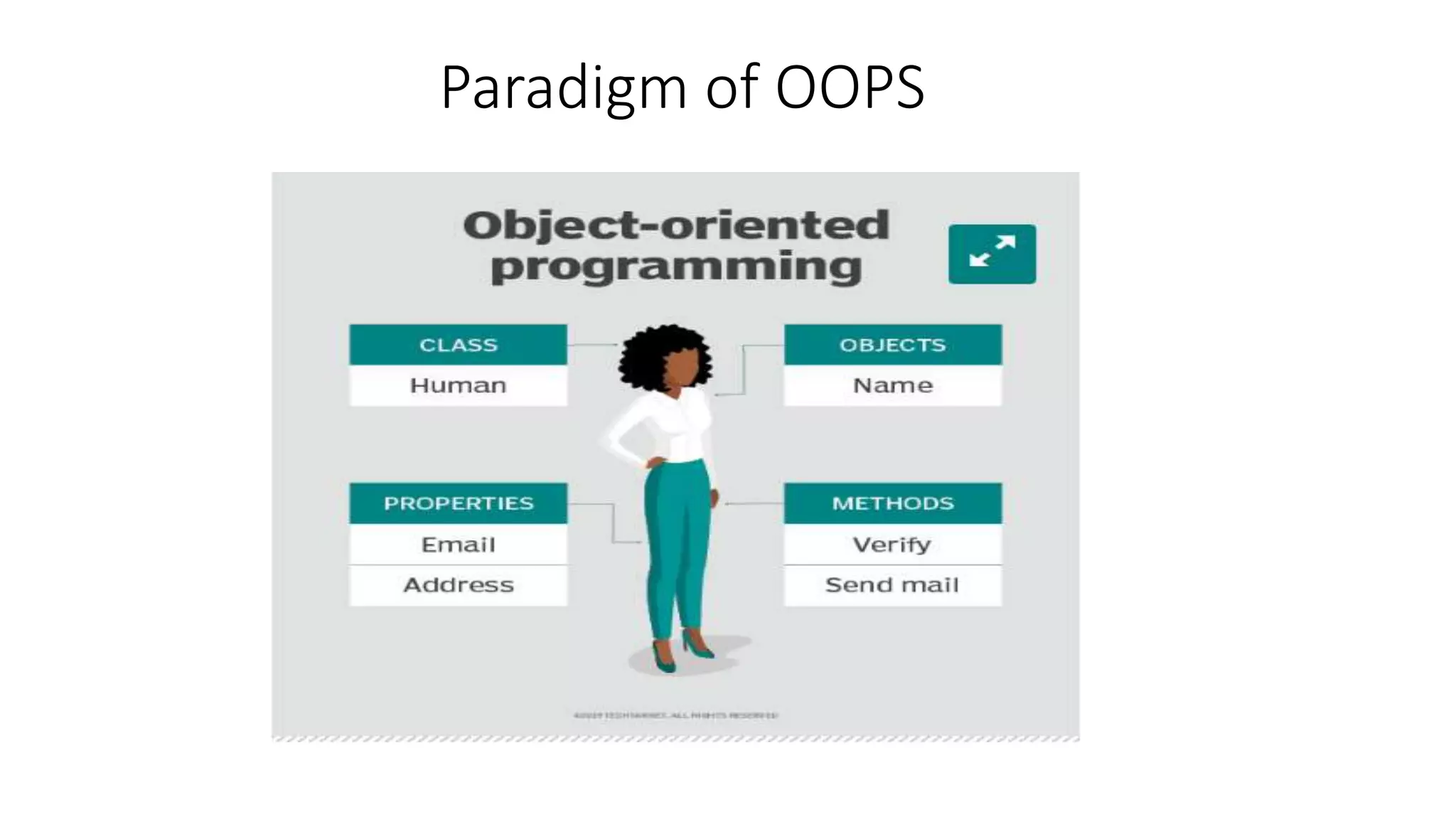
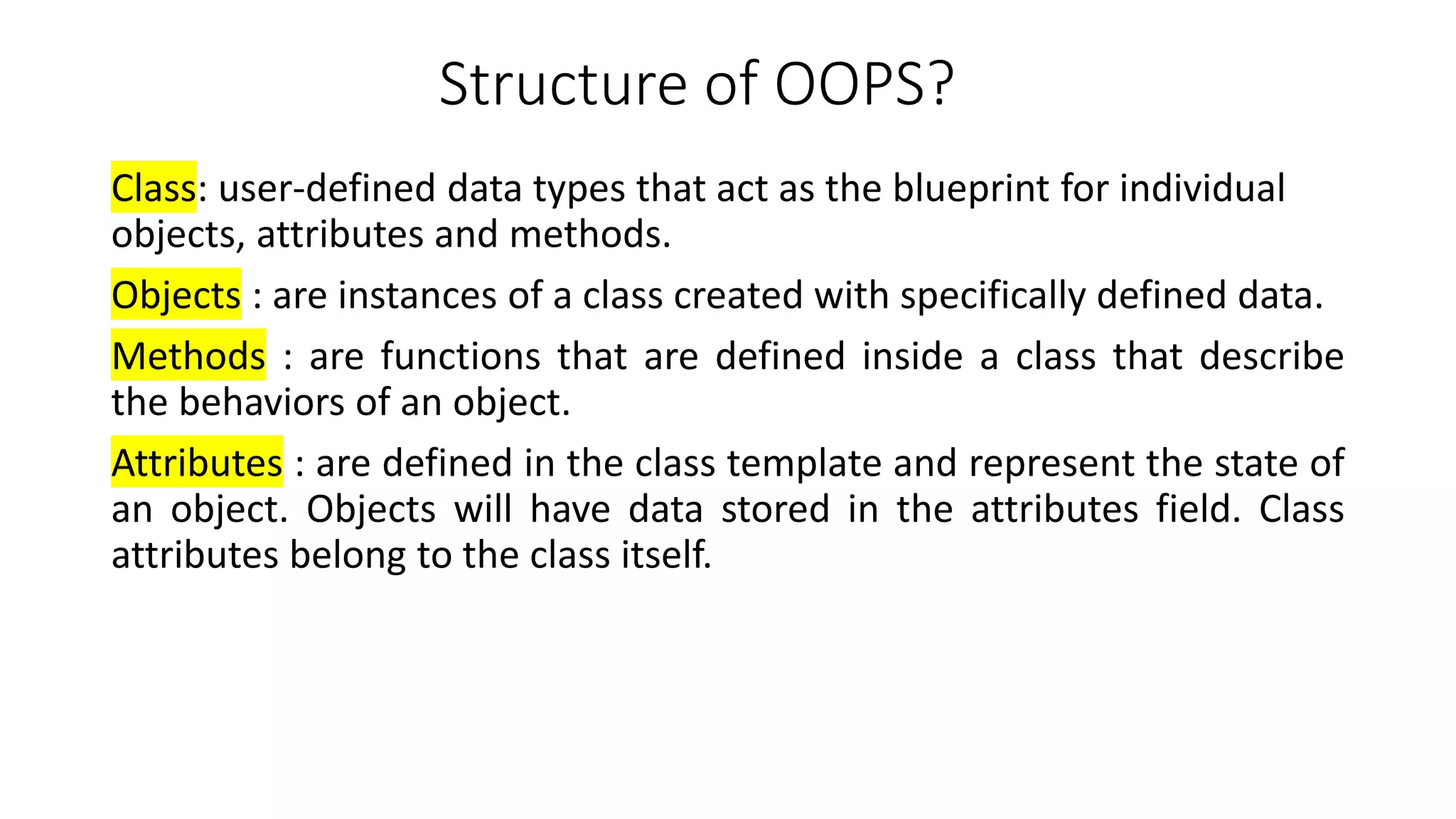
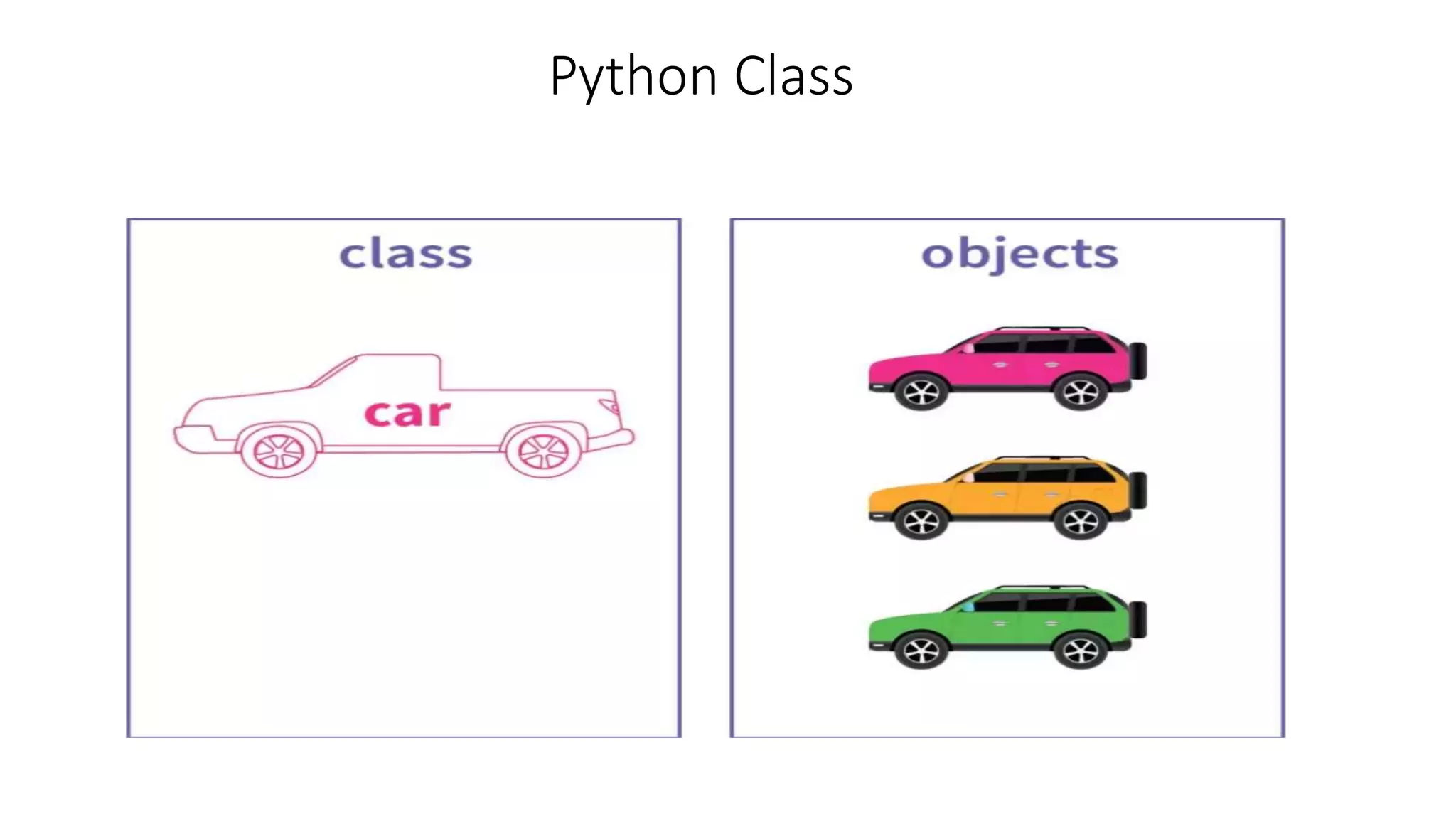
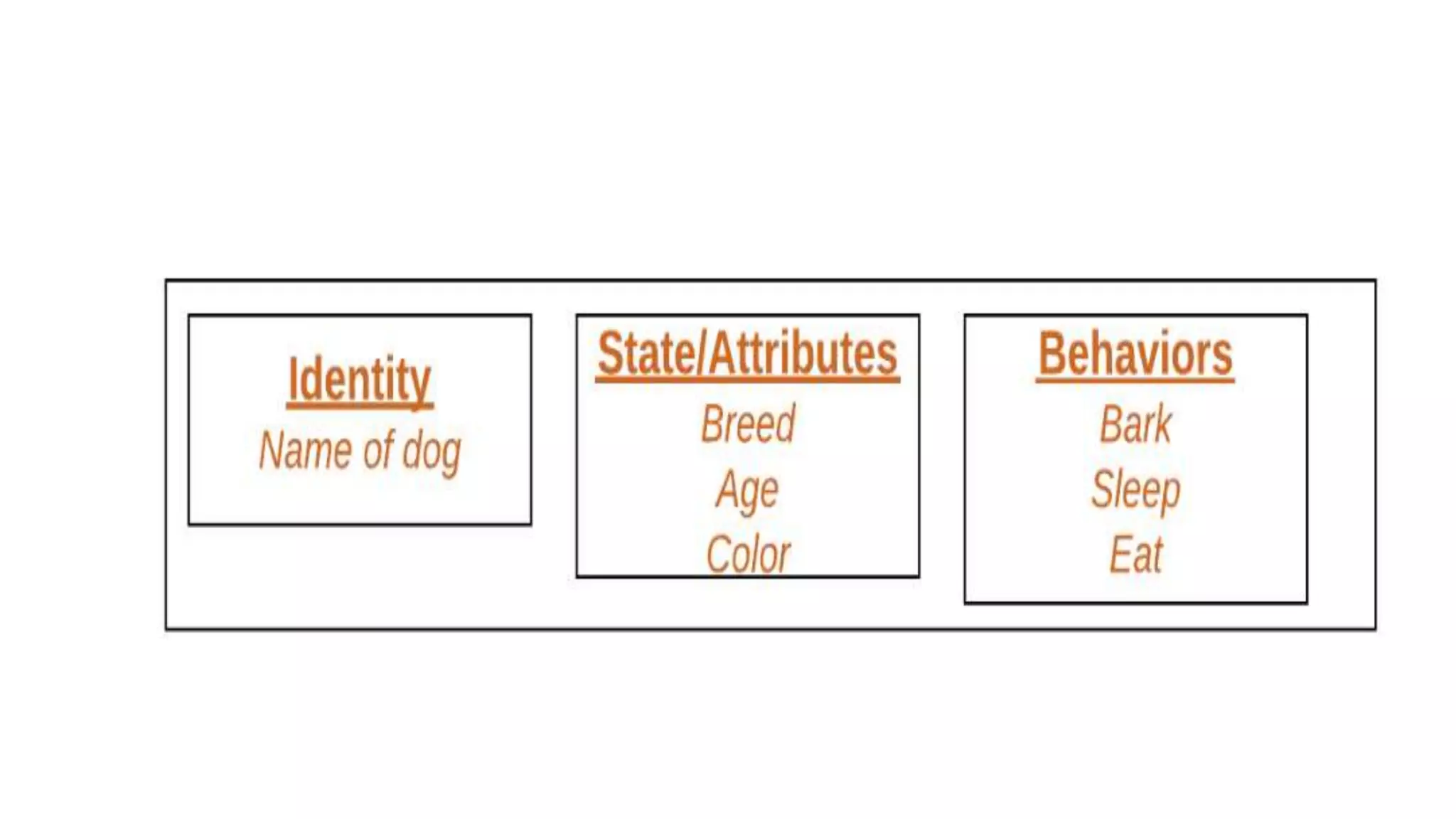
