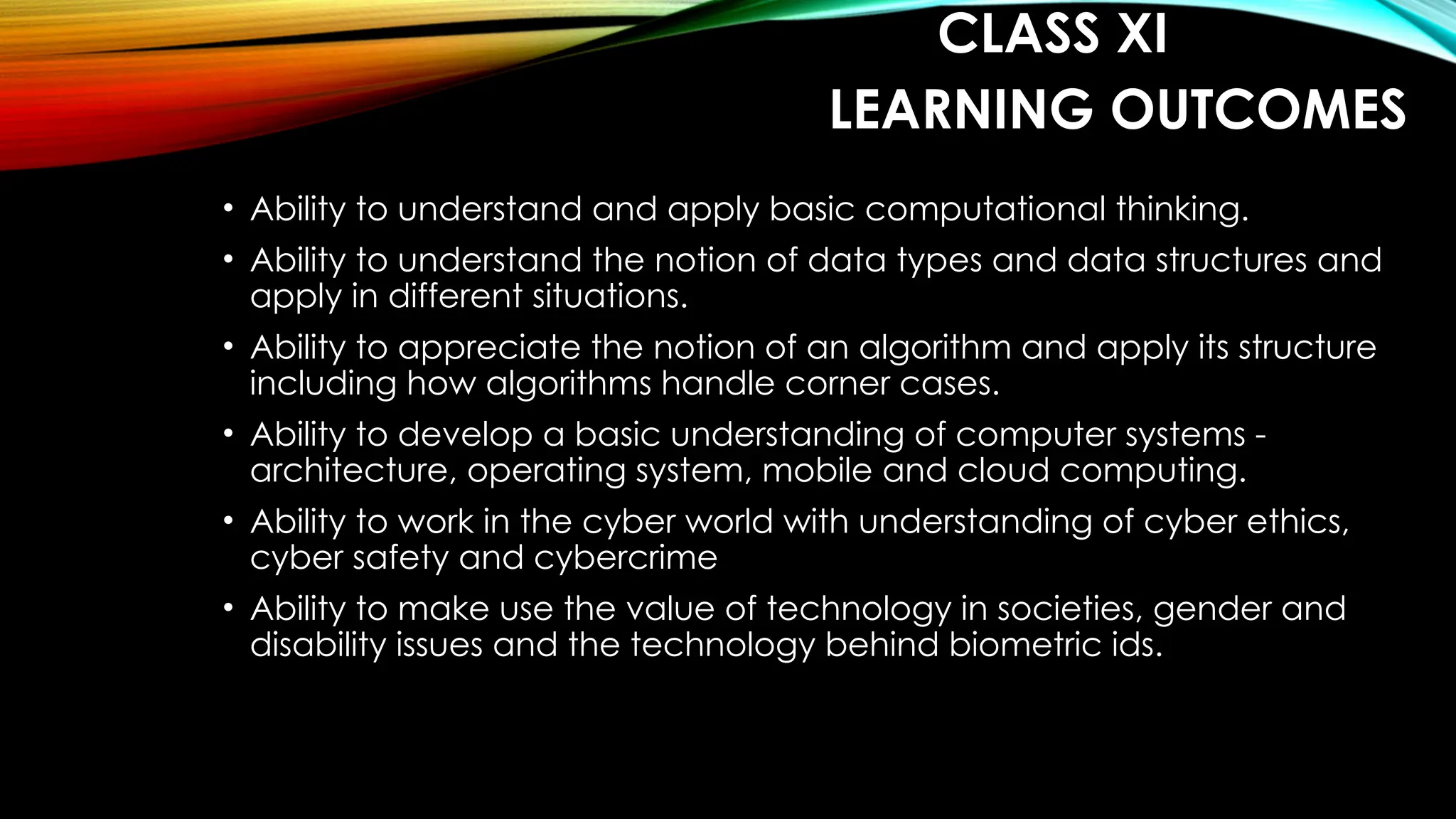
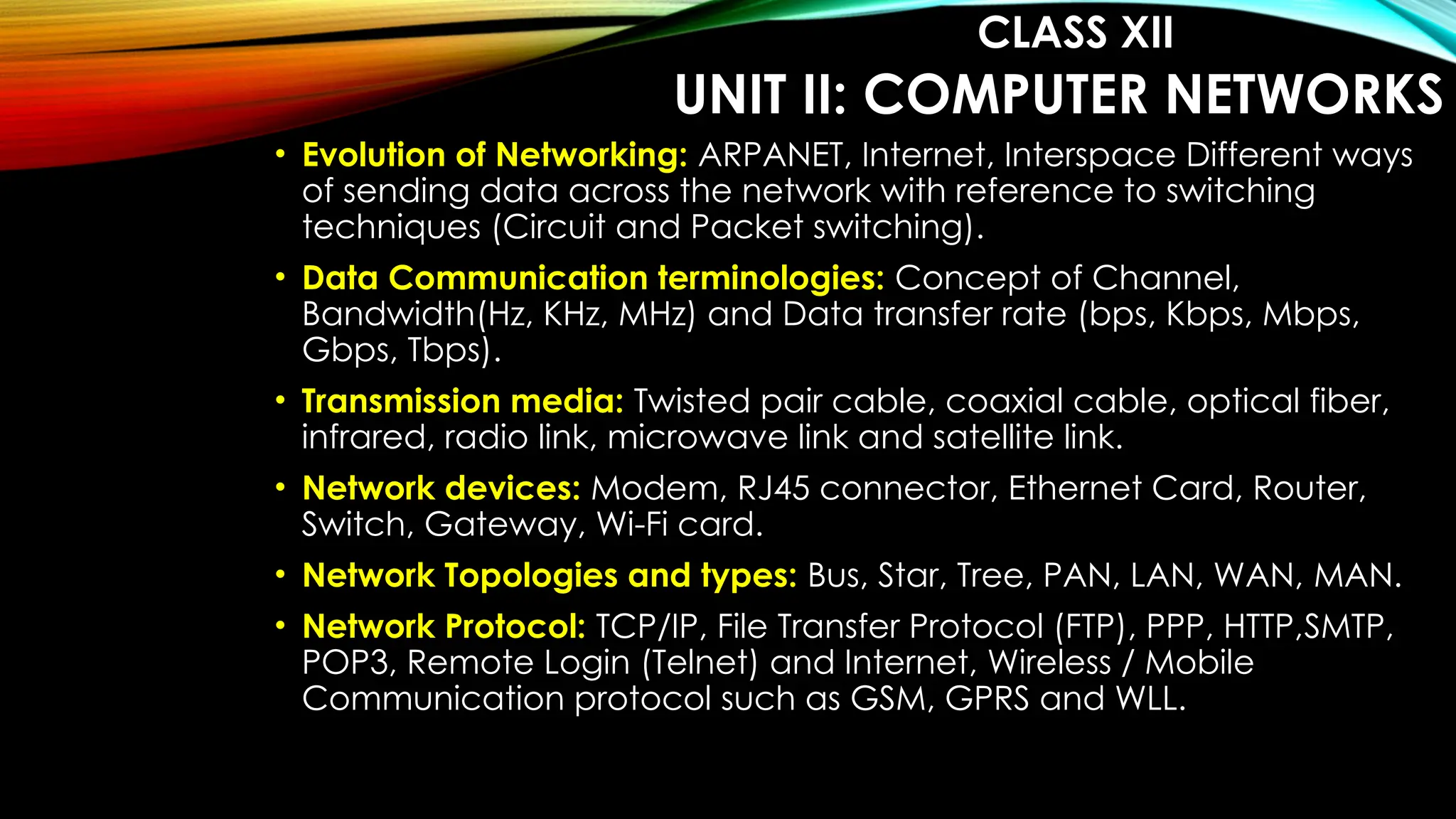
The computer science syllabus for classes XI and XII outlines key learning outcomes including computational thinking, data structures, programming using Python, and understanding computer systems. It emphasizes practical skills in programming, problem-solving, cyber safety, and the ethical use of technology. The curriculum also covers database management, computer networks, and advanced concepts like cloud computing and web services.