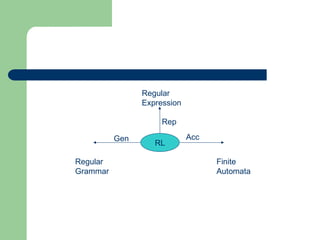
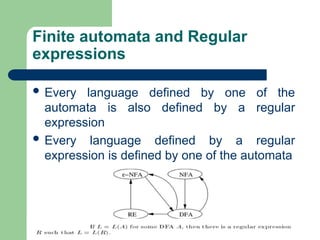
The document explains the relationship between regular expressions, finite automata, and regular grammars. It outlines how to construct non-deterministic finite automata (NFA) and deterministic finite automata (DFA) from regular expressions, and illustrates various examples of regular expressions over a binary alphabet. Additionally, it details the identities and precedence of regular expression operators.