1) The document describes general relativistic simulations of collapsing supermassive stars with and without rotation using a numerical code called Nada.
2) The simulations include effects of gas pressure, radiation, electron-positron pairs, and thermonuclear energy from hydrogen and helium burning.
3) Objects with a mass of around 5×105 solar masses explode if non-rotating with a metallicity over 0.007, while rotation lowers the threshold to 0.001. More massive objects have a higher critical metallicity for explosion.
![Submitted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal
Preprint typeset using L TEX style emulateapj v. 8/13/10
A
RELATIVISTIC COLLAPSE AND EXPLOSION OF ROTATING SUPERMASSIVE STARS WITH
THERMONUCLEAR EFFECTS
Pedro J. Montero1 , Hans-Thomas Janka1 , and Ewald Muller1
¨
(Dated: August 17, 2011)
Submitted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal
ABSTRACT
arXiv:1108.3090v1 [astro-ph.CO] 15 Aug 2011
We present results of general relativistic simulations of collapsing supermassive stars with and
without rotation using the two-dimensional general relativistic numerical code Nada, which solves
the Einstein equations written in the BSSN formalism and the general relativistic hydrodynamics
equations with high resolution shock capturing schemes. These numerical simulations use an equation
of state which includes effects of gas pressure, and in a tabulated form those associated with radiation
and the electron-positron pairs. We also take into account the effect of thermonuclear energy released
by hydrogen and helium burning. We find that objects with a mass of ≈ 5 × 105 M⊙ and an initial
metallicity greater than ZCN O ≈ 0.007 do explode if non-rotating, while the threshold metallicity for
an explosion is reduced to ZCN O ≈ 0.001 for objects uniformly rotating. The critical initial metallicity
for a thermonuclear explosion increases for stars with mass ≈ 106 M⊙ . For those stars that do not
explode we follow the evolution beyond the phase of black hole formation. We compute the neutrino
energy loss rates due to several processes that may be relevant during the gravitational collapse of
these objects. The peak luminosities of neutrinos and antineutrinos of all flavors for models collapsing
to a BH are Lν ∼ 1055 erg/s. The total radiated energy in neutrinos varies between Eν ∼ 1056 ergs
for models collapsing to a BH, and Eν ∼ 1045 − 1046 ergs for models exploding.
Subject headings: Supermassive stars
1. INTRODUCTION massive BHs would form and then grow via merger and
There is large observational evidence of the presence accretion (Haiman & Loeb 2001; Yoo & Miralda-Escud´ e
of supermassive black holes (SMBHs) in the centres of 2004; Alvarez et al. 2009).
most nearby galaxies (Rees 1998). The dynamical evi- Another possible scenario proposes that if sufficient
dence related to the orbital motion of stars in the cluster primordial gas in massive halos, with mass ∼ 108 M⊙ , is
surrounding Sgr A∗ indicates the presence of a SMBH unable to cool below Tvir 104 K, it may lead to the for-
with mass ≈ 4 × 106 M⊙ (Genzel et al. 2000). In addi- mation of a supermassive object (Bromm & Loeb 2003;
tion, the observed correlation between the central black Begelman et al. 2006), which would eventually collapse
hole masses and the stellar velocity dispersion of the to form a SMBH. This route assumes that fragmenta-
bulge of the host galaxies suggests a direct connection tion, which depends on efficient cooling, is suppressed,
between the formation and evolution of galaxies and possibly by the presence of sufficiently strong UV radi-
SMBHs (Kormendy & Gebhardt 2001). ation, that prevents the formation of molecular hydro-
The observation of luminous quasars detected at red- gen in an environment with metallicity smaller than a
shifts higher than 6 in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey given critical value (Santoro & Shull 2006; Omukai et al.
(SDSS) implies that SMBHs with masses ∼ 109 M⊙ , 2008). Furthermore, fragmentation may depend on
which are believed to be the engines of such powerful the turbulence present within the inflow of gas, and
quasars, were formed within the first billion years af- on the mechanism redistributing its angular momen-
ter the Big Bang (e.g. Fan 2006 for a recent review). tum (Begelman & Shlosman 2009). The “bars-within-
However, it is still an open question how SMBH seeds bars” mechanism (Shlosman et al. 1989; Begelman et al.
form and grow to reach such high masses in such a short 2006) is a self-regulating route to redistribute angular
amount of time (Rees 2001). momentum and sustain turbulence such that the inflow
A number of different routes based on stellar dynamical of gas can proceed without fragmenting as it collapses
processes, hydrodynamical processes or a combination of even in a metal-enriched environment.
