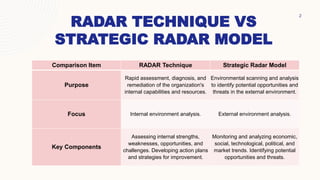
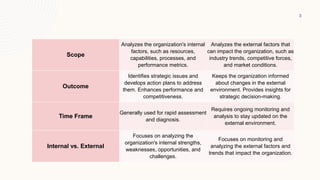
The document compares the RADAR technique and the Strategic RADAR Model. The RADAR technique focuses on internal analysis to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges. It develops action plans to address strategic issues and enhance performance. The Strategic RADAR Model focuses on external environmental scanning and analysis to identify opportunities and threats. It monitors trends in 8 sectors - customers, competitors, economy, technology, society, politics, law, and geophysics - to inform strategic decision making.