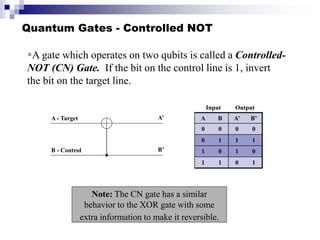
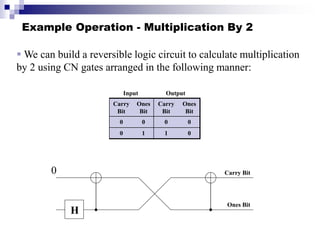
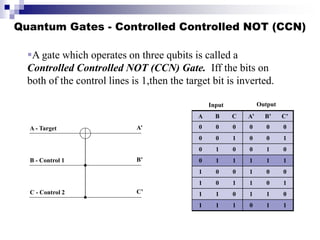
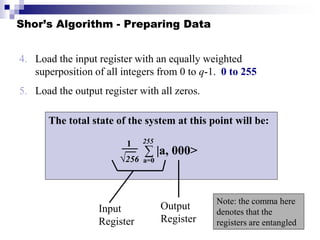
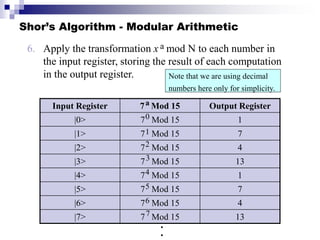
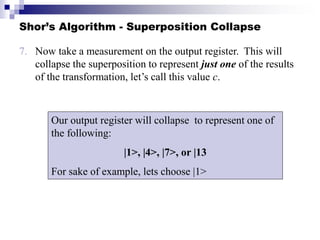
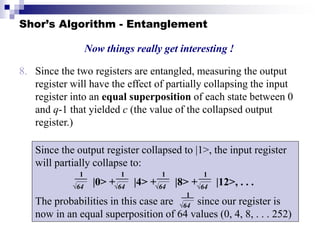
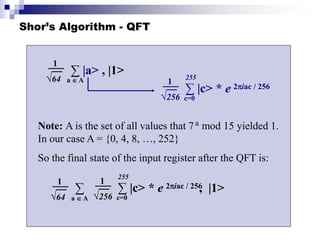
Quantum computing uses quantum bits (qubits) that can exist in superpositions of states. A controlled-NOT (CN) gate inverts the target qubit if the control qubit is 1. A controlled-controlled-NOT (CCN) gate inverts the target qubit if both control qubits are 1. Shor's algorithm uses quantum Fourier transforms and modular exponentiation to factor integers into prime factors exponentially faster than classical computers. It finds the period of the function x raised to a power (mod N), from which the factors can be derived.