both have been suggested (e.g. Volonteri 2010 for a re- Depending on the rate and efficiency of the inflow-
cent review). One of the theoretical scenarios for SMBH ing mass, there may be different outcomes. A low
seed formation is the gravitational collapse of the first rate of mass accumulation would favor the formation
generation of stars (Population III stars) with masses of isentropic supermassive stars (SMSs), with mass ≥
M ∼ 100M⊙ that are expected to form in halos with 5 × 104 M⊙ , which then would evolve as equilibrium con-
virial temperature Tvir < 104 K at z ∼ 20 − 50 where figurations dominated by radiation pressure (Iben 1963;
cooling by molecular hydrogen is effective. As a result Hoyle & Fowler 1963; Fowler 1964). A different outcome
of the gravitational collapse of such Pop III stars, very could result if the accumulation of gas is fast enough so
that the outer layers of SMSs are not thermally relaxed
montero@mpa-garching.mpg.de during much of their lifetime, thus having an entropy
1 Max-Planck-Institut f¨ r Astrophysik, Karl-Schwarzschild-
u stratification (Begelman 2009).
Str. 1, D-85748 Garching, Germany; A more exotic mechanism that could eventually lead to](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relativisticcollapseandexplosionofrotatingsupermassivestarswiththermonucleareffects-110828194019-phpapp01/75/Relativistic-collapse-and-explosion-of-rotating-supermassive-stars-with-thermonuclear-effects-1-2048.jpg)


![4 Montero, Janka and M¨ller
u
become unstable when the adiabatic index drops below possible to compute the temperature T by a Newton-
the critical value Raphson algorithm that solves the equation ǫ∗ (ρ, T ) = ǫ
for T ,
4 2GM
Γcrit = + 1.12 . (18)
3 Rc2 ∂ǫ∗ (ρ, T )
−1
This happens when the stabilizing gas contribution to Tn+1 = Tn − (ǫ∗ (ρ, Tn ) − ǫ) , (22)
∂T Tn
the EOS does not raise the adiabatic index above 4/3 to
compensate for the destabilizing effect of general relativ- where n is the iteration counter.
ity expressed by the second term on the righ-hand-side
of Eq. (18). 3.3. Nuclear burning
Rotation can stabilize configurations against the ra- In order to avoid the small time steps, and CPU-time
dial instability. The stability of rotating SMSs with demands connected with the solution of a nuclear reac-
uniform rotation was analyzed by Baumgarte & Shapiro tion network coupled to the hydrodynamic evolution, we
(1999a,b). They found that stars at the onset of the apply an approximate method to take into account the
instability have an equatorial radius R ≈ 640GM/c2, a basic effects of nuclear burning on the dynamics of the
spin parameter q ≡ cJ/GM 2 ≈ 0.97, and a ratio of rota- collapsing SMSs. We compute the nuclear energy re-
tional kinetic energy to the gravitational binding energy lease rates by hydrogen burning (through the pp-chain,
of T /W ≈ 0.009. cold and hot CNO cycles, and their break-out by the rp-
process) and helium burning (through the 3-α reaction)
3.2. Equation of State as a function of rest-mass density, temperature and mass
To close the system of hydrodynamic equations (Eq. 9) fractions of hydrogen X, helium Y and CNO metallicity
we need to define the EOS. We follow a treatment which ZCN O . These nuclear energy generation rates are added
includes separately the baryon contribution on the one as a source term on the right-hand-side of the evolution
hand, and photons and electron-positron pairs contri- equation for the conserved quantity E∗ .
butions, in a tabulated form, on the other hand. The The change rates of the energy density due to nuclear
baryon contribution is given by the analytic expressions reactions, in the fluid frame, expressed in units of [erg
for the pressure and specific internal energy cm−3 s−1 ] are given by:
RρT • pp-chain (Clayton 1983):
Pb = , (19)
µb
2 RρT ∂e
ǫb = , (20) = ρ(2.38 × 106 ρg11 X 2 T6
−0.6666
3 µb ∂t pp
0.3333
where R the universal gas constant, T the temperature, e−33.80/T6 ), (23)
ǫb the baryon specific internal energy, and µb is the mean
molecular weight due to ions, which can be expressed as where T6 = T /106K, and g11 is given by
a function of the mass fractions of hydrogen (X), helium 0.3333
g11 = 1 + 0.0123T6 0.66666
+ 0.0109T6 +
(Y ) and heavier elements (metals) (ZCN O ) as
0.0009T6. (24)
1 Y ZCN O
≈X+ + , (21)
µb 4 A • 3-α (Wiescher et al. 1999):
where A is the average atomic mass of the heavy el- ∂e
ements. We assume that the composition of SMSs (ap- = ρ(5.1 × 108 ρ2 Y 3 T9 e−4.4/T9 ),
−3
(25)
∂t 3α
proximately that of primordial gas) has a mass fraction of
hydrogen X = 0.75 − ZCN O and helium Y = 0.25, where where T9 = T /109K.
