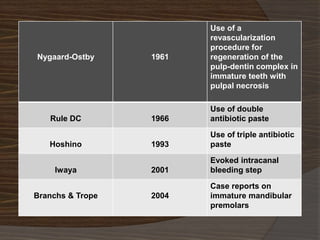
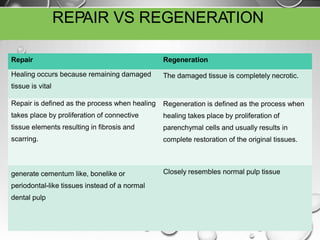
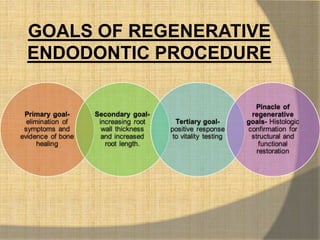
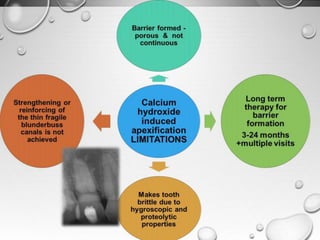
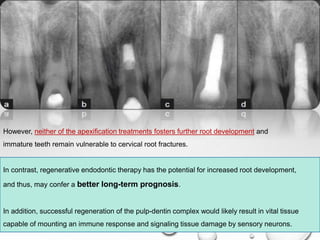
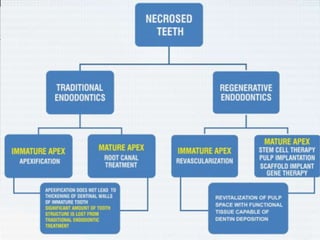
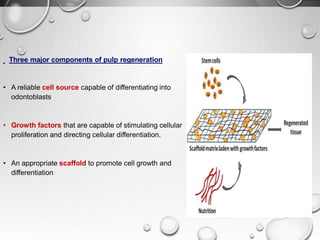
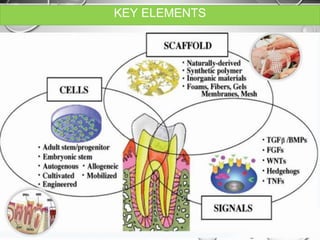
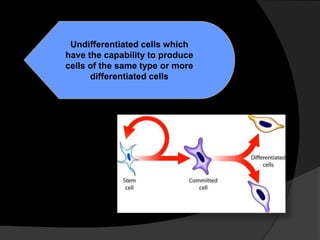
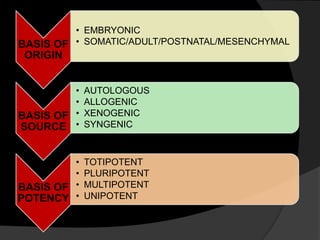
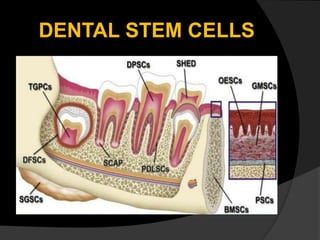
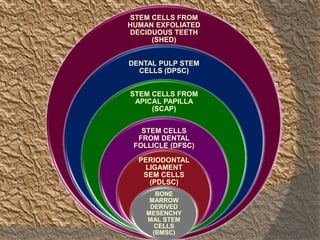
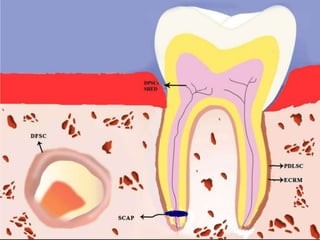
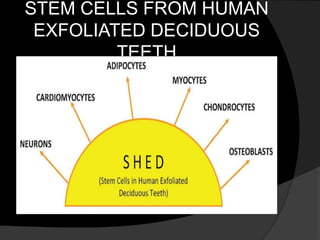
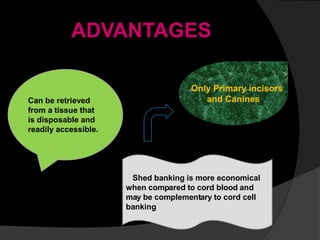
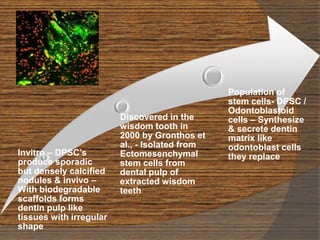