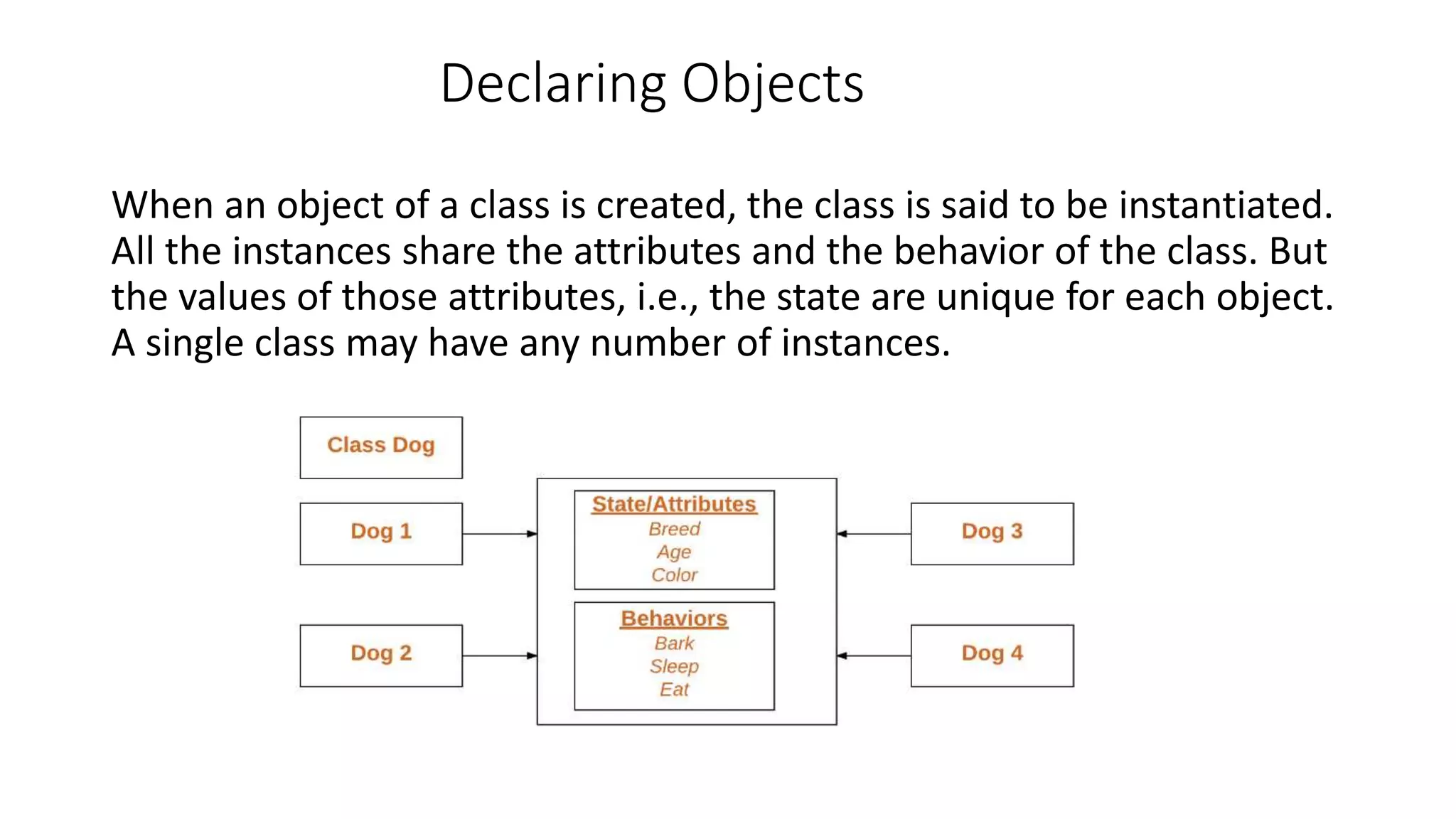
Object-oriented programming (OOP) organizes code around data objects rather than functions. In Python, classes are user-defined templates for objects that contain attributes (data) and methods (functions). When a class is instantiated, an object is created with its own copies of the attributes. Self refers to the object itself and allows methods to access and modify its attributes. Classes in Python allow for code reusability, modularity, and flexibility through encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.