the metallity ZCN O = 1 − X − Y is an initial parameter,
typically of the order of ZCN O ∼ 10−3 (see Table 1 de- • Cold-CNO cycle (Shen & Bildsten 2007):
tails). Thus, for the initial compositions that we consider
the mean molecular weight of baryons is µb ≈ 1.23 (i.e.
corresponding to a molecular weight for both ions and ∂e
= 4.4 × 1025 ρ2 XZCN O
electrons of µ ≈ 0.59). ∂t CCN O
Effects associated with photons and the creation of 1/3
−2/3 −15.231/T9
electron-positron pairs are taken into account employ- (T9 e +
ing a tabulated EOS. At temperatures above 109 K, not + 8.3 × 10 −5 −3/2 −3.0057/T9
T9 e ). (26)
all the energy is used to increase the temperature and
pressure, but part of the photon energy is used to create
the rest-mass of the electron-positron pairs. As a result • Hot-CNO cycle (Wiescher et al. 1999):
of pair creation, the adiabatic index of the star decreases,
which means that the stability of the star is reduced. ∂e
Given the specific internal energy, ǫ and rest-mass den- = 4.6 × 1015 ρZCN O . (27)
sity, ρ, as evolved by the hydrodynamic equations, it is ∂t HCN O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relativisticcollapseandexplosionofrotatingsupermassivestarswiththermonucleareffects-110828194019-phpapp01/75/Relativistic-collapse-and-explosion-of-rotating-supermassive-stars-with-thermonuclear-effects-4-2048.jpg)

![6 Montero, Janka and M¨ller
u
TABLE 1
Main properties of the initial models studied. From left to right the columns show: model, gravitational mass, initial
central rest-mass density, Tk /|W |, angular velocity, initial central temperature, metallicity, the fate of the star, radial
kinetic energy after thermal bounce, and total neutrino energy output.
Model M ρc Tk /|W | Ω Tc Initial metallicity Fate ERK Eν
[105 M⊙ ] [10−2 g/cm3 ] [10−5 rad/s] [107 K] [10−3 ] [1056 erg] [erg]
S1.a 5 2.4 0 0 5.8 5 BH ... 3.4 × 1056
S1.b 5 2.4 0 0 5.8 6 BH .. ...
S1.c 5 2.4 0 0 5.8 7 Explosion 5.5 9.4 × 1045
R1.a 5 40 0.0088 2.49 13 0.5 BH ... 5.4 × 1056
R1.b 5 40 0.0088 2.49 13 0.8 BH ... ...
R1.c 5 40 0.0088 2.49 13 1 Explosion 1.0 ...
R1.d 5 40 0.0088 2.49 13 2 Explosion 1.9 8.9 × 1045
S2.a 10 0.23 0 0 2.6 30 BH ... 6.8 × 1056
S2.b 10 0.23 0 0 2.6 50 Explosion 35 8.0 × 1046
R2.a 10 12 0.0087 1.47 9.7 0.5 BH ... 3.1 × 1056
R2.b 10 12 0.0087 1.47 9.7 0.8 BH ... ...
R2.c 10 12 0.0087 1.47 9.7 1.0 BH ... ...
R2.d 10 12 0.0087 1.47 9.7 1.5 Explosion 1.5 2.1 × 1046
M as for the onset of the collapse of a configuration with
L L
given mass and entropy. A list of the different SMSs
M∗ = 4π xdx ρ∗ dz, (29) we have considered is provided in Table 1. Models S1
0 0
and S2 represent a spherically symmetric, nonrotating
L L
SMS with gravitational mass of M = 5 × 105 M⊙ and
eφ ˜ M = 1 × 106 M⊙ , respectively, while models R1 and R2
M = −2 xdx dz −2πEe5φ + R
0 0 8 are uniformly rotating initial models again with masses
of M = 5 × 105 M⊙ and M = 1 × 106 M⊙ , respec-
e5φ ˜ ˜ 2 tively. The rigidly and maximally rotating initial models
− Aij Aij − K 2 , (30)
8 3 R1 and R2 are computed with the Lorene code (URL
http://www.lorene.obspm.fr). We also introduce a per-
where E = nµ nν T µν (nµ being the unit normal to the turbation to trigger the gravitational collapse by reduc-
˜
hypersurface) and R is the scalar curvature associated to ing the pressure overall by ≈ 1.5%.
the conformal metric γij .
