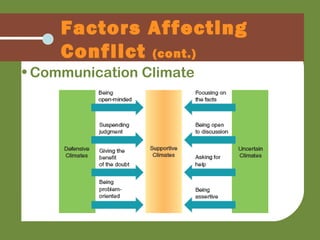
This chapter discusses managing conflict in relationships. It identifies factors that can lead to productive or unproductive conflict, such as inaccurate perceptions, incompatible goals, or provocation. Conflict triggers include aggression, identity threats, or lack of fairness. How people handle conflict is influenced by power dynamics, culture, gender differences, communication channels, and anonymity online. Strategies for managing conflict include escapist, challenging, or cooperative approaches. Outcomes can include compromise, win-win resolutions where both sides' goals are met, lose-lose where neither side wins, separation, or allocating decision-making power.