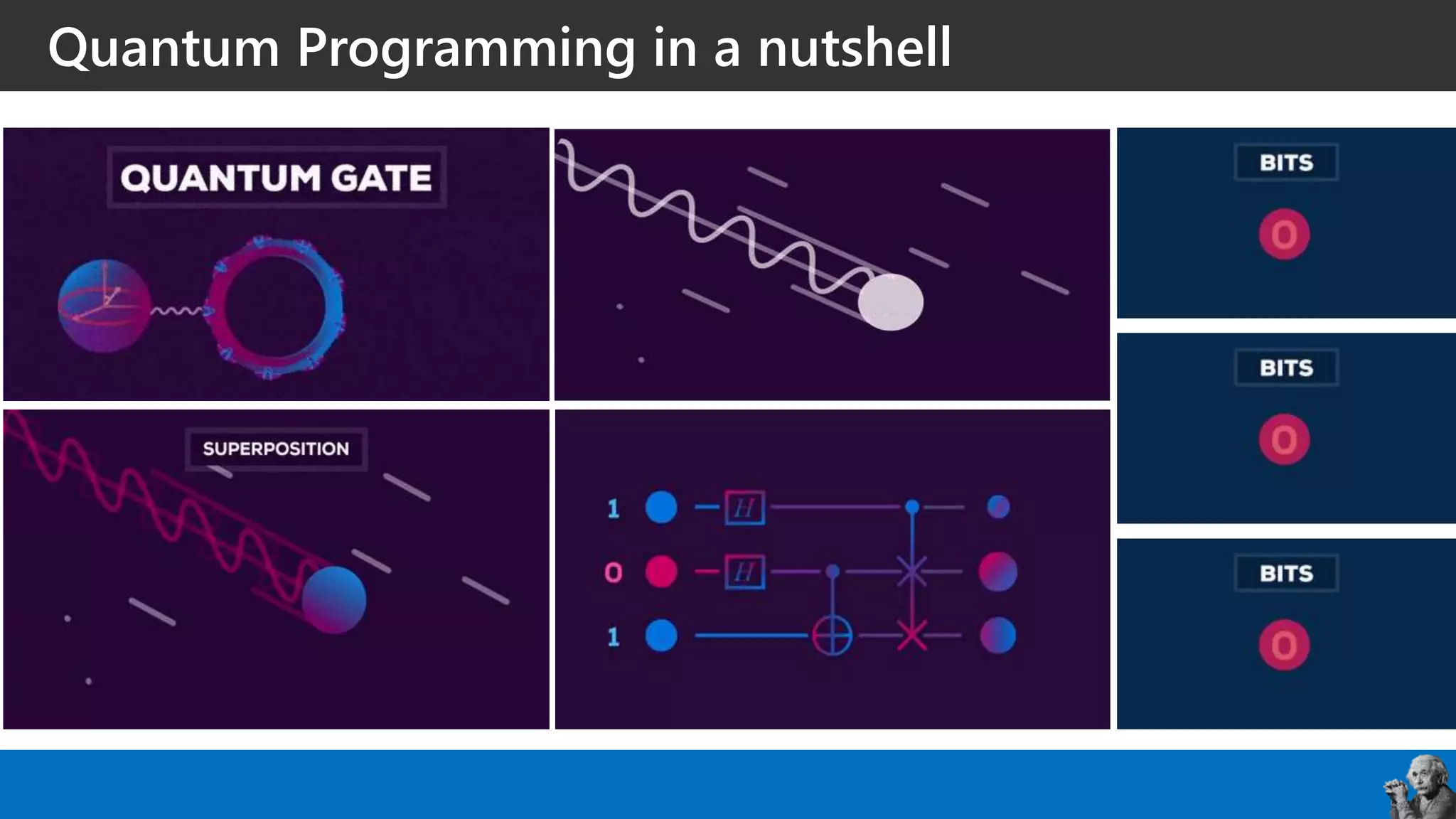
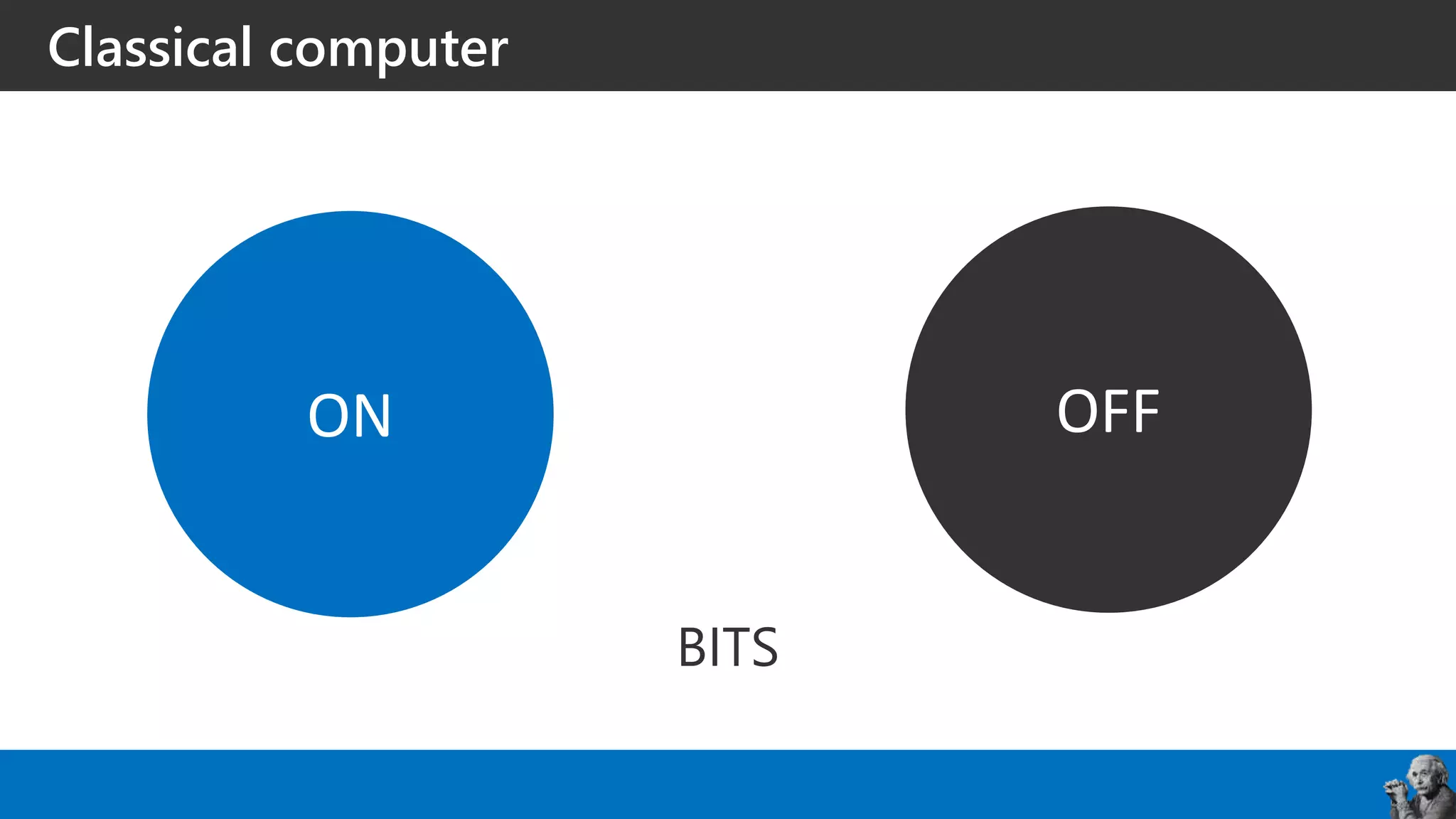
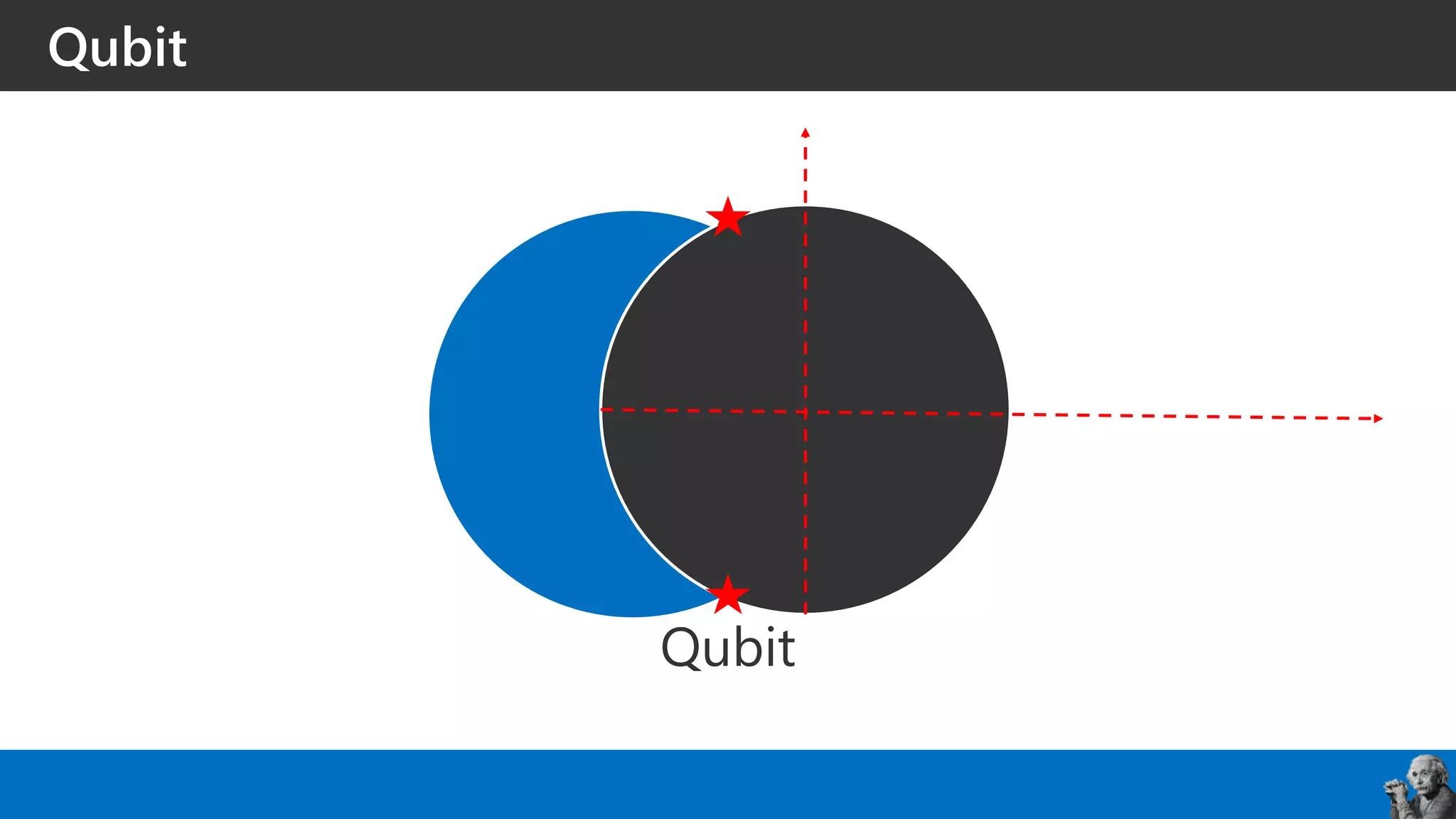