˜ In order to determine the threshold metallicity re-
The rotational kinetic energy Tk and the gravitational quired to halt the collapse and produce an explosion we
potential energy W are given by carry out several numerical simulations for each initial
L L model with different values of the initial metallicity. The
Tk = 2π x2 dx ρ∗ uy Ωdz,
ˆ (31) initial metallicities along with the fate of the star are
0 0 given in Table 1.
where Ω is the angular velocity.
6. RESULTS
W = M − (M∗ + Tk + Eint ), (32)
6.1. Collapse to BH vs. Thermonuclear explosion
where the internal energy is computed as First we consider a gravitationally unstable spheri-
L L cally symmetric SMS with a gravitational mass of M =
Eint = 4π xdx ρ∗ ǫdz. (33) 5 × 105 M⊙ (S1.a, S1.b and S1.c), which corresponds to
0 0 a model extensively discussed in Fuller et al. (1986),
and therefore allows for a comparison with the results
In axisymmetry the AH equation becomes a nonlinear presented here. Fuller et al. (1986) found that unstable
ordinary differential equation for the AH shape function,
spherical SMSs with M = 5×105 M⊙ and an initial metal-
h = h(θ) (Shibata 1997; Thornburg 2007). We employ
licity ZCN O = 2 × 10−3 collapse to a BH while models
an AH finder that solves this ODE by a shooting method
with an initial metallicity ZCN O = 5 × 10−3 explode due
using ∂θ h(θ = 0) = 0 and ∂θ h(θ = π/2) = 0 as boundary
to the nuclear energy released by the hot CNO burning.
conditions. We define the mass of the AH as
They also found that the central density and tempera-
A ture at thermal bounce (where the collapse is reversed to
MAH = , (34) an explosion) are ρc,b = 3.16 g/cm3 and Tc,b = 2.6 × 108
16π
K, respectively.
where A is the area of the AH. The left panels in Figure 1 show the time evolution of
the central rest-mass density (upper panel) and central
5. INITIAL MODELS temperature (lower panel) for models S1.a, S1.c, R1.a
The initial SMSs are set up as isentropic objects. All and R1.d, i.e., non-rotating and rotating models with a
models are chosen such that they are gravitationally un- mass of M = 5 × 105 M⊙ . In particular, the solid lines
stable, and therefore their central rest-mass density is represent the time evolution of the central density and
slightly larger than the critical central density required temperature for model S1.c (ZCN O = 7×10−3 ) and R1.d](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relativisticcollapseandexplosionofrotatingsupermassivestarswiththermonucleareffects-110828194019-phpapp01/75/Relativistic-collapse-and-explosion-of-rotating-supermassive-stars-with-thermonuclear-effects-6-2048.jpg)
