This document explains the differences between lists and dictionaries in Python, highlighting their characteristics and usage. It also discusses string formatting using dictionaries, including methods for inserting dynamic data into strings and handling missing keys. Practical applications of these concepts include generating reports and dynamic web content.

![Lists vs. Dictionaries
Lists are ordered collections of items, accessed
by index.
Dictionaries are unordered collections of key-
value pairs, accessed by keys.
Lists use square brackets [] for declaration, while
dictionaries use curly braces {}.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pyhon23b81a6625-240606004408-e9740e3e/75/Python_23B81A6625presentationlistvsdict-pptx-3-2048.jpg)


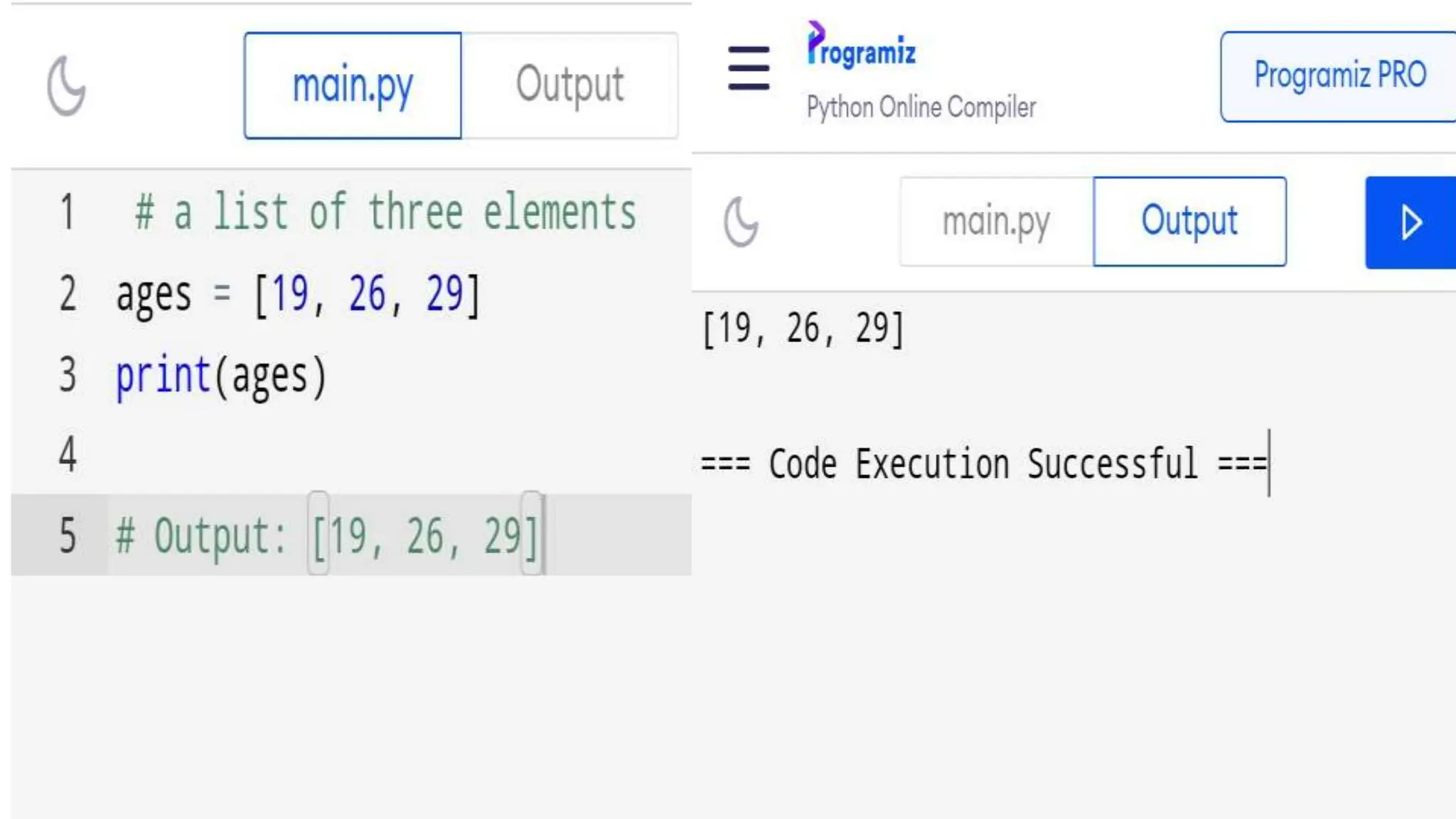
![List Example
Example of a list: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Accessing elements in a list: list_name[index]
Modifying a list: list_name[index] = new_value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pyhon23b81a6625-240606004408-e9740e3e/75/Python_23B81A6625presentationlistvsdict-pptx-6-2048.jpg)
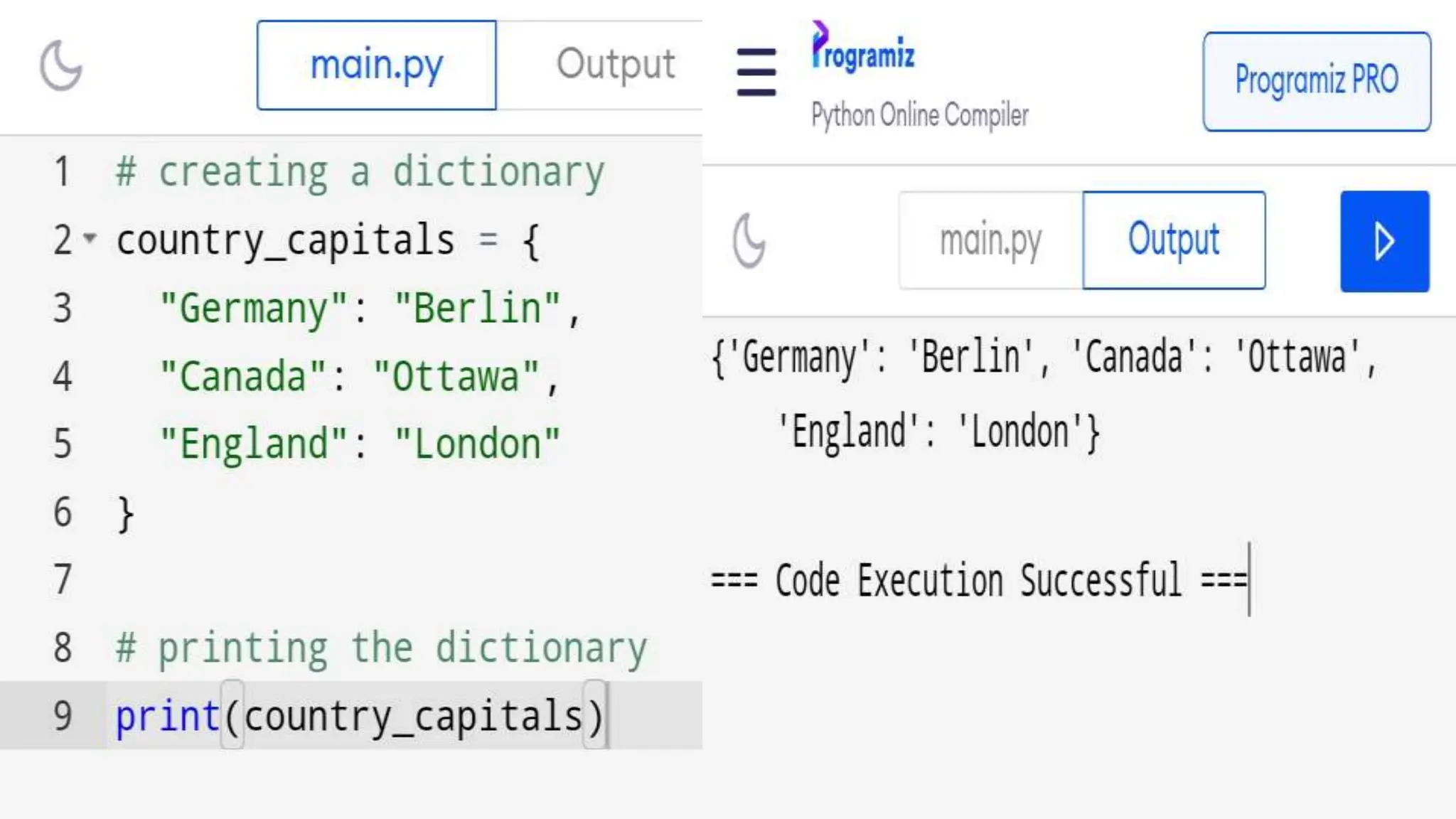
![Dictionary Example
Example of a dictionary: {'key1': 'value1', 'key2':
'value2'}
Accessing values in a dictionary: dict_name[key]
Modifying a dictionary: dict_name[key] =
new_value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pyhon23b81a6625-240606004408-e9740e3e/75/Python_23B81A6625presentationlistvsdict-pptx-8-2048.jpg)