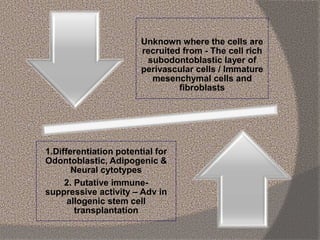
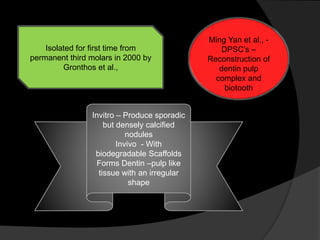
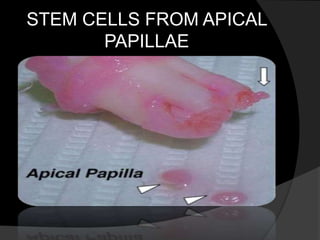
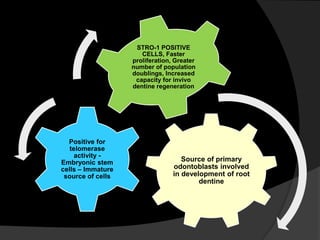
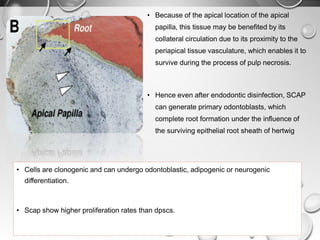
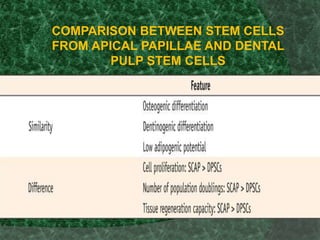
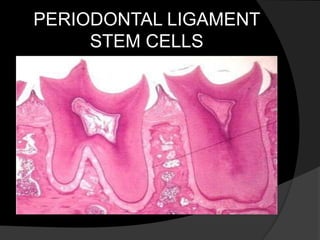
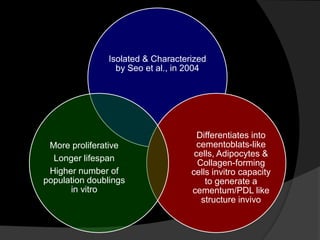
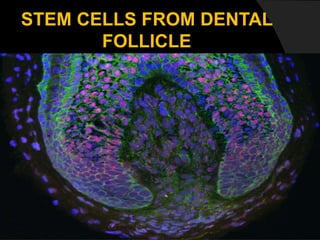
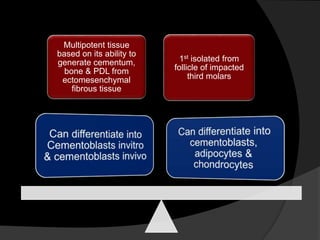
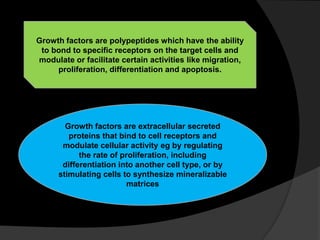
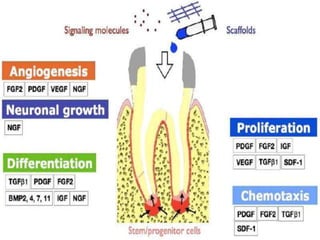
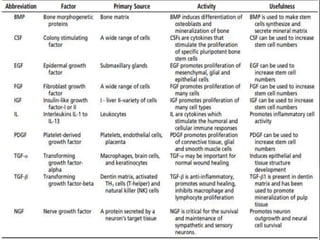
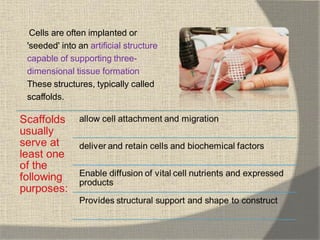
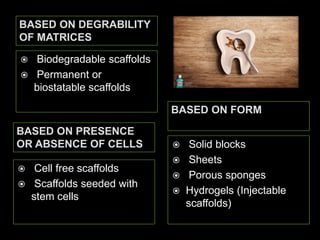
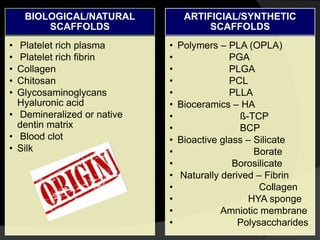