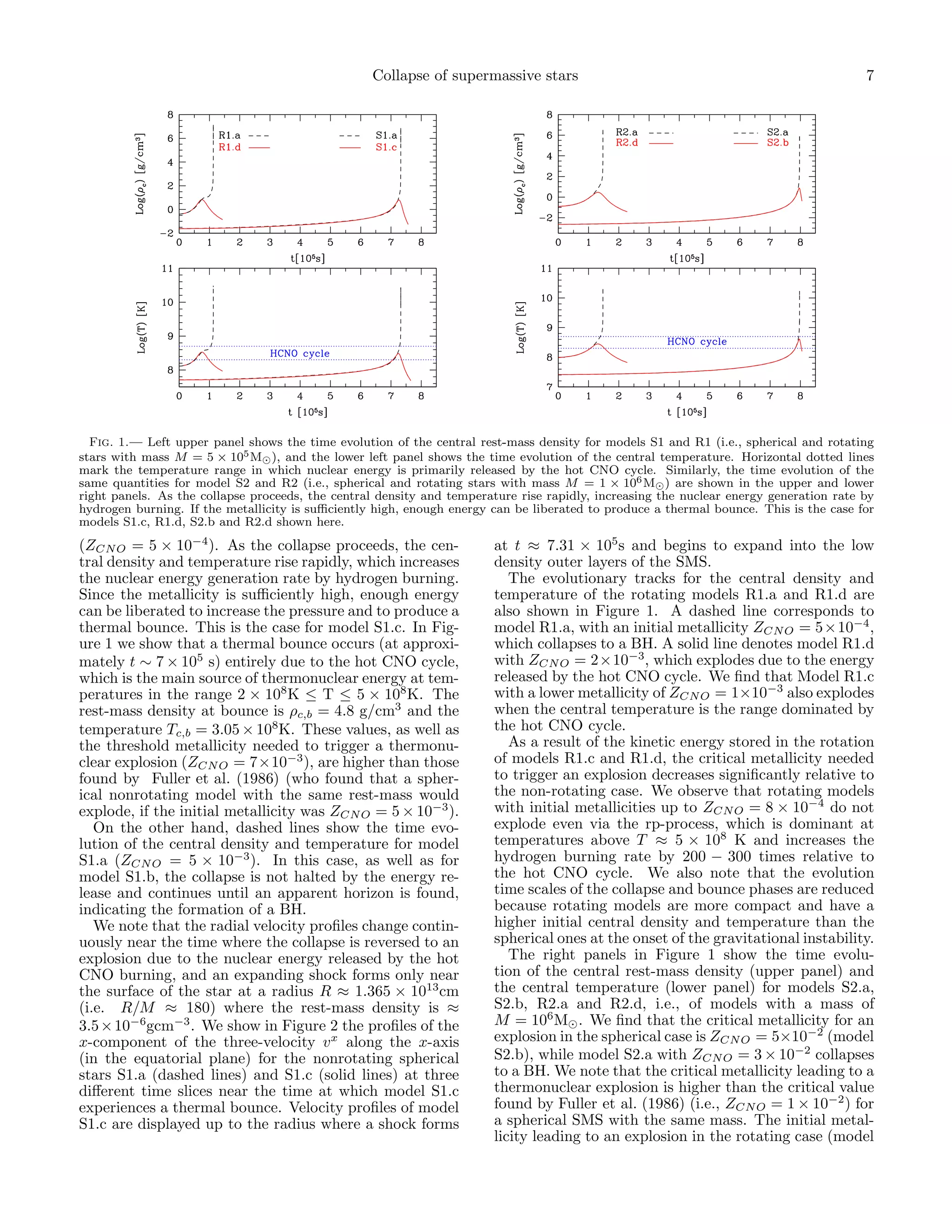
![8 Montero, Janka and M¨ller
u
Fig. 2.— Profiles of the x-component of the three-velocity vx Fig. 3.— Nuclear energy generation rate in erg/s for the explod-
along the x-axis (in the equatorial plane) for the nonrotating spher- ing models (S1.c, R1.d, R1.c, S2.b and R2.d) as a function of time
ical stars S1.a (dashed lines) and S1.c (solid lines) at three different near the bounce. The contribution to the nuclear energy gener-
time slices near the time at which model S1.c experiences a ther- ation is mainly due to hydrogen burning by the hot CNO cycle.
mal bounce. Velocity profiles of model S1.c are displayed up to the The peak values of the energy generation rate at bounce lie be-
radius where takes place the formation of a shock that expands tween ≈ 1051 [erg/s] for the rotating models (R1.d and R2.d), and
into the low density outer layers of the SMS. ≈ 1052 − 1053 [erg/s] for the spherical models (S1.c and S2.b).
R2.d) is more than an order of magnitude smaller than in estimate the photon luminosity produced in association
the spherical case. As for the models with a smaller grav- with the thermonuclear explosion, we make use of the
itational mass, the thermal bounce takes place when the fact that within the diffusion approximation the radia-
physical conditions in the central region of the star allow tion flux is given by
for the release of energy by hydrogen burning through
the hot CNO cycle. Overall, the dynamics of the more c
massive models indicates that the critical initial metal- Fγ = − ∇U, (35)
3κes ρ
licity required to produce an explosion increases with the
rest-mass of the star. where U is the energy density of the radiation, and κes is
Figure 3 shows the total nuclear energy generation rate the opacity due to electron Thompson scattering, which
in erg/s for the exploding models as a function of time is the main source of opacity in SMSs. The photon lumi-
during the late stages of the collapse just before and af- nosity in terms of the temperature gradient and for the
ter bounce. The main contribution to the nuclear energy spherically symmetric case can be written as
generation is due to hydrogen burning by the hot CNO 16πacr2 T 3 ∂T
cycle. The peak values of the energy generation rate Lγ = − , (36)
at bounce lie between several 1051 erg/s for the rotating 3κes ρ ∂r
models (R1.d and R2.d), and ≈ 1052 − 1053 erg/s for the where a is the radiation constant, and c the speed of light.
