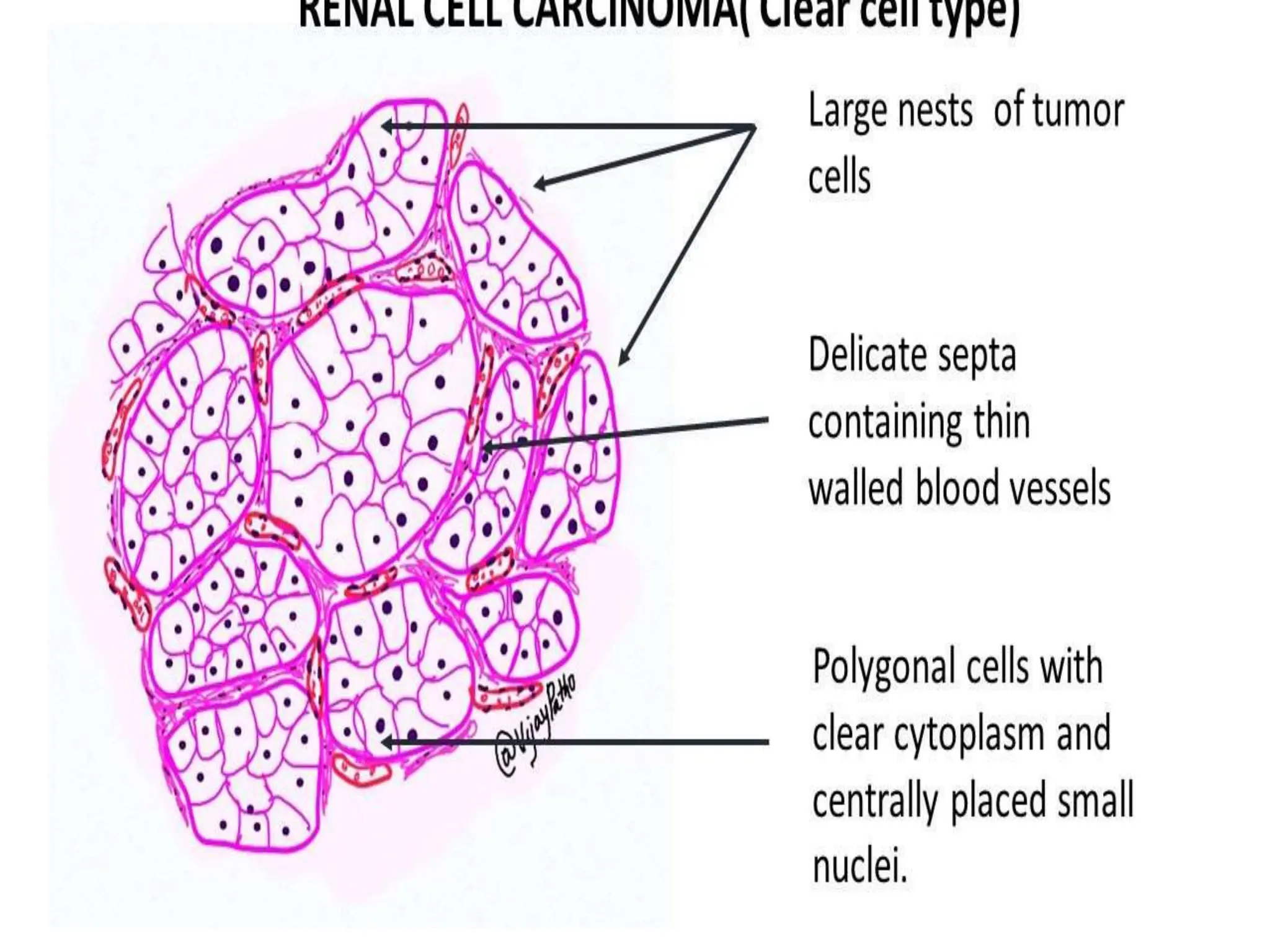
This document discusses renal system objectives, including cystic diseases of the kidney, Wilms tumor, and renal cell carcinoma. It details hereditary and acquired kidney disorders, associated symptoms, complications, and diagnostic characteristics of cystic diseases, as well as the genetic factors and pathology of Wilms tumor and renal cell carcinoma. Additionally, it provides insights into the types and histological features of renal cell carcinoma.