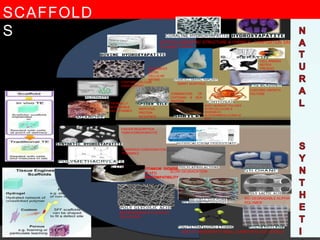
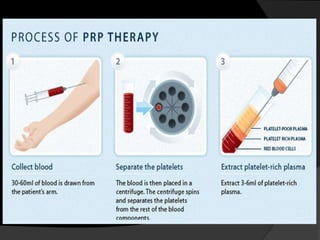
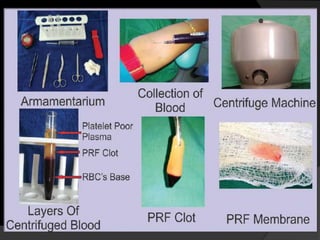
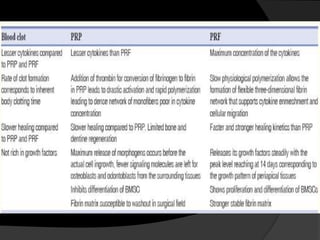
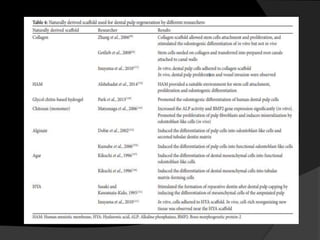
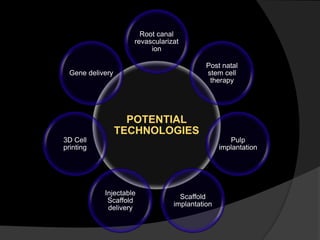
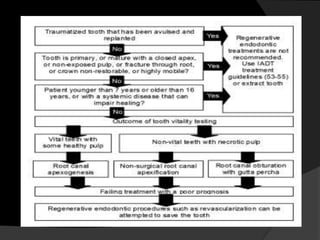
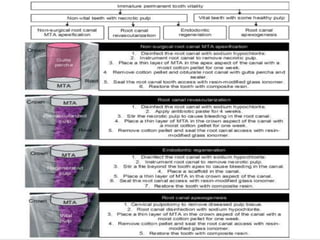
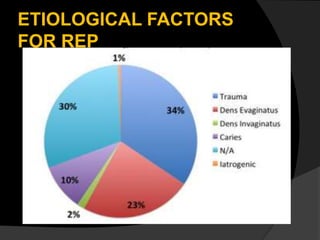
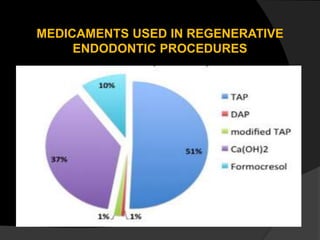
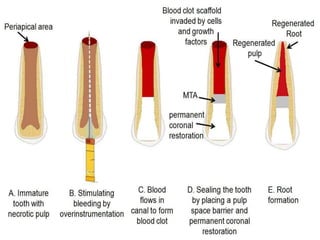
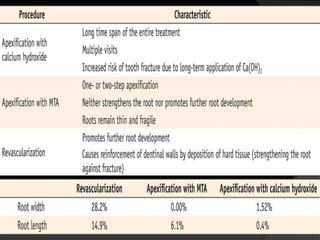
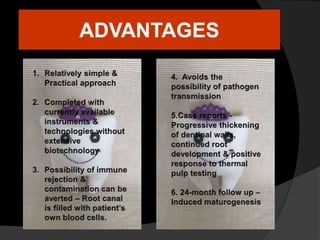
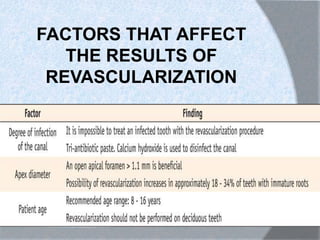
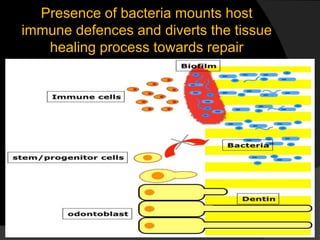