spherical models (S1.c and S2.b). As expected the max- As can be seen in the last panel of Figure 4 the distribu-
imum nuclear energy generation rate needed to produce tion of matter becomes spherically symmetric during the
an explosion is lower in the rotating models. Moreover, phase of expansion after the thermonuclear explosion. In
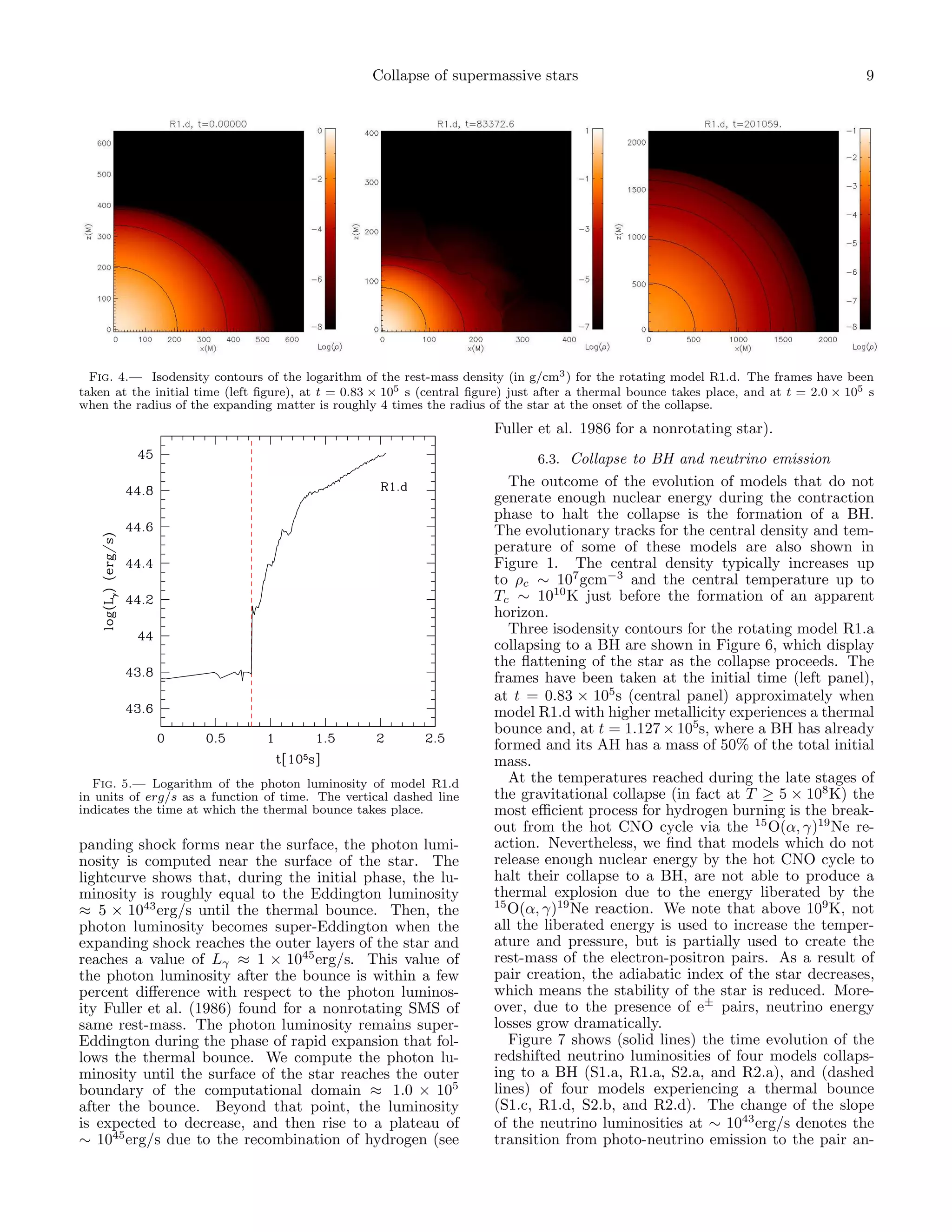
as the explosions are due to the energy release by hy- this figure (Fig. 4) we show the isodensity contours for
drogen burning via the hot CNO cycle, the ejecta would the rotating model R1.d. The frames have been taken at
mostly be composed of 4 He. the initial time (left figure), at t = 0.83 × 105 s (central
As a result of the thermal bounce, the kinetic energy figure) just after the thermal bounce (at t = 0.78 × 105 s),
rises until most of the energy of the explosion is in the and at t = 2.0 × 105 s when the radius of the expanding
form of kinetic energy. We list in the second but last matter is roughly 4 times the radius of the star at the
column of Table 1 the radial kinetic energy after thermal onset of the collapse.
