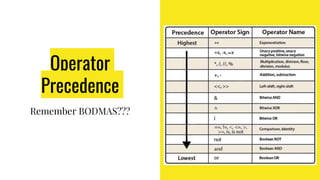
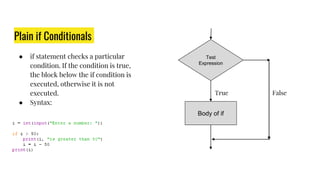
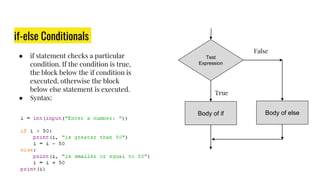
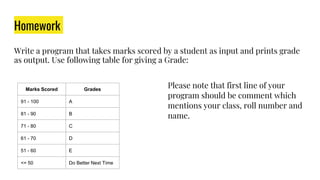
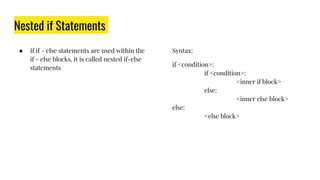
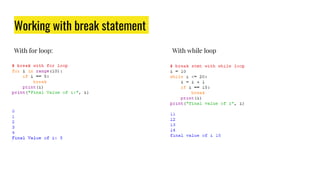
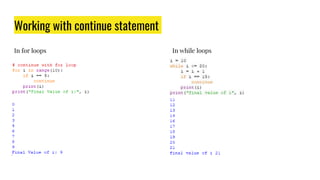
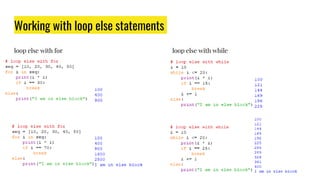
The document provides an overview of expressions, operators, data types, and control flow statements in Python. It discusses arithmetic, relational, logical, and string expressions. It covers evaluating expressions, operator precedence, implicit and explicit type conversions, and built-in math functions. Control flow statements like if/else, for/while loops, break, continue, and nested loops are explained along with examples. Homework is assigned to write a program to print grades based on marks scored by a student.