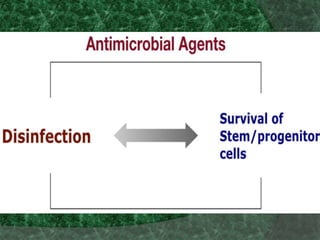
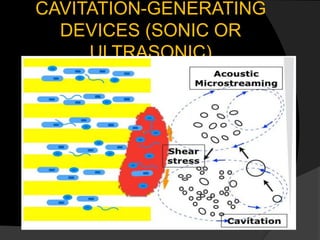
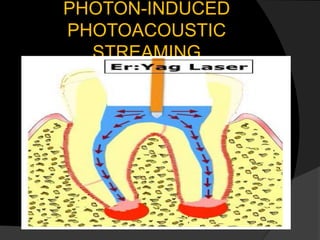
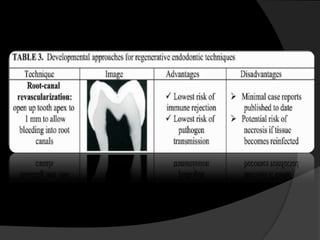
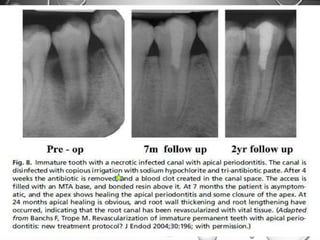
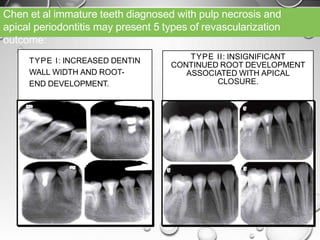
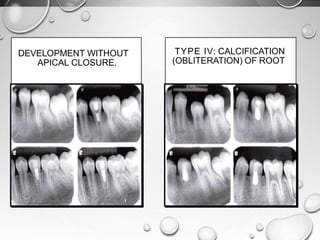
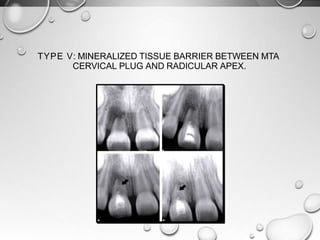
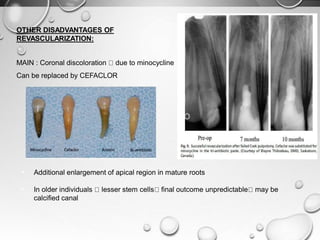
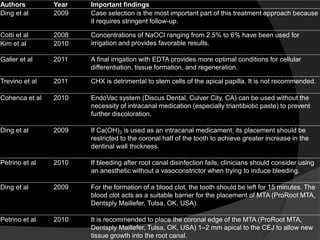
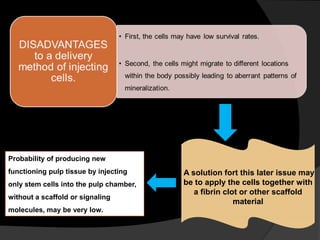
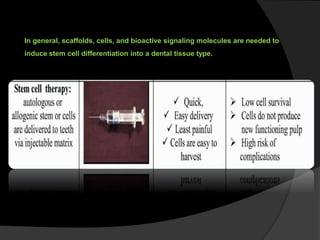
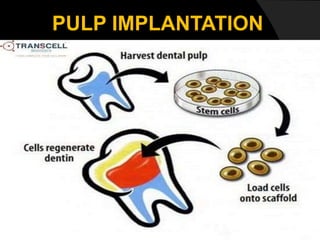
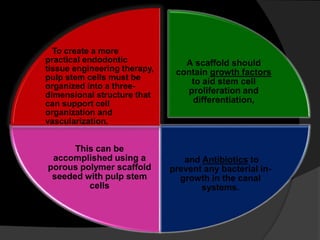
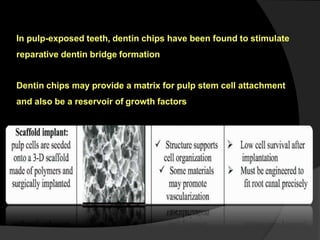
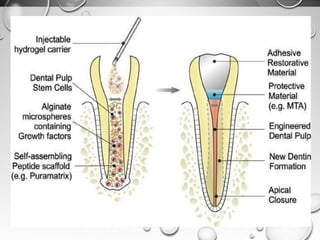