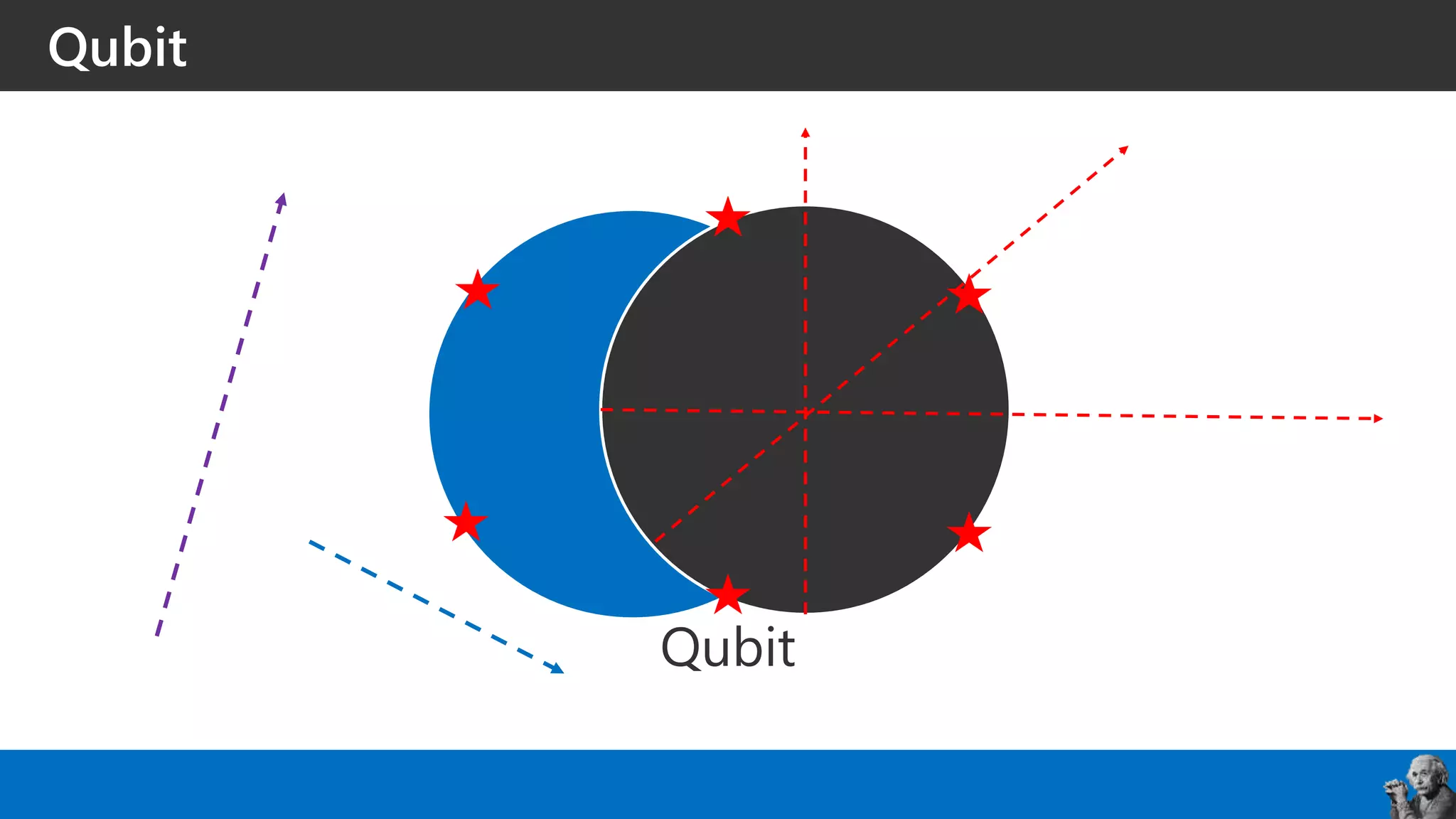
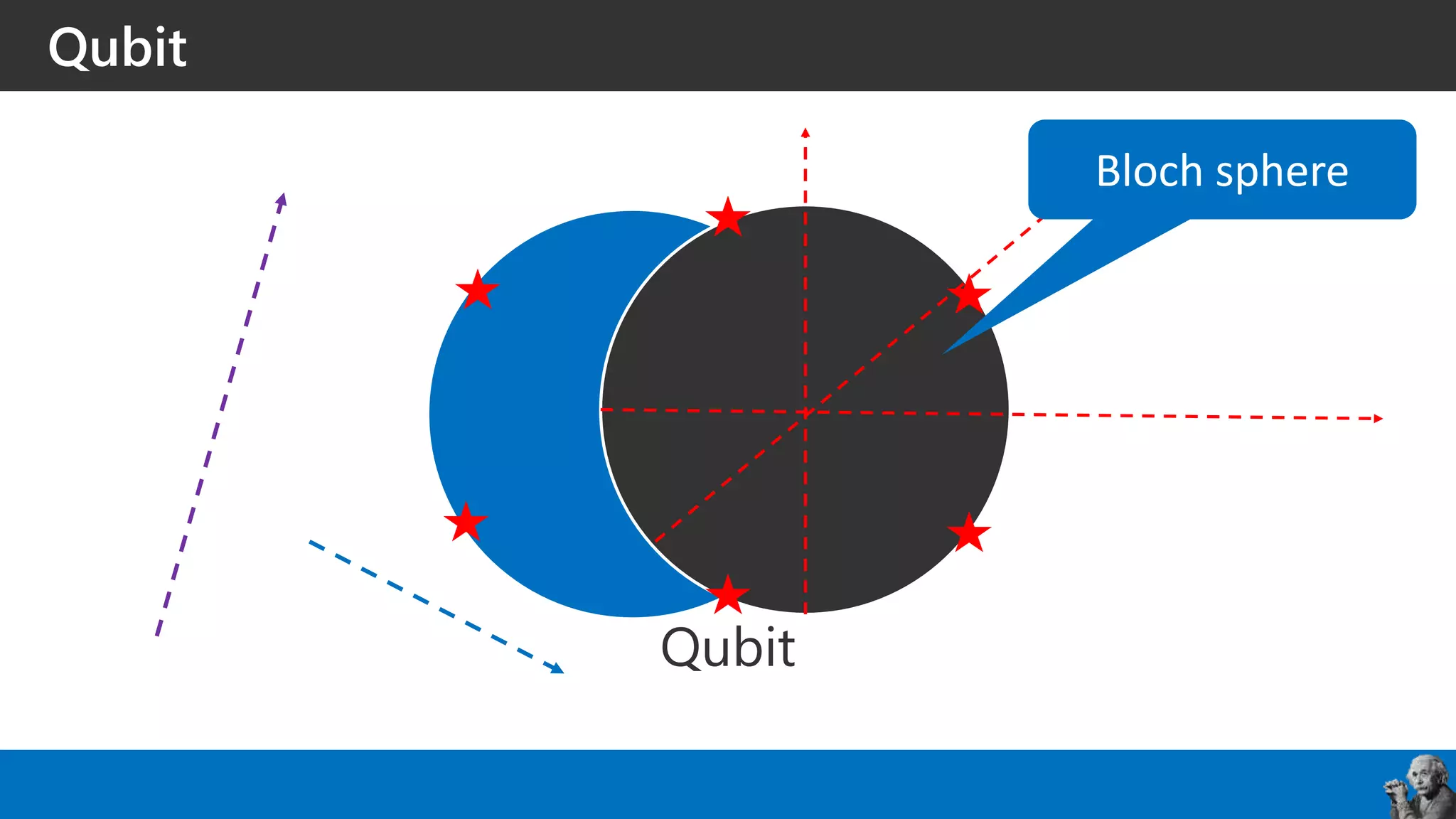