bounce, which ranges between ERK = 1.0 × 1055 ergs for The photon luminosity computed using Eq.(36) for
the rotating star R1.c, and ERK = 3.5 × 1057 ergs for the model R1.d is displayed in Figure 5, where we also in-
spherical star S2.b. dicate with a dashed vertical line the time at which the
thermal bounce takes place. The photon luminosity be-
6.2. Photon luminosity fore the thermal bounce is computed at radii inside the
Due to the lack of resolution at the surface of the star, star unaffected by the local dynamics of the low den-
it becomes difficult to compute accurately the photo- sity outer layers which is caused by the initial pressure
sphere and its effective temperature from the criterion perturbation and by the interaction between the surface
that the optical depth is τ = 2/3. Therefore, in order to of the SMS and the artificial atmosphere. Once the ex-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relativisticcollapseandexplosionofrotatingsupermassivestarswiththermonucleareffects-110828194019-phpapp01/75/Relativistic-collapse-and-explosion-of-rotating-supermassive-stars-with-thermonuclear-effects-8-2048.jpg)
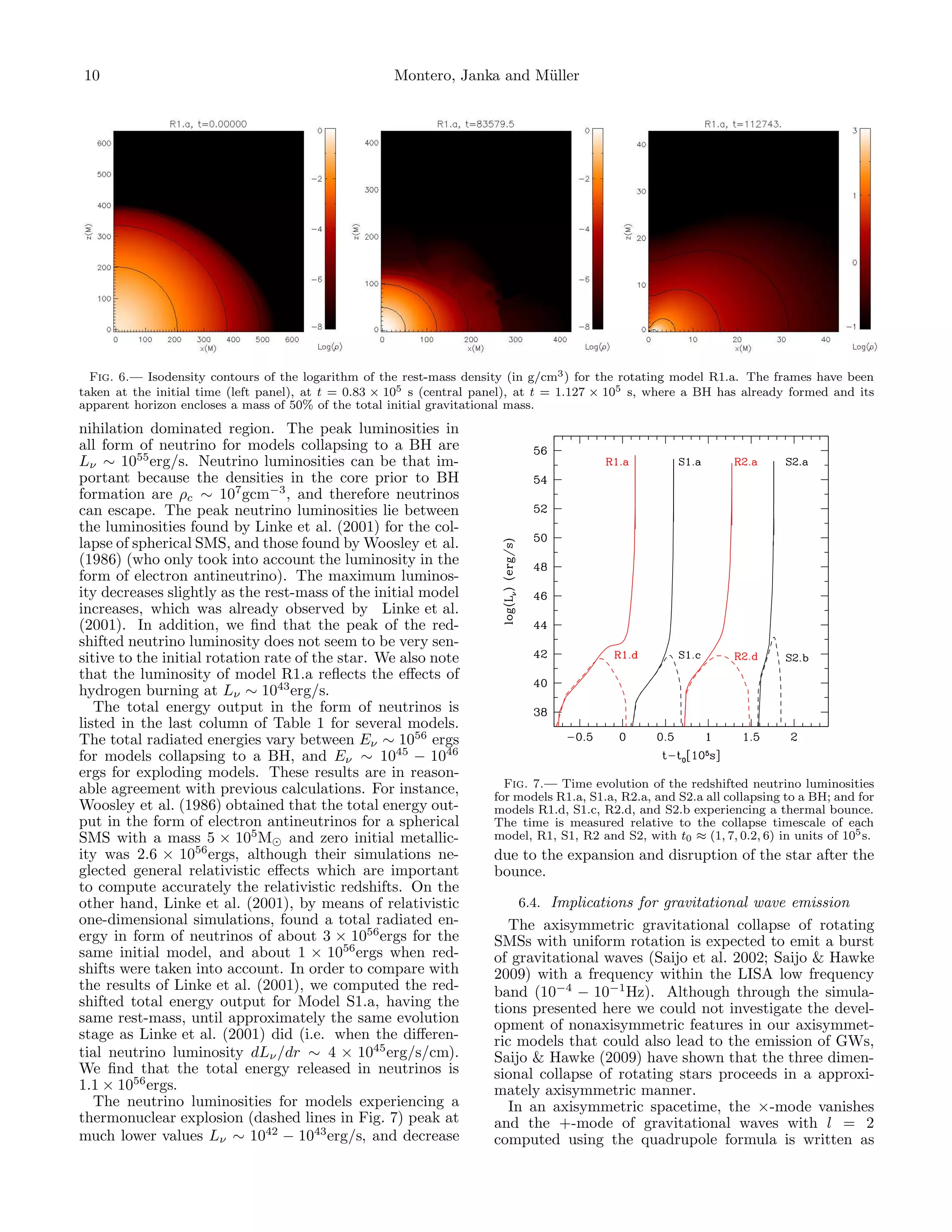
![Collapse of supermassive stars 11
(Shibata & Sekiguchi 2003)
¨ ¨
Ixx (tret ) − Izz (tret )
hquad =
+ sin2 θ, (37)
r
¨
where Iij refers to the second time derivative of the
quadrupole moment. The gravitational wave quadrupole
¨ ¨
amplitude is A2 (t) = Ixx (tret ) − Izz (tret ). Following
Shibata & Sekiguchi (2003) we compute the second time
derivative of the quadrupole moment by finite differenc-
ing the numerical results for the first time derivative of
Iij obtained by
˙
Iij = ρ∗ v i xj + xi v j d3 x. (38)
We calculate the characteristic gravitational wave
strain (Flanagan & Hughes 1998) as
2 G 1 dE(f )
hchar (f ) = , (39)
π c3 D2 df
where D is the distance of the source, and dE(f )/df Fig. 8.— Characteristic gravitational wave strain for model R1.a
the spectral energy density of the gravitational radiation assuming that the source is located at a distance of 50 Gpc, to-
gether with the design noise spectrum h(f ) = f Sh (f ) for LISA
given by detector.