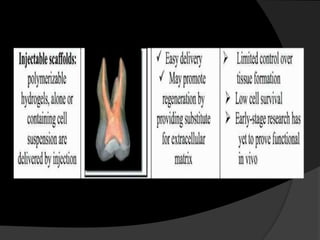
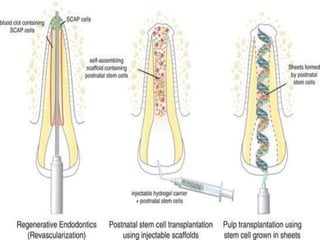
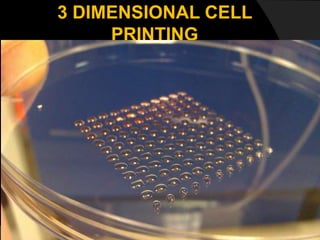
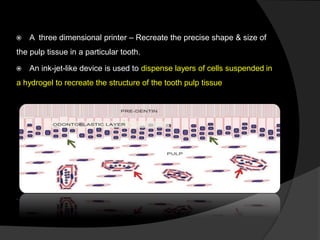
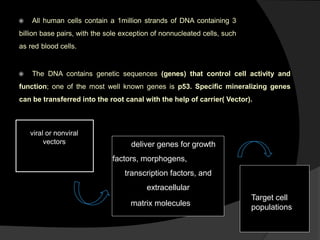
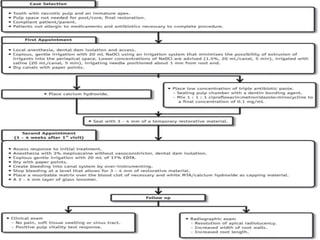
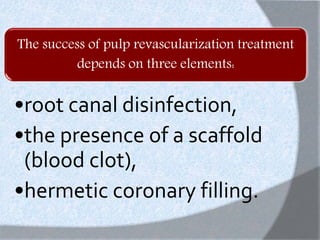
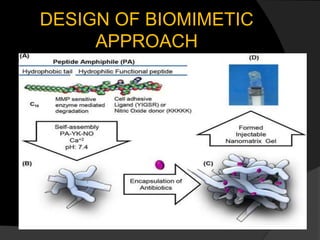
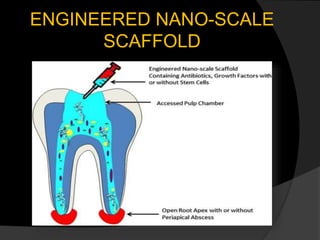
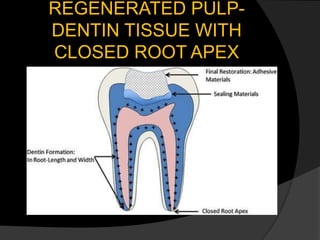
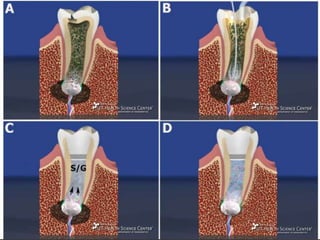
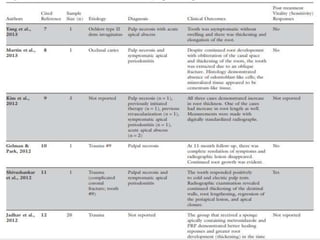
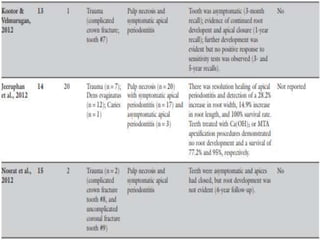
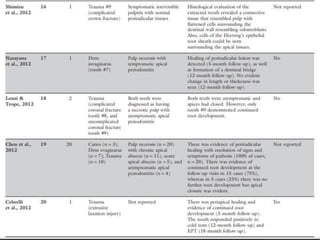
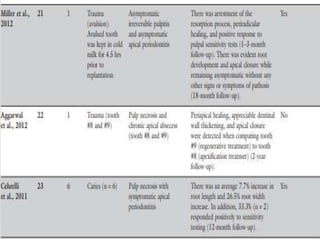
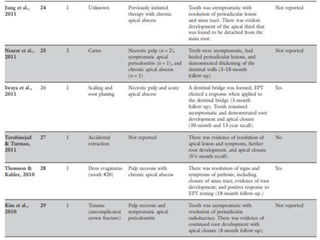