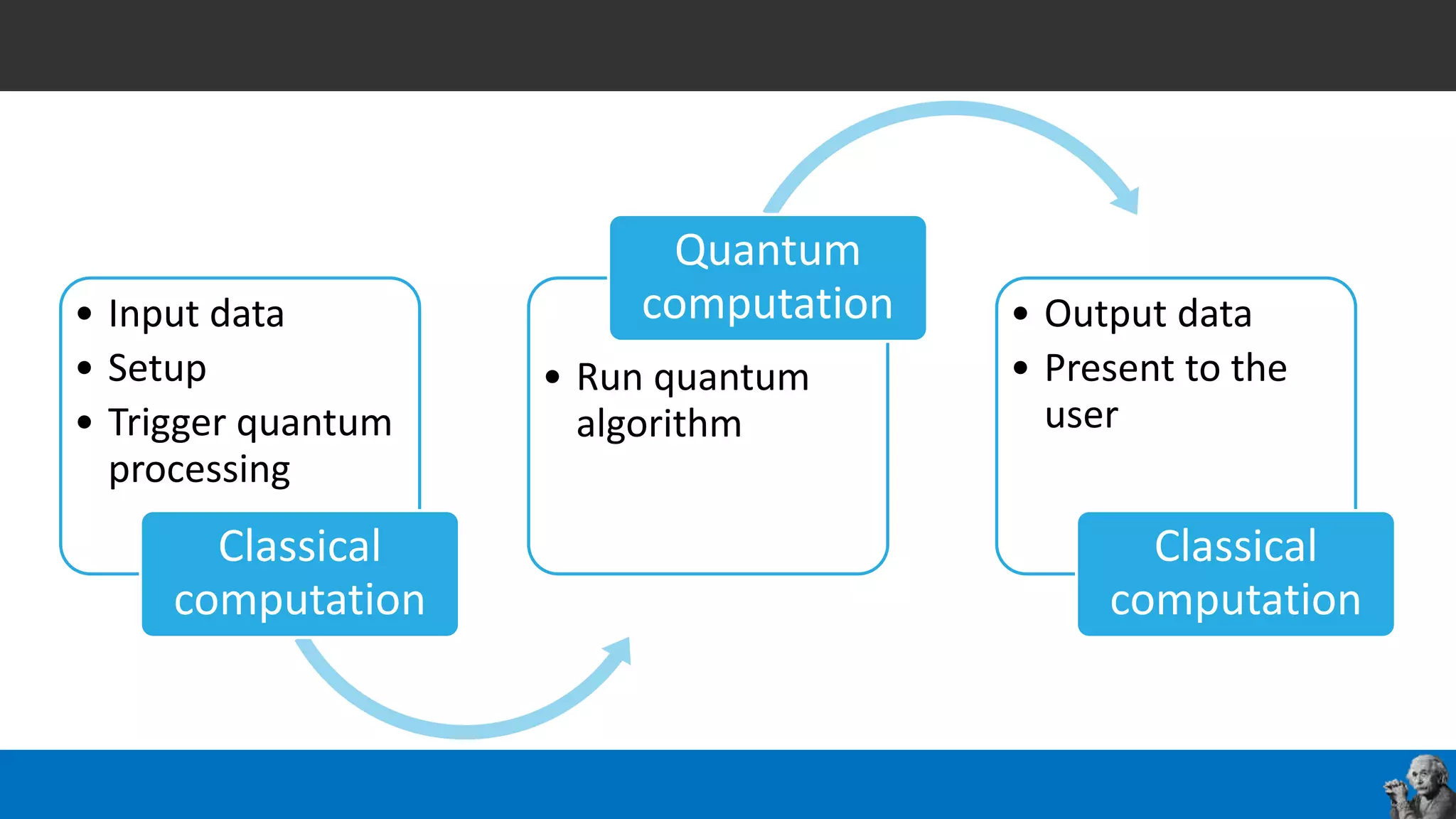
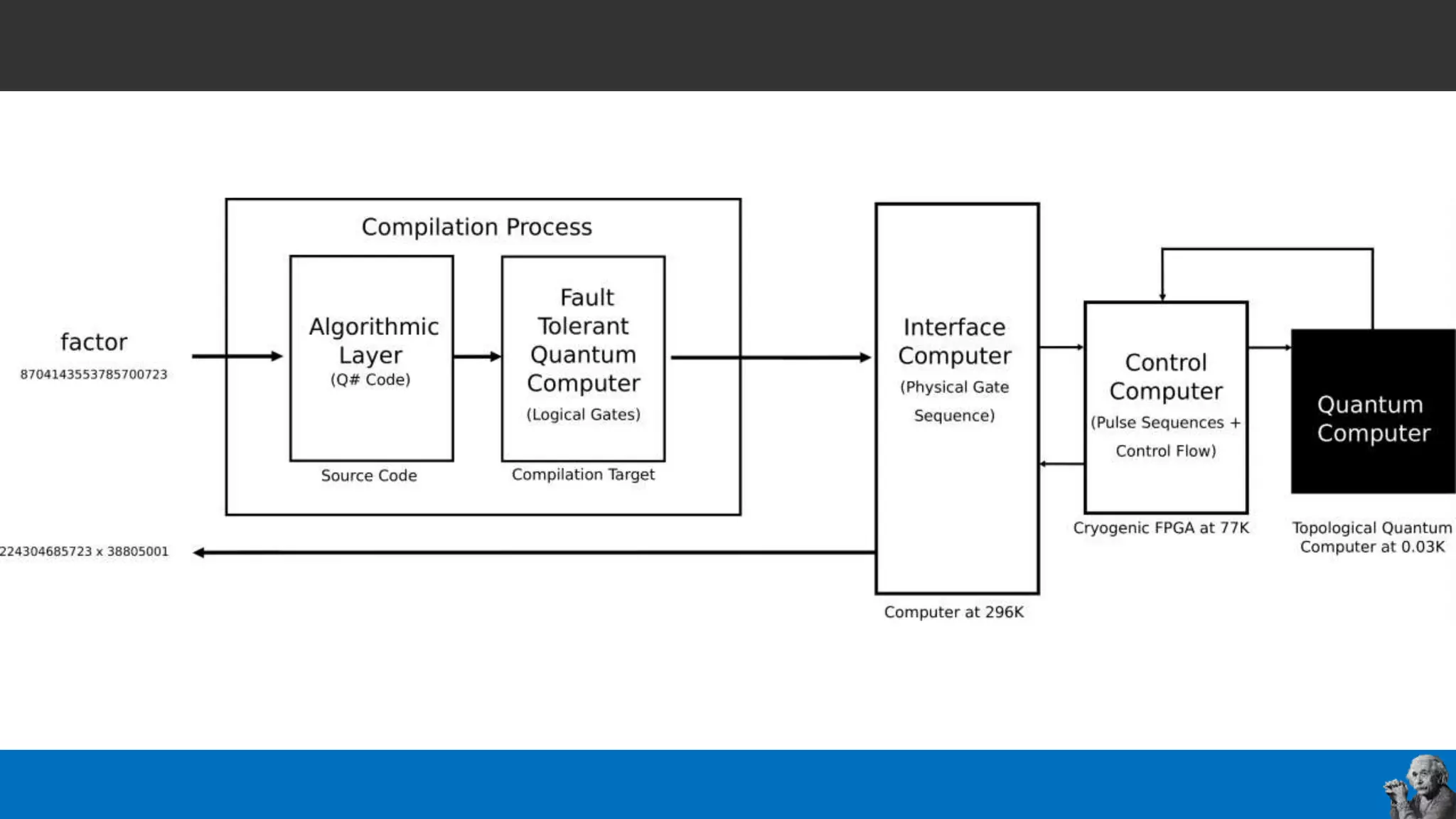
The document covers the fundamentals of quantum programming, highlighting its reliance on vectors, probabilities, and superpositions in contrast to classical programming. It introduces key concepts like qubits, quantum gates, and the potential applications of quantum computing in fields such as AI and machine learning. Additionally, it discusses the current state of quantum technology and specific programming implementations, particularly in relation to Microsoft's Q# language.