dE(f ) c3 (2πf )2 ˜ 2
= A2 (f ) , (40) development of the nonaxisymmetric Papaloizou-Pringle
df G 16π instability during the evolution of such tori would lead to
with the emission of quasiperiodic GWs with peak amplitude
˜ ∼ 10−18 −10−19 and frequency ∼ 10−3 Hz and maintained
A2 (f ) = A2 (t)e2πif t dt. (41)
during the accretion timescale ∼ 105 s.
We have calculated the quadrupole gravitational wave 6.5. Conclusions
emission for the rotating model R1.a collapsing to a BH.
We plot in Figure 8 the characteristic gravitational wave We have presented results of general relativistic simu-
strain (Eq.39) for this model assuming that the source lations of collapsing supermassive stars using the two-
is located at a distance of 50 Gpc (i.e., z ≈ 11) , to- dimensional general relativistic numerical code Nada,
which solves the Einstein equations written in the BSSN
gether with the design noise spectrum h(f ) = f Sh (f )
formalism and the general relativistic hydrodynamic
of the LISA detector (Larson et al. 2000). We find that,
equations with high resolution shock capturing schemes.
in agreement with Saijo et al. (2002), Saijo & Hawke
These numerical simulations have used an EOS that in-
(2009) and Fryer & New (2011), the burst of gravita-
cludes the effects of gas pressure, and tabulated those
tional waves due to the collapse of a rotating SMS could
associated with radiation pressure and electron-positron
be detected at a distance of 50 Gpc and at a frequency
pairs. We have also taken into account the effects of
which approximately takes the form (Saijo et al. 2002)
thermonuclear energy release by hydrogen and helium
burning. In particular, we have investigated the effects
3/2 of hydrogen burning by the β-limited hot CNO cycle and
106 M⊙ 5M
fburst ∼ 3 × 10−3 [Hz], (42) its breakout via the 15 O(α, γ)19 Ne reaction (rp-process)
M R
on the gravitational collapse of nonrotating and rotating
where R/M is a characteristic mean radius during black SMSs with non-zero metallicity.
hole formation (typically set to R/M = 5). We have found that objects with a mass of ≈ 5×105M⊙
Furthermore, Kiuchi et al. (2011) have recently in- and an initial metallicity greater than ZCN O ≈ 0.007
vestigated, by means of three-dimensional general explode if non-rotating, while the threshold metallicity
relativistic numerical simulations of equilibrium tori for an explosion is reduced to ZCN O ≈ 0.001 for ob-
orbiting BHs, the development of the nonaxisym- jects which are uniformly rotating. The critical initial
metric Papaloizou-Pringle instability in such systems metallicity for a thermal explosion increases for stars
(Papaloizou & Pringle 1984), and have found that a non- with a mass of ≈ 106 M⊙ . The most important con-
axisymmetric instability associated with the m = 1 mode tribution to the nuclear energy generation is due to the
grows for a wide range of self-gravitating tori orbiting hot CNO cycle. The peak values of the nuclear energy
BHs, leading to the emission of quasiperiodic GWs. In generation rate at bounce range from ∼ 1051 erg/s for ro-
particular, Kiuchi et al. (2011) have pointed out that tating models (R1.d and R2.d), to ∼ 1052 − 1053 erg/s
the emission of quasiperiodic GWs from the torus result- for spherical models (S1.c and S2.b). After the ther-
ing after the formation of a SMBH via the collapse of a mal bounce, the radial kinetic energy of the explosion
SMS could be well above the noise sensitivity curve of rises until most of the energy is kinetic, with values
LISA for sources located at a distance of 10Gpc. The ranging from EK ∼ 1056 ergs for rotating stars, to up](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relativisticcollapseandexplosionofrotatingsupermassivestarswiththermonucleareffects-110828194019-phpapp01/75/Relativistic-collapse-and-explosion-of-rotating-supermassive-stars-with-thermonuclear-effects-11-2048.jpg)