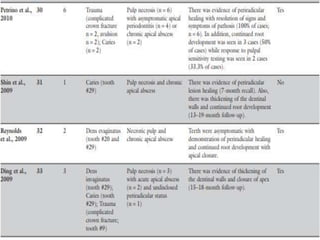
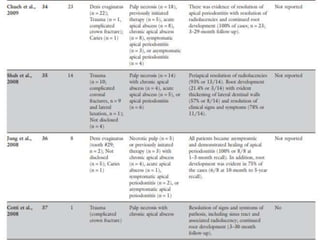
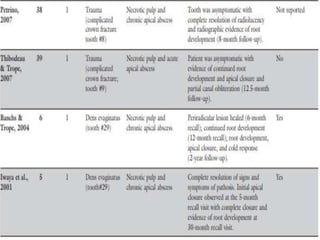
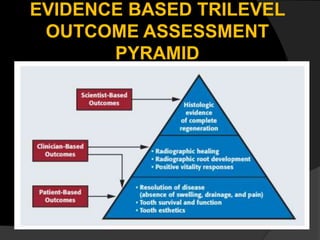
The document discusses regenerative endodontics, which involves biologically based procedures aimed at replacing damaged dental tissues, particularly the pulp-dentin complex. It highlights the importance of stem cells, growth factors, and scaffolds in tissue engineering, along with historical advancements in regenerative techniques. The document also examines the challenges and advantages of using regenerative endodontic therapy compared to traditional root canal treatments.