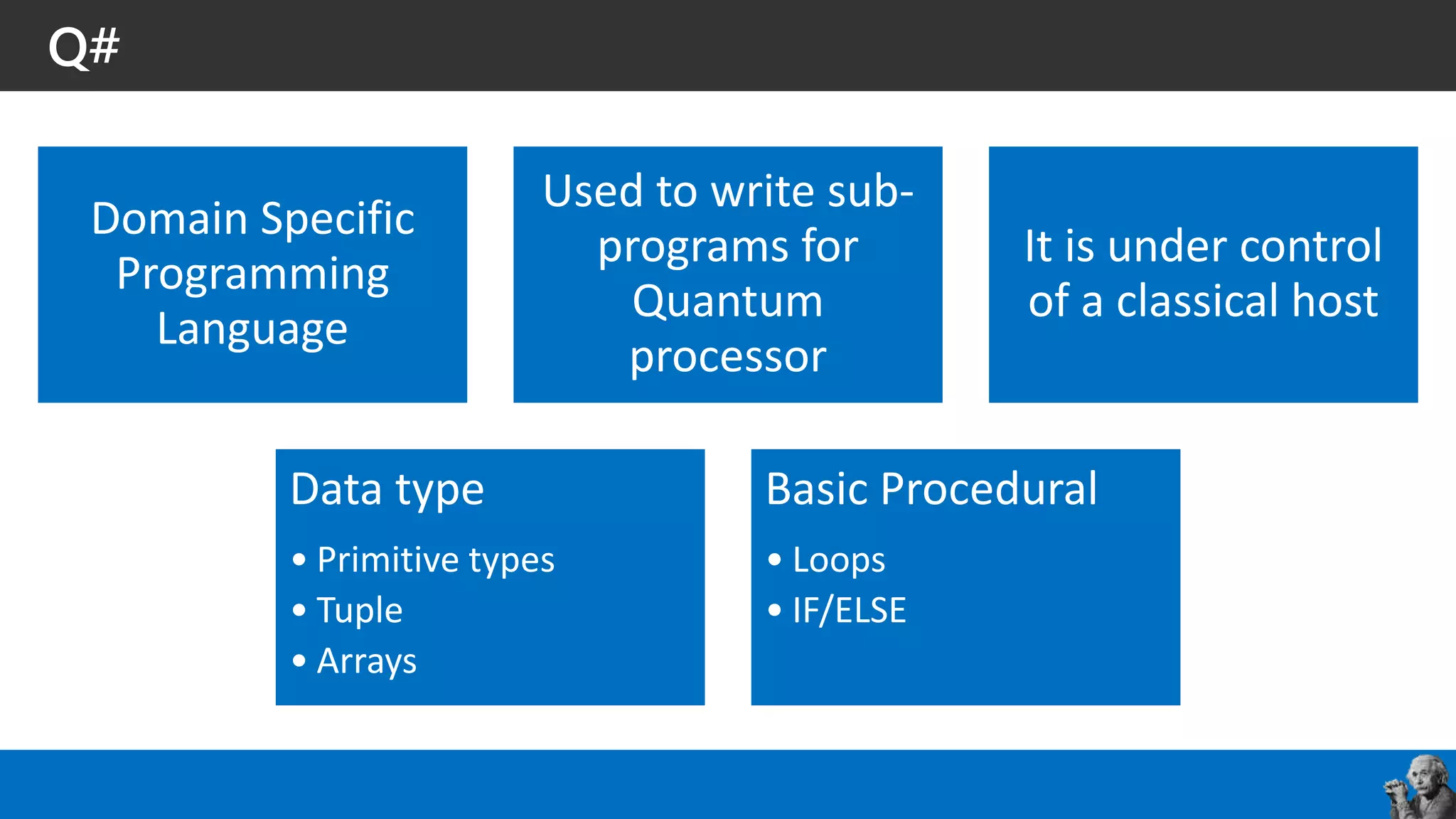
![Q#
Int, Bool,
Qubit
Pauli (I,X,Y,Z)
Arrays []
Tuples ()
Result Zero One
User defined types](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codecamp2018-quantumprogramminginanutshellraduvunvulea-copy-181129143816/75/Quantum-programming-in-a-nutshell-42-2048.jpg)
![1. Int integer = 10;
2. Bool boolean = true;
3. Qubit qubit = Qubit[5];
4. Int[] array = Int[5];
5. (String, Qubit) tuple2 = (2, qubit[0]);
6. newtype event = (String, String);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codecamp2018-quantumprogramminginanutshellraduvunvulea-copy-181129143816/75/Quantum-programming-in-a-nutshell-43-2048.jpg)
![1. set
2. newtype LogicalRegister = Qubit[]; //Callable expression
3. newtype EncodeOp = ((Qubit[], Qubit[]) =>
LogicalRegister);
4. // Range expression
5. 1..1..4; // 1234
6. 1..3..9; // 1369
7. 3..8..8; // 3
8. 1..-1..2; //Empty
9. array[1..2..5]; // Items on the index 1,3,5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codecamp2018-quantumprogramminginanutshellraduvunvulea-copy-181129143816/75/Quantum-programming-in-a-nutshell-44-2048.jpg)






